The job module
On this page :
- Example: Using job and fab module attributes in a parametric dialog
- Defining the object to be your current Job Options file
- Methods
- Base/Cap Plate Schedule
- Design Settings
- Plate Design Settings
- Moment Plate Design Settings
- Flange Plate Clearances
- Weld Design Settings
- Schedule of Minimums for Structural Members
- Schedule of Minimums for Single-Plate Shear Connections
- Field Clearances
- Reaction Factors
- Bolt Settings
- Bolt Specifications
- Nut and Washer Schedule
- Washer Settings
- Steel Grades
- Material Usage Descriptions
- Member Revisions
- Predefined Colors
- Member, Material, Bolt and Weld Colors
- Job North
- Zone and Sequence
- Joist Manufacturers
- Job Custom Properties
- Concrete Strength
- Concrete Finish
- Concrete Cover Surfaces
- Rebar Definitions
- Rebar Usage Descriptions
Also see :
PR 34746 In parametrics added access to the job's member revision table via the job module. See
help(job.Job().member_revisions) help(job.Job().update_member_revision) help(job.Job().add_member_revisions)Gain access to the member's revision history through a model.object member's
rev_level,revision_cnt, andrevision_historyattributes. (v2016)
Example: Using job and fab module attributes in a parametric dialog
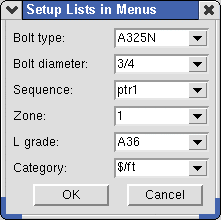
|
This dialog, and Job().sequences() , Job().avail_bolts() , Job().bolt_sched() which can be generated from the script that follows, uses links to Setup to fill out options on the menus. Note the use of Fabricator().category_defs in the script.
|
# Script that generates the dialog that is shown above.
from dialog import Dialog
from dialog.combobox import Combobox
from dialog.dialog import ResponseNotOK
from job import Job
from fab import Fabricator
import Tkinter
# Warning: For this to run, a member category must be in line 1 of Home > Project Settings > Fabricator > Category Settings.
Dlg0 = Dialog( "Setup Lists In Menus" )
Menu1 = Combobox(Dlg0, "bolt_type", ( Job().bolt_sched() ),
label="Bolt type:", default="Item 1" )
Menu2 = Combobox(Dlg0, "bolt_dia", ( Job().avail_bolts() ),
label="Bolt diameter:", default="Item 1"
)
Menu3 = Combobox(Dlg0, "mem_seq", ( Job().sequences() ),
label="Sequence:", default="Item 1" )
Menu4 = Combobox(Dlg0, "mem_zone", ( Job().zones() ),
label="Zone:", default="Item 1" )
Menu5 = Combobox(Dlg0, "L_grade", ( Job().steel_grades("Angle").keys() ),
label="L grade:", default="Item 1" )
Menu6 = Combobox(Dlg0, "category", ( Fabricator().category_defs ),
label="Category:", default="Item 1" )
dd = Dlg0.done()
# insert code to use choices made to dialog
Note: Item 1 is just a place holder in the above script. Replacing Item 1 with an expression like Job().bolt_sched()[2] causes the third item in the list to be selected by default in the Bolt type: menu.
Defining the object to be your current Job Options file :
obj = Job()
JobName()returns the name of your current Job.
JobProperties()returns a dictionary of job custom properties entered in the Custom Properties Window when you choose Home > Project Settings > Job > Job Property Settings .# Prints entries to Job properties named 'JobAwardedDate' from job import JobProperties job_prop = JobProperties() # no argument, current Job print(job_prop['JobAwardedDate'])
ProcessJob()does a Process and Create Solids on all parametrically added members and all members that are marked for processing.# Demonstration of when to use ProcessJob(). ... # insert startup code ... # insert code for adding members ProcessJob()# Processes the selected members. from member import MultiMemberLocate from job import ProcessJob from param import ClearSelection mem_list = MultiMemberLocate("Select some members") for each_mem in mem_list: MarkMemberForProcess(each_mem) ProcessJob() ClearSelection()
ProcessOneMem(idx), whereidxis a member number (integer), performs Process and Create Solids on the member with that member number. The following script processes the member that you select (mem) when you Run the parametric. The attributemem.MemberNumberis used to return the idx.# Processes the member that the user selects. from member import MemberLocate from job import ProcessOneMem from param import ClearSelection ClearSelection() mem = MemberLocate("Select one member") ProcessOneMem(mem.MemberNumber) ClearSelection()The next script processes the members whose compression loads are changed.
