C beam, left end, toe out
Click a point label ( A or B or etc.) to get an expression defining that point.
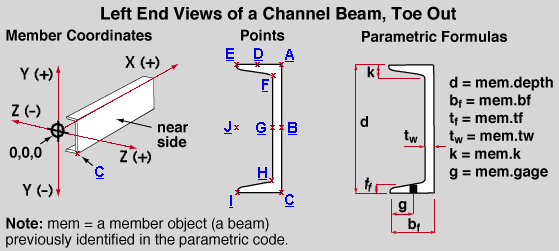
| point | position on left end plane | mem.left.location + mem.trans_to_global(X,Y,Z) | ||
| X | Y | Z | ||
| A | top corner of heel | mem.left.minus_dim | 0 | 0 |
| B | heel, half depth | mem.left.minus_dim | - mem.depth*.5 | 0 |
| C | bottom corner of heel | mem.left.minus_dim | - mem.depth | 0 |
| D | top flange gage line | mem.left.minus_dim | 0 | - mem.gage |
| E | top flange, corner of toe | mem.left.minus_dim | 0 | - mem.bf |
| F | web, toe of upper fillet | mem.left.minus_dim | - mem.k | - mem.tw |
| G | web, half depth | mem.left.minus_dim | - mem.depth *.5 | - mem.tw |
| H | web, toe of lower fillet | mem.left.minus_dim | - mem.depth +mem.k | - mem.tw |
| I | bottom flange, corner of toe | mem.left.minus_dim | - mem.depth | - mem.bf |
| J | half depth, aligned with channel toes | mem.left.minus_dim | - mem.depth *.5 | - mem.bf |
Columns on the above table :
point - the points ( A , B , etc.) in the above parametric point map are a few examples of reference points.
position on left end - entries to this column on the table describe (in words) the position where a particular point (A or B or etc.) is placed on the left end surface of a "toe out" channel beam.
mem.left.location + mem.trans_to_global(X,Y,Z) - an expression similar to this one is automatically entered to the " Point 1 " and " Point 2 " fields of the parametric material window that appears when you Add Material operation. The expression "mem.left.location" is the left end work point of the member. The operation "+ mem.trans_to_global(X,Y,Z)" defines individual X, Y and Z member coordinate distances and adds those distances to the member's left end work point in order to define a new point in global coordinates .
X is the X member coordinate distance from the left end member work point (mem.left.location) where the new point generated by the parametric will be placed. As illustrated above , a positive X distance translates the point away from the left end work point of the beam (the beam's 0,0,0 point ) and toward the right end, whereas a negative X distance translates the point in the opposite direction.
Y is the Y member coordinate distance from the left end member work point (mem.left.location) where the new point generated by the parametric will be placed. As illustrated above , a positive Y distance places the point above the top flange of the beam, whereas a negative Y distance places the point below the top flange.
Z is the Z member coordinate distance from the left end member work point (mem.left.location) where the new point generated by the parametric will be placed. As illustrated above , for a "toe out" channel beam a positive Z distance translates the point away from the heel of the channel toward the near side of the channel (off of the material), whereas a negative Z distance translates the point in the direction that the channel toes point. Note that all entries to the Z column above are either negative or 0.







