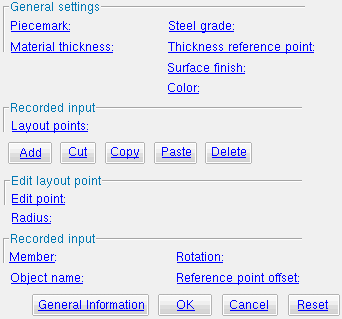
The Parametric Multi-sided Flat Plate Material window
| Quick Notes |
Also see :
- Objects & Attributes (entries you can make to this window)
- Multi-Sided Flat Plate Material (similar window -- for Modeling )
------ General settings ------
Piecemark ( obj . MinorMark or obj.mark ) : You can add a line of code such as obj.MinorMark = "xxx" in a text editor.
For submaterials :
If you Run a script that does not include obj.MinorMark , SDS2 piecemarking looks for materials in the current Job that are physically identical to this material and assigns to this material the same submaterial mark assigned to those materials. If no matching materials are found, piecemarking assigns this material a submaterial mark using the appropriate piecemark prefix listed in Home > Project Settings > Fabricator > Member and Material Piecemarking > the " Prefixes " tab .
If you Run a script with obj.MinorMark = "xxx" , SDS2 piecemarking applies that submaterial mark ( xxx ) to the parametrically added material if no other material has yet been assigned that mark. It also applies that mark ( xxx ) if other materials that have that mark ( xxx ) are exactly like the parametrically added material. If the model contains materials with a different submaterial mark ( yyy ) that are exactly like the parametrically added material, the submaterial mark of those materials ( yyy ) is re-named to that of the parametrically added material ( xxx ). If the model contains materials with the same submaterial mark that the script designates to be assigned to the parametrically added material ( xxx ) and those materials are different than the parametrically added material, the submaterial mark in the script is not applied -- instead you get a warning and the parametrically added material is assigned a different submaterial mark using the appropriate piecemark prefix listed in Home > Project Settings > Fabricator > Member and Material Piecemarking > the " Prefixes " tab .
Tip 1: A Python script can read the submaterial mark of a material as shown in the following example.
# Prints the piecemark of the material the user selects. from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate mtrl1 = MtrlLocate("Select material", "Single") print("The material piecemark is: ", mtrl1.MinorMark)
Material thickness ( obj . Thickness or obj.thick ): The thickness (a floating point number in the startup code " Units ") of the plate material. This dimension is measured along the material's Z axis .
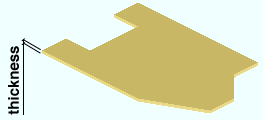
Example 1: Entering a specific distance (in the " Units " designated in the startup code) sets the thickness of the material to be that value when this script is Run.
Example 2: Entering obj.Member.WebThickness (where obj is the " Object name ") sets the thickness of the multi-sided flat plate to be the web thickness of the " Member ." The result is a line of parametric code that reads: obj.Thickness = obj.Member.WebThickness .
Steel grade ( obj . MaterialGrade or obj.grade ): Any steel grade ( "A36" or "A572" or etc.) from the list of Steel Grades for Plates & Bar Stock can be selected on the menu ( ![]() ) for this field.
) for this field.
Example: Selecting A36 results in a line of parametric code that reads: obj.MaterialGrade = "A36" (where obj is the " Object name " and "A36" is a string from the aforementioned setup table).
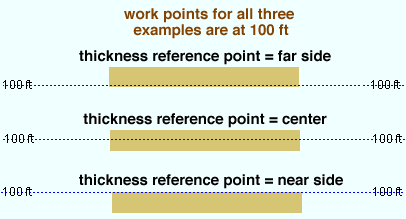
Thickness reference point ( obj . MaterialOriginPoint or obj.origin ): "FS" or "Center" or "NS" . This sets whether the work points are to the near side, far side or center of the thickness of the material. The work points for the plate in the example below are both at 100 ft. In the parametric code, the choice you make here results in the entry of a string ( "FS" or "Center" or "NS" ).
Surface finish ( obj . SurfaceFinish or obj.finish ): "None" or "Sand Blasted" or "Red Oxide" or "Yellow Zinc" or "Gray Oxide" or "Blued Steel" or "Galvanized" can be selected on the list box ( ![]() ) for this field. The choice you make here assigns the selected string as the SurfaceFinish attribute in the parametric code.