# Applies right-end compression and processes. from member import MemberLocate from job import ProcessOneMem from param import ClearSelection mem1 = MemberLocate("Select a member") if mem1.Type in ["Beam", "Vertical Brace", "Horizontal Brc"]: mem1.RightEnd.CompressionLoad = 60.0 mem1.RightEnd.AutoCompressionLoadCalculation = "No" mem1.Update() ProcessOneMem(mem1.MemberNumber) else: print("You selected a", mem1.Type) print("You need to select a beam or brace!") ClearSelection()
JobRepositoryPath()returns the job repository path; for example,"C:/Users/Someone/Documents/LocalJobRepo".
Job().plate_def()returns alistofplate_defobjects, each of which corresponds to a line on the Base/Cap Plate Schedule . Attributes ofplate_defobjects are:obj.pcmk obj.thick obj.length obj.width obj.cc_length obj.cc_width obj.bolt_dia obj.hole_type obj.steel_grade
Job().plate_def()can accept a line number as its argument. In the following script, the line number is 1.# Prints attributes for plate definition line 1. from job import Job print("Piecemark:", Job().plate_def(1).pcmk) print("Thickness:", Job().plate_def(1).thick) print("Length:", Job().plate_def(1).length) print("Width:", Job().plate_def(1).width) print("Hole spacing, length:", Job().plate_def(1).cc_length) print("Hole spacing, width:", Job().plate_def(1).cc_width) print("Bolt diameter:", Job().plate_def(1).bolt_dia) print("Hole type:", Job().plate_def(1).hole_type) print("Steel grade:", Job().plate_def(1).steel_grade)
Job().plate_def()can also accept any " Piecemark " that appears on the Base/Cap Plate Schedule as its argument. In the following script, the piecemark is"bp1".# Prints attributes for plate definition bp1. from job import Job print("Piecemark:", Job().plate_def("bp1").pcmk) print("Thickness:", Job().plate_def("bp1").thick) print("Length:", Job().plate_def("bp1").length) print("Width:", Job().plate_def("bp1").width) print("Hole spacing, length:", Job().plate_def("bp1").cc_length) print("Hole spacing, width:", Job().plate_def("bp1").cc_width) print("Bolt diameter:", Job().plate_def("bp1").bolt_dia) print("Hole type:", Job().plate_def("bp1").hole_type) print("Steel grade:", Job().plate_def("bp1").steel_grade)
Job().design_method Job().round_met_cut_dim Job().moment_design_method Job().non_AISC_shear_conn Job().non_AISC_welds Job().alternate_ecc Job().tee_conn_specs Job().angle_conn_specs Job().channel_conn_specs Job().plate_schedule_grade Job().percent_composite_load Job().concrete_strength Job().concrete_thick Job().flg_force_load Job().bm_design_reaction Job().bm_design_moment Job().design_mom_conn Job().min_setup_conn Job().brc_design_tension Job().brc_design_compression Job().hbrc_design_tension Job().hbrc_design_compression Job().vbrc_design_tension Job().vbrc_design_compression Job().guss_beam_interface_force Job().ufm_special_case Job().seismic_vb_guss_dsgn Job().min_bolt_rows_hbrace Job().min_bolt_rows_vbrace Job().shear_tab_base_flex Job().transverse_bm_stiff
Job().design_plate_closer_than Job().multi_factor_dist Job().increment_gusset Job().round_flat_plate Job().min_stiff_thick Job().total_stiff_clear Job().use_reinf_plate
Job().min_doubler_plate_thick Job().top_doubler_plate_ext Job().bot_doubler_plate_ext Job().flg_stiff_criteria Job().thick_criteria_percent Job().thick_criteria_dim Job().moment_plate_ext Job().use_full_depth_stiff is out of date -- this is new
Job().moment_gap()returns alistofmoment_gapobjects, each of which corresponds to a line on the Flange Plate Clearances table.Job().moment_gap()accepts a nominal depth value as its argument. Attributes ofmoment_gapobjects are:obj.nom_depth obj.gap# Prints the first line of the Flange Plate Clearances. from job import Job print(Job().moment_gap()[0].nom_depth) print(Job().moment_gap()[0].gap)# Prints setup values for a nominal depth of 19. from job import Job print(Job().moment_gap(19).nom_depth) print(Job().moment_gap(19).gap)
Job(). moment_gap_locationreturns "gap at top" or "gap at bottom" or "gap at both".
Job(). hbr_wflg_br_gusset_gapreturns the setup value entered as the clearance between a wide flange or S shape horizontal brace's bottom gusset and its bottom flange.
