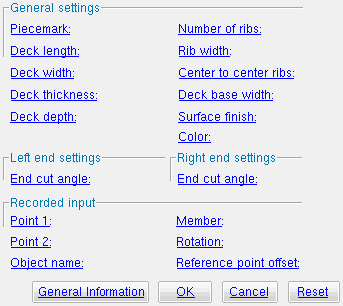
The Parametric Deck Material window
Also see :
| Quick Notes |
- Parametric Point Maps
- Objects, Attributes, Methods and Functions
- Deck Material (a similar window in Modeling )
Warning : If your startup code specifies imperial Units("...") , make entries to distance fields on this window in decimal inches, not fractions. Also, do not use hyphens (-). If you enter a fraction using integers, Python truncates the results of the division operation to an integer (examples: 1/8 = 0 ; 5/4 = 1 ). If you enter fractions with decimal points, Python calculates the precise decimal value (examples: 1.0/8.0 = .125 ; 5.0/4.0 = 1.25 ). If you enter a hyphen, Python interprets the hyphen as a minus sign (examples: 1-2 = -1 ; 3-2 = 1 ). See numbers (floating point numbers and integers).
Tips :
To enter a dimension string and convert it to a floating point distance that is properly factored based on the startup code Units("...") , you can use the dim("...") function. See the warning above for an explanation of why the dim() function is needed.
------ General settings ------
Piecemark: You can add a line of code such as obj.MinorMark = "xxx" or obj.Piecemark = "xxx" in a text editor.
For submaterials ( obj . MinorMark or obj.mark ):
If you Run a script that does not include obj.MinorMark , SDS2 piecemarking looks for materials in the current Job that are physically identical to this material and assigns to this material the same submaterial mark assigned to those materials. If no matching materials are found, piecemarking assigns this material a submaterial mark using the appropriate piecemark prefix listed in Home > Project Settings > Fabricator > Member and Material Piecemarking > the " Prefixes " tab .
If you Run a script with obj.MinorMark = "xxx" , SDS2 piecemarking applies that submaterial mark ( xxx ) to the parametrically added material if no other material has yet been assigned that mark. It also applies that mark ( xxx ) if other materials that have that mark ( xxx ) are exactly like the parametrically added material. If the model contains materials with a different submaterial mark ( yyy ) that are exactly like the parametrically added material, the submaterial mark of those materials ( yyy ) is re-named to that of the parametrically added material ( xxx ). If the model contains materials with the same submaterial mark that the script designates to be assigned to the parametrically added material ( xxx ) and those materials are different than the parametrically added material, the submaterial mark in the script is not applied -- instead you get a warning and the parametrically added material is assigned a different submaterial mark using the appropriate piecemark prefix listed in Home > Project Settings > Fabricator > Member and Material Piecemarking > the " Prefixes " tab .
For miscellaneous members ( obj . Piecemark or obj.piecemark ):
If you Run a script that does not include an obj.Piecemark , SDS2 assigns a system piecemark to the parametrically added member.
If you Run a script with an obj.Piecemark , be careful. You are responsible for ensuring that members that have been assigned the same user piecemark are physically the same. SDS2 will not do this for you.
Tip 1: A Python script can read the submaterial mark of a material as shown in the following example.
# Prints the piecemark of the material the user selects. from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate mtrl1 = MtrlLocate("Select material", "Single") print("The material piecemark is: ", mtrl1.MinorMark)Tip 2: A script can also read member piecemarks (user or system).
# Prints the piecemark of the member that the user selects. from member import MemberLocate from param import ClearSelection mem1 = MemberLocate("Select a member") print("The piecemark is: ", mem1.Piecemark) ClearSelection()
Deck length ( obj . Length or obj.length ): The length of the deck along its longitudinal axis ( X material axis ). The length is a floating point number in mm or inches, depending on the startup code Units(' ... ') .
Example 1: Entering a specific distance sets the length of the material to be that value when this script is Run.
Example 2: The expression dk1.Point1.Distance(dk1.Point2) calculates the deck length based on the distance between the two work points (" Point 1 " and " Point 2 "). The resulting line of parametric code reads: dk1.Length = dk1.Point1.Distance(dk1.Point2).
Deck width ( obj . Width or obj.width ): The width of the deck along its Y material axis . The width is a floating point number in mm or inches, depending on the startup code Units(' ... ') .
Example: The expression dk1.RibSpacingCenterToCenter * dk1.NumberOfRibs (where dk1 is the " Object name ") calculates the deck width by multiplying ( number of ribs )( C to C ribs ). The result is a line of parametric code that reads: dk1.Width = dk1.RibSpacingCenterToCenter * dk1.NumberOfRibs .
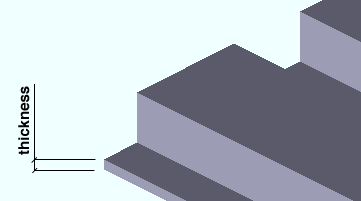
Deck thickness ( obj . Thickness or obj.thick ): The thickness of the steel used to fabricate the deck. The thickness is a floating point number in mm or inches, depending on the startup code Units(' ... ') .
Deck depth ( obj . RibDepth or obj.deck ): The distance measured perpendicular to the workline of the deck from the bottom of the deck to the top of any one rib. All ribs are this same depth. A distance is a floating point number in mm or inches, depending on the startup code Units(' ... ') .