) for this field. The choice you make here assigns the selected string as the SurfaceFinish attribute in the parametric code.
|
||||||
| The colors of materials erection views in ' Drawing Editor on Solid ' or ' Stick + solid ' are based on their surface finish. |
Example: Selecting Yellow Zinc results in a line of parametric code that reads: obj.SurfaceFinish = "Yellow Zinc" (where obj is the " Object name ").
Also note: When you export a KISS file using Model as the " Data source ," surface finish data on materials are compiled into the P lines in the KISS download. Surface finish data can also be output to a fabtrol_assembly_parts_list.XSR file.
Color ( obj . MaterialColor3d or obj.color ): A "named_color" or a custom color . The choice you make here assigns three values (RGB values) from 0 to 255, which define the color of the multi-sided flat plate when it is displayed in one of the three solid forms .
The "named_colors" are set up on the Predefined Colors window. The color swatch next to the list box (
) displays the color that is selected. Example: Selecting Medium_beam results in a line of parametric code that reads: obj.MaterialColor3d = "Medium_beam" (where obj is the " Object name ").
Select Custom Color (last option on the menu) to launch your operating system's color picker and define any color you like. Example: Selecting a custom color results in a line of parametric code that reads: obj.MaterialColor3d = (r, g, b) where r or g or b is an integer value from 0 to 255 and obj is the " Object name ."
------ Edit layout point ------
Edit Point: Prompt or a point . This applies to the point that is currently selected on the " Layout Points " list. In the following examples, the color green identifies the part of an expression that locates the end point. The " Radius " is shown in red .
When the box for " Prompt " is checked (
) and this script is Run or Tested, the user is prompted (in the status line ) with whatever prompt string is entered. For example, if you were to enter Locate a point, the resulting parametric code would read: obj.pts.append(PointLocate ("Locate a point") , 0 ) ) where obj is the " Object name ."
When the box for " Prompt " is not checked (
), you can enter a point. For example, entering obj.pts.append( (Member.LeftEnd.Location + obj.Member.TranslateToGlobal (30.0, 0.0, 2.0) , 0 ) ) would define a point with respect to the 0, 0, 0 member coordinate of obj.Member and convert those member coordinates into global coordinates.
Radius: A distance (a floating point number in the startup code " Units ") that defines the corner rounding radius for the point that is currently selected on the " Layout Points " list. In the following example, the " Radius " is shown in red :
obj.pts.append( (Member.LeftEnd.Location + obj.Member.TranslateToGlobal(30.0, 0.0, 2.0), 0.5 ) )
Member ( obj . Member or obj.member ): Prompt or a member object .
When " Prompt " is checked (
) and this script is Run or Tested, the user is prompted (in the status line ) with whatever prompt string is entered. For example, if you were to enter Select column to add plate to, the resulting parametric code would read obj.Member = MemberLocate("Select column to add plate to") where obj is the " Object name ."
When " Prompt " is not checked (
), you can enter a member object. For example, if this is the second plate of a pair of multi-sided flat plates (both of which are Features of the same script), you might want to enter obj.Member as the variable (where obj = the " Object name " of the first plate that you added).
Also see: mem1 = (declaring a member object).
Object name: The name that identifies this multi-sided flat plate in the parametric code associated with this window.
How the object name affects the code : You enter an " Object name " of ply1 . The first line in the parametric code that is recorded from this window will read: ply1 = PlateLayout() . This first line defines the material object. Subsequent lines in the code, in the form ply1.xxx = yyy , assign attributes to the material object. The next-to-last line in the code, ply.Add() , adds the multi-sided flat plate. Rotation is done on the last line, after the material is added.
Note: Multi-sided flat plate cannot be added as a member.
Rotation ( obj . Rotate or obj.rotate ): .
Reference point offset ( obj . ReferencePointOffset or obj.ref_pt_offset ):
Show edit window at runtime ( obj . ShowWindow() or obj.show_window() ): Not applicable at this time.
![]()
![]()
![]()
"OK" (or the Enter key) closes this window and saves your changes to RAM.
"Cancel" (or the Esc key) closes this window without saving any changes.
"Reset" undoes all changes made to this window since you originally opened it. The window remains open.