Job(). vbr_wflg_br_gusset_gapreturns the setup value entered as the clearance between a wide flange or S shape or welded plate wide flange vertical brace's bottom gusset and its bottom flange.
Job().weld_tensile_strength Job().weld_electrode_type Job().weld_gap_field_moment Job().weld_reent_cut_moment Job().weld_root_face Job().weld_web_setback Job().weld_groove_angle Job().fema_reent_depth Job().fema_reent_length Job().fema_reent_rad Job().fema_flg_flush_length Job().weld_min_size Job().weld_max_size Job().weld_around_base_plate Job().weld_around_cap_plate
Schedule of Minimums for Structural Members
Job().min_struct()returns alistofmin_structobjects, each of which corresponds to a line on the Schedule of Minimums for Structural Members . Attributes ofmin_structobjects are:obj.nom_depth obj.bolt_dia obj.num_rows obj.tos_to_firstAn index of
[0]is used in the following script to get data from the first line in the Schedule of Minimums for Structural Members . Substituting[1]for[0]in this script would get data from the second line.# Prints the first line of the Schedule of Minimums. from job import Job print(Job().min_struct()[0].nom_depth) print(Job().min_struct()[0].bolt_dia) print(Job().min_struct()[0].num_rows) print(Job().min_struct()[0].tos_to_first)
Job().min_struct()accepts a nominal depth value as its argument. In the following example, that value is24.5. The following script returns the values on the line on the schedule that is closest to, but not less than, 24.5:# Prints setup values for a nominal depth of 24.5. from job import Job print(Job().min_struct(24.5).nom_depth) print(Job().min_struct(24.5).bolt_dia) print(Job().min_struct(24.5).num_rows) print(Job().min_struct(24.5).tos_to_first)
Schedule of Minimums for Single-Plate Shear Connections.
Job().min_shear()returns alistofmin_shearobjects, each of which corresponds to a line on the Schedule of Minimums for Single Plate Shear Connections. Attributes ofmin_shearobjects are:obj.nom_depth obj.bolt_dia obj.thick obj.num_rowsAn index of
[0]is used in the following script to get the values stored in the first line in the Schedule of Minimums for Single Plate Shear Connections . Substituting[1]for[0]in this script would get data from the second line.# Prints the first line of the Schedule of Minimums. from job import Job print(Job().min_shear()[0].nom_depth) print(Job().min_shear()[0].bolt_dia) print(Job().min_shear()[0].thick) print(Job().min_shear()[0].num_rows)
Job().min_shear()accepts a nominal depth value as its argument. In the following example, that value is22. The following script returns the values on the line on the schedule that is closest to, but not less than, 22:# Prints setup values for a nominal depth of 22. from job import Job print(Job().min_shear(22).nom_depth) print(Job().min_shear(22).bolt_dia) print(Job().min_shear(22).thick) print(Job().min_shear(22).num_rows)
Job().shear_plate_clear or Job().beam_conn_shear_plates
Job().beam_conn_shear_tees
Job().clip_angle_clear or Job().beam_conn_clip_angles
Job().beam_conn_bent_plates
Job().beam_conn_end_plates
Job().seated_bm_clear or Job().beam_conn_seats
Job().bm_splice_clear or Job().beam_conn_splice
Job().beam_plain_end
Job().steel to concrete
Job().brc_clear or Job().brace_conn_other
Job().brace_conn_guss
Job().joist_clear or Job().joist_conn_beam
Job().joist_conn_seats
Job().joist_conn_bcx
Job().welded_conn_brc2brc
Job().welded_conn_brc2supp
Job().brg_pocket_grout_thick
Job().react_fact()returns alistofreact_factobjects, each of which corresponds to a line on the Composite Reaction Factors table. Attributes ofreact_factobjects are:obj.nom_depth obj.react_factAn index of
[0]is used in the following script to get data from the first line in the Composite Reaction Factors table. Substituting[1]for[0]in this script would get data from the second line.# Prints the first line of the Composite Reaction Factors table. from job import Job print(Job().react_fact()[0].nom_depth) print(Job().react_fact()[0].react_fact)
Job().react_fact()can accept a nominal depth value as its argument. In the following example, that value is10.5. This script returns the values on the line on the table that is closest to, but not less than, 10.5:# Prints setup values for a nominal depth of 10.5. from job import Job print(Job().react_fact(10.5).nom_depth) print(Job().react_fact(10.5).react_fact)
Job().bolt_non_moment_dia
Job().bolt_non_moment_type
Job().bolt_moment_dia
Job().bolt_moment_type
Job().bolt_dia_VB
Job().bolt_dia_HB
Job().bolt_dia_K_joist
Job().bolt_K_joist_type
Job().bolt_dia_KCS_joist
Job().bolt_KCS_joist_type
Job().bolt_dia_LH_joist
Job().bolt_LH_joist_type
Job().bolt_dia_DLH_joist
Job().bolt_DLH_joist_type
Job().bolt_dia_SLH_joist
Job().bolt_SLH_joist_type
Job().bolt_dia_joist_grdrs (G joist)
Job().bolt_joist_grdrs_type (G joist)
Job().bolt_dia_BG_joist
Job().bolt_BG_joist_type
Job().bolt_dia_VG_joist
Job().bolt_VG_joist_type
Job().bolt_min_stick_thru
Job().bolt_max_stick_thru
Job().bolt_min_length
Job().bolt_max_field_gap
Job().bolt_max_shop_gap
Job().bolt_class
Job(). avail_bolts()returns alistof available bolt diameters.Job().avail_bolts("Imperial")returns available imperial bolts.Job().avail_bolts("Metric")returns available metric bolts.Job().avail_bolts("Both")returns available bolt diameters.