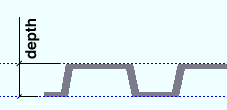
|
| The bottom of the deck is at the elevation of the workline. |
Number of ribs ( obj . NumberOfRibs or obj.num_ribs ): The total number (an integer > 0) of ribs.
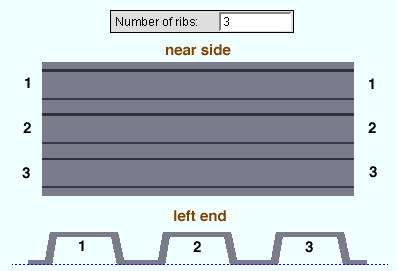
|
| In this example of a deck added in a plan view , the ribs are the surfaces at the highest elevation. They are parallel with the deck's X material axis , and each rib is as long as the " Deck length >" is long. |
Rib width ( obj . RibWidth or obj.rib_width ): The width of the top surface of any one rib. All ribs are this same width. The width is a floating point number in mm or inches, depending on the startup code Units(' ... ') .
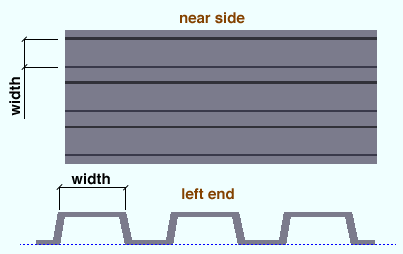
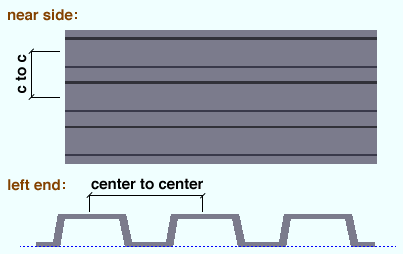
Center to center ribs ( obj . RibSpacingCenterToCenter or obj.c_to_c ): The distance from the center of any one rib to the center of an adjacent rib. A distance is a floating point number in mm or inches, depending on the startup code Units(' ... ') .
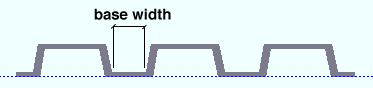
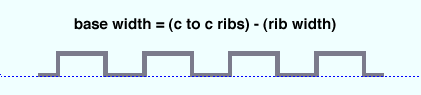
Deck base width ( obj . BaseWidth or obj.base_width ): The distance from the inside corners of one bend to the next at the base of the deck. The returned value is a floating point number in mm or inches, depending on the startup code Units(' ... ') .
Example 1: Entering a deck base width that is the same as the spacing between ribs sets the deck to be squared off as shown below:
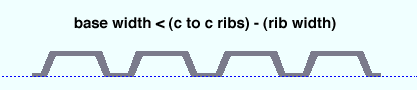
Example 2: Entering a deck base width that is less than the spacing between ribs sets the bend pattern of the deck to be as shown below:
Surface finish ( obj . SurfaceFinish or obj.finish ): "None" or "Sand Blasted" or "Red Oxide" or "Yellow Zinc" or "Gray Oxide" or "Blued Steel" or "Galvanized" can be selected on list box ( ![]() ) for this field. The choice you make here assigns the selected string as the SurfaceFinish attribute for this " Object name " in the parametric code.
) for this field. The choice you make here assigns the selected string as the SurfaceFinish attribute for this " Object name " in the parametric code.
|
||||||
| The colors of materials on Drawing Editor erection views in ' Solid ' or ' Stick + solid are based on their surface finish. |
Example: Selecting Yellow Zinc results in a line of parametric code that reads: obj.SurfaceFinish = "Yellow Zinc" (where obj is the " Object name ").
Also note: When you export a KISS file using Model as the " Data source ," surface finish data on materials are compiled into the P lines in the KISS download. Surface finish data can also be output to a fabtrol_assembly_parts_list.XSR file.
Color ( obj . MaterialColor3d or obj.color ): A "named_color" or a custom color . The choice you make here assigns three values (RGB values) from 0 to 255, which define the color of the deck when it is displayed in one of the three solid forms .
The "named_colors" are set up on the Predefined Colors window. The color swatch next to the list box (
) displays the color that is selected. Example: Selecting Medium_beam results in a line of parametric code that reads: obj.MaterialColor3d = "Medium_beam" (where obj is the " Object name ").
Select Custom Color (last option on the menu) to launch your operating system's color picker and define any color you like. Example: Selecting a custom color results in a line of parametric code that reads: obj.MaterialColor3d = (r, g, b) where r or g or b is an integer value from 0 to 255.
------ Left end settings ------ | ------ Right end settings ------
| Tip : The left end is the " Point 1 " end of this material. |
End cut angle ( obj . LeftEndCutAngle or obj . RightEndCutAngle ):
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
" General Information " opens the Parametric General Information window so that you can assign a " Description " or " Material usage description " or " Material routing " to this material. Making entries to the Parametric General Information window adds extra lines to the parametric code. Those extra lines override default settings.
"OK" (or the Enter key) closes this window and saves your changes to RAM.
"Cancel" (or the Esc key) closes this window without saving any changes.
"Reset" undoes all changes made to this window since you first opened it. The window remains open.