 The Parametric Cut Layout window (Parametric)
The Parametric Cut Layout window (Parametric)
Warning: If you are using imperial dimensioning, make entries to this window in decimal inches, not fractions. Also, do not use hyphens ( -). If you enter a fraction using integers, Python truncates the results of the division operation to an integer (1/8 = 0; 5/4 = 1). If you enter fractions with decimal points, Python calculates the precise decimal value (1.0/8.0 = .125; 5.0/4.0 = 1.25). If you enter a hyphen, Python interprets the hyphen as a minus sign (1-2 = -1; 3-2 = 1). See numbers (floating point numbers and integers). Also seeUnits('...').
Example, instructions, undoing the operation :
Also see :
| Quick Notes |
Example of a cut layout of a circle :
# Cuts a circle around cntr that is the radius (rr) specified by the user.
from point import PointLocate
from param import Prompt, Units
from mtrl_cut import MtrlCut
from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate
Units('feet')
cntr = PointLocate("Locate center of circle")
rr = Prompt("1-0", "Radius of circle:")
mcut1 = MtrlCut()
mcut1.Material = MtrlLocate("Select material to cut")
mcut1.Rotate = (((0, 0, 0)))
mcut1.Points.append( (cntr + mcut1.Material.TranslateToGlobal(
- rr, rr, 0), rr) )
mcut1.Points.append( (cntr + mcut1.Material.TranslateToGlobal(
- rr, - rr, 0), rr) )
mcut1.Points.append( (cntr + mcut1.Material.TranslateToGlobal(rr,
- rr, 0), rr) )
mcut1.Points.append( (cntr + mcut1.Material.TranslateToGlobal(rr,
rr, 0), rr) )
mcut1.Points.append( (cntr + mcut1.Material.TranslateToGlobal(
- rr, rr, 0), rr) )
mcut1.Cut("Layout")This script cuts a circle that is the radius that the user enters (
rr). The center of the circle is a point that the user locates (cntr). The cut layout points (mcut1.pts.append()) form a square. Each side of this square is exactly two times the radius of the circle (rr). The center point of the square is also the center point of the circle (cntr).
------ Radius and Point ------
Step-by-step instructions:
1 . Select the point and radius you want.
2 . The point's location can be reviewed/edited in the " Point " field. Its radius can be reviewed or edited in the " Radius " field. Also, once you have selected a point, you can use " Cut " " Copy " " Paste " or " Delete ."
Example of a point
mcut1.mtrl.location + mcut1.mtrl.trans_to_global(10, 0, 0), 0.5
ThisPointis 10 inches to the right of the material's reference point. TheRadiusfor this point is 0.5 inches.Resulting code
mcut1.pts.append ((mcut1.mtrl.location + mcut1.mtrl.trans_to_global(10, 0, 0), 0.5))
"Cut" removes the selected point from the list so that you can " Paste " it elsewhere.
"Copy" creates a copy of the selected point so that you can " Paste " that copy elsewhere on the list.
"Paste" places the most recently " Cut " or " Copied " point above the selected entry on the list.
"Delete" removes the selected point from the list.
"Add" lets you add a point to the list. Make entries for that point to " Point " and " Radius " (below).
------ Current Point and Radius ------
Point ( obj .pts.append(obj.mtrl.location + obj.mtrl.trans_to_global(dx, dy, dz), arg2) ): The global coordinate location of the currently selected point. The obj.mtrl.location is the global coordinates of the material's " Reference location " as reported on the General Information window. The function obj.mtrl.trans_to_global (dx, dy, dz) translates that point the dx, dy, dz distances that are entered. Translation of these X, Y, Z distances is done with respect to global coordinates . If you change the entry made here, then press Tab , the currently selected point is updated in the Radius and Point list.
Radius ( obj .pts.append(arg1, radius) : A corner radius is a floating point number in mm or inches, depending on the startup code Units('...') . This corner radius is associated with the currently selected point. The currently selected point is defined using the value ( arg2 ) in the Point field. If you change the entry here, then press Tab , the currently selected point is updated in the Radius and Point list.
| The corner radius is the radius of a circle. Two lines that are tangent to that circle meet at the located point. The corner's arc ends at the points of tangency of these two lines. |
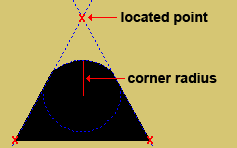
|
To close the Parametric_Material_Cut_Layout window :
"OK" (or the Enter key) closes this window and saves your changes to RAM.
"Cancel" (or the Esc key) closes this window without saving any changes.