Job().bolt_sched()returns alistof bolt types from the tab in theBolt Specificationsthat corresponds to the " Connection design method " that you are using. The strings in that list are acceptable arguments for bolt_sched("arg")."A325N"is"arg"in the examples below:
Job().bolt_sched("A325N").mtrl Job().bolt_sched("A325N").conn_method Job().bolt_sched("A325N").surface_class Job().bolt_sched("A325N").shear Job().bolt_sched("A325N").tensionOnly applicable when the " Connection design method " is ' ASD14 ' or ' LRFD14 ' Job().bolt_sched("A325N").mtrl Job().bolt_sched("A325N").conn_method Job().bolt_sched("A325N").surface_class Job().bolt_sched("A325N").hsc_std Job().bolt_sched("A325N").hsc_short Job().bolt_sched("A325N").hsc_oversized Job().bolt_sched("A325N").hsc_long Job().bolt_sched("A325N").shear Job().bolt_sched("A325N").tensionOnly applicable when the " Connection design method " is ' ASD13 ' or ' LRFD13 ' Job().bolt_sched("A325N").mtrl Job().bolt_sched("A325N").conn_method Job().bolt_sched("A325N").surface_class Job().bolt_sched("A325N").shear_long Job().bolt_sched("A325N").shear_over Job().bolt_sched("A325N").shear_short Job().bolt_sched("A325N").shear_standard Job().bolt_sched("A325N").tensionOnly applicable when the " Connection design method " is ' ASD9 '. Job().bolt_sched("A325N").mtrl Job().bolt_sched("A325N").conn_method Job().bolt_sched("A325N").surface_class Job().bolt_sched("A325N").shear_long Job().bolt_sched("A325N").shear_over Job().bolt_sched("A325N").shear_short Job().bolt_sched("A325N").shear_standard Job().bolt_sched("A325N").tensionOnly applicable when the " Connection design method " is ' LRFD3 '. Job().bolt_sched("F1852SC").mtrl Job().bolt_sched("F1852SC").conn_method Job().bolt_sched("F1852SC").surface_class Job().bolt_sched("F1852SC").ks Job().bolt_sched("F1852SC").cl Job().bolt_sched("F1852SC").thread_factor Job().bolt_sched("F1852SC").limit_dia Job().bolt_sched("F1852SC").tension Job().bolt_sched("F1852SC").red_tensionOnly applicable when the " Connection design method " is ' CISC '. Job().bolt_sched("8.8/S").mtrl Job().bolt_sched("8.8/S").mthd_tension Job().bolt_sched("8.8/S").conn_method Job().bolt_sched("8.8/S").mu Job().bolt_sched("8.8/S").kh_std Job().bolt_sched("8.8/S").kh_ovr Job().bolt_sched("8.8/S").kh_short Job().bolt_sched("8.8/S").kh_long Job().bolt_sched("8.8/S").tensionOnly applicable when the " Connection design method " is ' AS 4100 '. Job().bolt_sched("4.6A").alpha_v Job().bolt_sched("4.6A").conn_method Job().bolt_sched("4.6A").f_ub Job().bolt_sched("4.6A").f_yb Job().bolt_sched("4.6A").mtrl Job().bolt_sched("4.6A").surface_classOnly applicable when the " Connection design method " is ' EUROCODE 3 ' or ' EUROCODE 3 UK '. Job().bolt_sched("5.6A").conn_method Job().bolt_sched("5.6A").f_ub Job().bolt_sched("5.6A").f_yb Job().bolt_sched("5.6A").long_slot_hole_factor Job().bolt_sched("5.6A").mtrl Job().bolt_sched("5.6A").oversized_slot_hole_factor Job().bolt_sched("5.6A").short_slot_hole_factor Job().bolt_sched("5.6A").slip_factor Job().bolt_sched("5.6A").standard_hole_factorOnly applicable when the " Connection design method " is ' CHINA GB50017-2003 '. Job().bolt_sched("3.6").conn_method Job().bolt_sched("3.6").f_ub Job().bolt_sched("3.6").f_yb Job().bolt_sched("3.6").long_slot_hole_factor Job().bolt_sched("3.6").mtrl Job().bolt_sched("3.6").oversized_slot_hole_factor Job().bolt_sched("3.6").short_slot_hole_factor Job().bolt_sched("3.6").slip_factor Job().bolt_sched("3.6").standard_hole_factorOnly applicable when the " Connection design method " is ' INDIA IS800-2007 '.
Job(). NutSchedule()returns alistoftuplesin the form[(grade1, nut_type1), (grade2, nut_type2), ... (' ', 'None'), (' ', 'None') ... ]. The following script strips out the tuples with 'None' as their type and prints the "Grade name" and "Nut type" for only those lines that are filled out in the schedule.# Prints the schedule's nut grade and type. from job import Job for grade, type in Job().NutSchedule(): if type != 'None': print(grade, type)
Job(). WasherSchedule()returns alistoftuplesin the form[(grade1, nut_type1), (grade2, nut_type2), ... (' ', 'None'), (' ', 'None') ... ]. The following script strips out the tuples with null entries and prints the "Grade name" and "Washer type" for each line that is filled out in the schedule.# Prints the schedule's washer grade and type. from job import Job for grade, type in Job().WasherSchedule(): if type != 'None': print(grade, type)
Job().washer_thick_flat
Job().washer_thick_hard
Job().washer_thick_bevel
Job().washer_thick_plate
Job().washer_thick_loadJob().washer_data("arg") returns a washer_data object when arg is a string that matches a name in the " Bolt " column under the " AISC 13th " tab on the Bolt Specifications .
Job().washer_data("A307").tc_shop
Job().washer_data("A307").tc_field
Job().washer_data("A307").s_washer_head_SH
Job().washer_data("A307").s_washer_head_OH
Job().washer_data("A307").s_washer_head_SS
Job().washer_data("A307").s_washer_head_LS
Job().washer_data("A307").f_washer_head_SH
Job().washer_data("A307").f_washer_head_OH
Job().washer_data("A307").f_washer_head_SS
Job().washer_data("A307").f_washer_head_LS
Job().washer_data("A307").s_washer_head2_SH
Job().washer_data("A307").s_washer_head2_OH
Job().washer_data("A307").s_washer_head2_SS
Job().washer_data("A307").s_washer_head2_LS
Job().washer_data("A307").f_washer_head2_SH
Job().washer_data("A307").f_washer_head2_OH
Job().washer_data("A307").f_washer_head2_SS
Job().washer_data("A307").f_washer_head2_LS
Job().washer_data("A307").s_washer_nut_SH
Job().washer_data("A307").s_washer_nut_OH
Job().washer_data("A307").s_washer_nut_SS
Job().washer_data("A307").s_washer_nut_LS
Job().washer_data("A307").f_washer_nut_SH
Job().washer_data("A307").f_washer_nut_OH
Job().washer_data("A307").f_washer_nut_SS
Job().washer_data("A307").f_washer_nut_LS
Job().washer_data("A307").s_washer_nut2_SH
Job().washer_data("A307").s_washer_nut2_OH
Job().washer_data("A307").s_washer_nut2_SS
Job().washer_data("A307").s_washer_nut2_LS
Job().washer_data("A307").f_washer_nut2_SH
Job().washer_data("A307").f_washer_nut2_OH
Job().washer_data("A307").f_washer_nut2_SS
Job().washer_data("A307").f_washer_nut2_LS
Job().steel_grades("arg")returns thedictionaryfor steel grade settings under the tab associated with your job's " Connection design method ." The grades are keys. Fy, Fu, and nonstandard notation are values assigned to particular grades.arg= "WFlange" or "Plate" or "Tee" or "Channel" or "Angle" or "Pipe" or "Tube" or "Round and Square Bars" or "Flat Bar" or "S Shape":# Prints the list of channel steel grades. from job import Job print(Job().steel_grades("Channel").keys()) # keys() is a Python method for dictionary objects# Prints the default steel grade for channel. from job import Job print(Job().steel_grades("Channel").keys()[0])
Job().steel_grades_dsgn("arg")is equivalent toJob().steel_grades("arg").
Job().us_steel_grades("arg")works the same asJob().steel_grades("arg"), but applies only to those steel grade settings under the " ASD/LRFD/CISC " tab. The grades are keys. Fy, Fu, and nonstandard notation are values assigned to entries made to particular grades.# Prints the dictionary of U.S. steel grades for channel. from job import Job print(Job().us_steel_grades("Channel"))
Job().us_steel_grades("arg")orJob().aus_steel_grades("arg")orJob().euro_steel_grades("arg")orJob().china_steel_grades("arg")orJob().india_steel_grades("arg")works the same asJob().steel_grades("arg"), but applies only to those steel grade settings under the " ASD/LRFD/CISC " or " AS4100 " or " Eurocode " or " China " or " IS800-2007 " tab. The grades are keys. Minimum thickness, maximum thickness, Fy, Fu, and nonstandard notation are values assigned to entries made to particular grades.# Prints the dictionary of Australian grades for channel. from job import Job print(Job().aus_steel_grades("Channel"))
Job().steel_grades("arg").default()orJob().us_steel_grades("arg").default()orJob().aus_steel_grades("arg").default()orJob().euro_steel_grades("arg").default()orJob().china_steel_grades("arg").default()orJob().india_steel_grades("arg").default()the default steel grade, andlistsof entries made to the grade.# Prints the default steel grade for wide flange. from job import Job print(Job().steel_grades("WFlange").default())
Job().steel_grades("arg").default()[num]orJob().us_steel_grades("arg").default()[num]orJob().aus_steel_grades("arg").default()[num]orJob().euro_steel_grades("arg").default()[num]orJob().china_steel_grades("arg").default()[num]orJob().india_steel_grades("arg").default()[num]returns a list of entries to the default steel grade. On the " ASD/LRFD/CISC " tab, there is only one entry line per steel grade, so '[0]' is the only valid index.# Prints the second entry to the default steel grade for wide flange. # Note that the first entry is numbered "0." from job import Job print(Job().aus.steel_grades("WFlange").default()[1])
Job().steel_grades("arg").default()[integer][num][num]returns Fy ([2]), Fu ([3]) and nonstandard notation ([4]) for the specified entry to the default steel grade for "arg".# Prints Fy of the default steel grade for wide flange. from job import Job print(Job().steel_grades("WFlange").default()[0][2])
Job().aus_steel_grades("arg").default()[num][num]orJob().euro_steel_grades("arg").default()[num][num]orJob().china_steel_grades("arg").default()[num][num]orJob().india_steel_grades("arg").default()[num][num]returns Minimum thickness ([0]), maximum thickness ([1]), Fy ([2]), Fu ([3]) and nonstandard notation ([4]) for the specified entry to the default steel grade for "arg".Example: Assume that you have the following entries for wide flanges on the " AS4100 " tab in the Default Steel Grades window. (The values you see in this window may differ, depending on the entries that have been made and on your choice of primary dimension " Units ."):
Steel Grade Nonstandard Notation Minimum Thickness Maximum Thickness Fy Fu DEFAULT 1 250 0 0.4375 38 59 2 0.4375 1.5625 36 59 3 1.5625 39.375 33 59 4 300 0.0 0.4375 46 64 Using values from the table above, the SDS2 Python Interpreter can return the following:
>>> Job().aus_steel_grades("WFlange") # Returns the dictionary of Australian grades for wide flange. You will usually have more lists of entries in the dictionary. The values shown here have been rounded for clarity. {'250': [[0.0, 0.4375, 38.0, 59.0, 'None'], [0.4375, 1.5625, 36.0, 59.0, 'None'], [1.5625, 39.375, 33.0, 59.0, 'None']], '300': [[0.0, 0.4375, 46.0, 64.0, 'None'], # etc. >>> Job().aus_steel_grades("WFlange").default() # Returns the default Australian steel grade for wide flange. '250' is the default, so only its three list entries for that grade -- one for each row of the table -- are returned. [[0.0, 0.4375, 38.0, 59.0, 'None'], [0.4375, 1.5625, 36.0, 59.0, 'None'], [1.5625, [1.5625, 39.375, 33.0, 59.0, 'None'] >>> Job().aus_steel_grades("WFlange").default()[1] # Returns the second ("[1]") entry to the default steel grade for wide flange; that is, the second row of the table. [0.4375, 1.5625, 36.0, 59.0, 'None'] >>> Job().aus_steel_grades("WFlange").default()[1][3] # Returns the fourth ("[3]") list item (Fu) from the second ("[1]") list entry. 59.0
Job().plate_conn_specsreturns the default steel grade for plates; that is, the first line of the Plate Grades table.
Job().mtrl_usage()returns alistoftuples('description', 'mtrl_type')that identify all descriptions that have been entered to the Material Usage Descriptions window. Nothing is returned if there are no descriptions.
Job().mtrl_usage("arg")returns alistof the descriptions for the material type identified by "arg". Material types represented by "arg" can be "Channel" or "Angle" or "Tube" or "Tee" or "Pipe" "Plate" or "WeldPlWFlange" or "WeldPlBox" or "Other"# Prints Material Usage Descriptions for channel. from job import Job print(Job().mtrl_usage("Channel"))
Job().member_revisions()returns alistofMemberRevisionTupleclass instances. Each of these objects contains a line that has been entered to the Member Revisions table.An index of
[0]is used in the following script to print the instance that contains data from the first line in the Member Revisions table. Substituting[1]for[0]in this script would instead print the instance containing data from the second line.# Prints the first line of the member revisions table. from job import Job print(Job().member_revisions()[0])Attributes of
member_revisionsobjects are:obj.short_description obj.long_description# Prints the second line of the member revisions table. from job import Job print(Job().member_revisions()[1].short_description)
Job().default_colors()returns alistof "strings" that are the predefined colors.
Job().default_colors_rgb()returns the rgb values of predefined colors.# Prints a list of tuples of default colors and their rgb values. from job import Job print(zip(Job().default_colors(), Job().default_colors_rgb()))
Member, Material, Bolt and Weld Colors
Each function returns instances of the class of the color selected for member types , bolt types , weld types , or submaterials . The color is represented in
rgba (red, green, blue, alpha)format.Job().default_color_beam() Job().default_color_column() Job().default_color_vbrace() Job().default_color_hbrace() Job().default_color_other() Job().default_color_conn() -- this returns the material default color. Job().default_color_field_bolt() Job().default_color_field_weld() Job().default_color_shop_bolt() Job().default_color_shop_weld()The following attributes (red, green, blue, alpha, and poundstring) work for every default modeling color function listed above. The following examples find values for beams.
Job().default_color_beam().redreturns the red value of the color selected for the beam member type.
Job().default_color_beam().greenreturns the green value of the color selected for the beam member type.
Job().default_color_beam().bluereturns the blue value of the color selected for the beam member type.
Job().default_color_beam().alphareturns the alpha value of the color selected for the beam member type. Alpha is always 255.
Job().default_color_beam().poundstringreturns the hexadecimal string of the color selected the beam member type.# Prints red value for beam. from job import Job print("Red:", Job().default_color_beam().red)# Prints the hex string for beam. from job import Job print("Hex:", Job().default_color_beam().poundstring)
Job().job_northreturns the value entered to " Degrees for job north ."# Prints setup value for "Degrees for job north." from job import Job print("Degrees for job north:", Job().job_north)
Job().sequences()returns alistof the sequence names.# Prints the list of sequence names. from job import Job print(Job().sequences())# Prints the name of the default sequence. from job import Job print(Job().sequences()[0]) # the default sequence is the first line
Job().zones()returns alistof the zone names.# Prints the list of zone names. from job import Job print(Job().zones())# Prints the name of the default zone. from job import Job print(Job().zones()[0]) # sequences are assigned to this zone by default
Job().seq_with_zones()returns alistoftuples('sequence_name', zone_number) that identify all sequence names and the number of the zone it has been placed in.# Prints the list of sequence names with zones. from job import Job print(Job().seq_with_zones())An index of
[0]is used in the following script to get data from the first sequence. Substituting[1]for[0]in this script would get data from the second sequence.# Prints the first sequence's name and its zone. from job import Job print(Job().seq_with_zones()[0])The script above can be further refined to only report the zone for that sequence:
# Prints the zone that the first sequence has been placed in. from job import Job print(Job().seq_with_zones()[0][1])
joist_mfg_default_manufacturerreturns the choice made to " Joist manufacturer ."# Prints setup choice for "Joist manufacturer" from job import Job print("Joist manufacturer:", Job().joist_mfg_default_manufacturer)
JobProperties() returns a
dictionaryof the "Properties " "
Log " and "
Notes " -- that are assigned to your current Job . ( read-only )
# Returns a dictionary of properties of the current Job. from job import * all_props = JobProperties() # no argument, current Job print(all_props)# Returns a list of the Job property keys. from job import * prop = JobProperties() # no argument, current Job print(prop.keys()) # .keys() is a Python method for dictionary objects# Prints Job property values named 'ArchitectContact', 'EngineerContact'. from job import * prop = JobProperties() # no argument, current Job print("Architect: ", prop['ArchitectContact']) print("Engineer: ", prop['EngineerContact'])# Prints the user notes of your current Job. from job import * prop = JobProperties() # no argument, current Job print(prop['Notes'])# Prints the event log of your current Job. from job import * prop = JobProperties() # no argument, current Job print(prop['Log'])
JobPropertySet("field" or "Notes", "setting")sets a particular Job custom property ("field") in your current Job to a particular "setting", or appends a note ( "Notes " ) whose string is the "setting".
# Enters "Sparky Silvershoes" to job property "EngineerContact". from job import * JobPropertySet("EngineerContact", "Sparky Silvershoes") # "EngineerContact" must be a Job property for this to work# Enters "string" from dialog to job property "ArchitectContact". # "ArchitectContact" must be a Job property for this to work from job import * from param import Prompt JobPropertySet("ArchitectContact", Prompt( "string", "Architect:"))# Writes a "Note" for the current Job. from job import JobPropertySet JobPropertySet("Notes", "Note RFIs 22, 32, 43."
Job().concrete_strengths()returns alistof concrete strengths, each item of which corresponds to a line on the Concrete Strength table.An index of
[0]is used in the following script to get data from the first line in the Concrete Strength table. Substituting[1]for[0]in this script would get data from the second line.# Prints the first line of the Concrete Strength table. from job import Job print(Job().concrete_strengths()[0])
Job().concrete_finish()returns alistof concrete finish descriptions, each item of which corresponds to a line on the Concrete Finish table.An index of
[0]is used in the following script to get data from the first line of the table. Substituting[1]for[0]in this script would get data from the second line.# Prints the first line of the Concrete Finish table. from job import Job print(Job().concrete_finish()[0])
Job().cover_surfaces()returns alistoftuplesin the form[( description 1, dimension 1, color 1), (description2, dimension2, color2), ... ], each of which identifies a line from the Concrete Cover Surfaces table.An index of
[0]followed by[2]is used in the following script to data first line and the third column, respectively. This is the hex color value from the first line in the Concrete Cover Surfaces table. Substituting[1]for[0]in this script would get data from the second line. Substituting[0]for[2]in this script would get the description.# Prints the color in the first line of the Concrete Cover Surfaces table. from job import Job print(Job().cover_surfaces()[0][2])
Job(). default_cover_surface ()returns line marked as the default cover surface. If0is returned, the first line of the table is the default.
Job().rebar_definitions()returns alistof reinforcing bar definitions, each item of which corresponds to its size designation as listed in the Rebar Definitions window.
Job().rebar_definition("arg")returns therebar_definitionobject corresponding to the argument.arg= one of the list items returned byJob().rebar_definitions(). Attributes ofrebar_definitionobjects are:obj.rebar_standard obj.size_designation obj.diameter obj.weight obj.min_bend_diam obj.end_hook_diam obj.end_hook_90_len obj.end_hook_180_len obj.stirrup_hook_diam obj.stirrup_hook_90_len obj.stirrup_hook_135_len obj.seismic_stirrup_diam obj.seismic_stirrup_135_len obj.max_mill_length obj.min_fab_length obj.stock_length obj.horz_concrete_splice obj.vert_concrete_splice obj.masonry_splice# Prints the size designation, a colon, and the weight for every rebar definition in the active rebar standard. from job import Job for i in Job().rebar_definitions(): print(i + ': ' + str(Job().rebar_definition(i).weight))
Each function below returns a
listof strings from the Rebar Usage Descriptions window.Job().rebar_usage_beam() Job().rebar_usage_column() Job().rebar_usage_footing() Job().rebar_usage_slab() Job().rebar_usage_wall()# Prints the list of rebar usage descriptions for beams. from job import Job print(Job().rebar_usage_beam())







