The mtrl_list module
| Quick Notes |
MtrlByGuid ( mem_num, GUID) can be used to access a material by its GUID. You might use this attribute, for example, to add a custom property to a material that you are adding parametrically. The following example adds a round bar, then uses the GUID of that round bar to set to "TRUE" a custom property named GALV . A material custom property named GALV must exist (in setup) for this example parametric to run.
# Adds a round bar to the top flange of a beam, sets it to be galvanized
from param import Units, ClearSelection
from member import MemberLocate
from rnd_bar import RndBar
from mtrl_list import MtrlByGuid, MtrlPropertySet
Units("feet")
ClearSelection()
rb = RndBar()
rb.Member = MemberLocate("Select a member")
x_trans = rb.Member.TranslateToGlobal(rb.Member.LeftEnd.minus_dim,
0, 0)
rb.Point1 = rb.Member.LeftEnd.Location + x_trans
rb.Point2 = rb.Point1 + rb.Member.TranslateToGlobal(0.0, 8.0,
0.0)
rb.BarDiameter = 1.0
rb.WorkpointSlopeDistance = rb.Point1.Distance(rb.Point2)
rb.OrderLength = rb.WorkpointSlopeDistance
rb.Centered = 'Yes'
rb.Add()
MtrlPropertySet(MtrlByGuid(rb.Member.number,
rb.GUID), "GALV", "TRUE")
ClearSelection() MtrlLocate("prompt") or MtrlLocate("prompt", "Hole") or MtrlLocate("prompt", "Weld") or MtrlLocate("prompt", "Fit") or MtrlLocate("prompt", "Weld To") invokes Select One Item mode. Each of these functions returns a mtrl_list object for a parametric Add Hole or Add Bolts or Fit or Add Weld operation. They return None if the user right-clicks ( Menu ) and chooses " Cancel ."
# Prints the selected mtrl_list object
from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate
object = MtrlLocate("Select a material")
print(object) MtrlLocate("prompt string", "Single") invokes Select One Item mode. Returns a material object if the user left-clicks ( Select ). Returns None if the user right-clicks ( Menu ) and chooses " Cancel " or presses the Esc key.
# Prints the piecemark of the selected material.
from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate
mtrl = MtrlLocate ("Select a material", "Single")
print(mtrl.piecemark)# Erases the selected rolled section.
from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate
from rolled_section import *
erasable = ["Angle", "Pipe", "W flange",
"W Tee", "Channel", "Tube"]
rs1 = MtrlLocate("Select a rolled section", "Single")
if rs1.MaterialType in erasable:
rs1.Erase()
else:
print("You selected a", rs1.MaterialType)
print("Only these materials are erasable:")
print(erasable)# Loop for erasing rolled sections; press Esc to cancel (break).
from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate
from rolled_section import *
redo = 1
while redo == 1:
mtrl_erase = MtrlLocate("Select a material",
"Single")
if mtrl_erase == None:
break
else:
mtrl_erase.erase() # use return instead of break in a function obj.modelobject() is a method that can be used to return, from a mtrl_list object, a model object (material or hole), whose attributes can be read/written to using parametric code from the model module. Following are examples that you can type at the Python Prompt .
For these two examples, the user needs to select a material:
>>> import mtrl_list >>> mtrl_list.MtrlLocate('Select a material').modelobject() <material 1 of member 8>>>> mtrl_list.MtrlLocate('Select one material', 'Single').modelobject() <material 3 of member 8>For this next example, the user needs to select a hole, then press Enter :
>>> mtrl_list.HoleLocate('Select a hole').modelobject() <hole 36 on material 0 of member 2>
MtrlProperties(mtrl_obj) returns a dictionary of the custom properties -- including the " ![]() Properties " "
Properties " " ![]() Log " and "
Log " and " ![]() Notes " -- that are assigned to the material object (
Notes " -- that are assigned to the material object ( mtrl_obj ). ( read-only )
# Returns a dictionary of properties assigned to the material.
from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate, MtrlProperties
mtrl = MtrlLocate("Select a material", "Single")
all_props = MtrlProperties(mtrl)
print(all_props)# Returns a list of the material property keys.
from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate, MtrlProperties
mtrl = MtrlLocate("Select a material", "Single")
prop = MtrlProperties(mtrl)
print(prop.keys())
# .keys() is a Python method for dictionary objects# Prints the entry to the material property named 'GALV'.
from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate, MtrlProperties
mtrl = MtrlLocate("Select a material", "Single")
prop = MtrlProperties(mtrl)
print(prop['GALV'])# Prints the log of the material that the user selects.
from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate, MtrlProperties
mtrl = MtrlLocate("Select a material", "Single")
prop = MtrlProperties(mtrl)
print(prop['Log'])# Prints the note of the material that the user selects.
from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate, MtrlProperties
mtrl = MtrlLocate("Select a material", "Single")
prop = MtrlProperties(mtrl)
print(prop['Notes']) MtrlPropertySet(mtrl_obj, "field" or "Notes", "setting") sets the material custom property ( field ) on the material object ( mtrl_obj ) to the "setting", or appends a note ("Notes") whose string is the "setting". The first argument must be a genmtrl object, or you will get a Python exception.
# Enters "True" (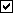 ) to boolean material property "GALV".
from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate, MtrlPropertySet
mtrl = MtrlLocate("Select a material", "Single")
MtrlPropertySet(mtrl, "GALV", "True")
) to boolean material property "GALV".
from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate, MtrlPropertySet
mtrl = MtrlLocate("Select a material", "Single")
MtrlPropertySet(mtrl, "GALV", "True")# Selects 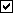 or
or 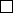 for boolean material property "GALV".
from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate, MtrlPropertySet
from param import yes_or_no
mtrl = MtrlLocate("Select a material", "Single")
true_false = yes_or_no("OK = 1; Cancel = 0")
MtrlPropertySet(mtrl, "GALV", str(true_false))
# 3rd argument must be a string -- hence str(true_false)
for boolean material property "GALV".
from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate, MtrlPropertySet
from param import yes_or_no
mtrl = MtrlLocate("Select a material", "Single")
true_false = yes_or_no("OK = 1; Cancel = 0")
MtrlPropertySet(mtrl, "GALV", str(true_false))
# 3rd argument must be a string -- hence str(true_false)# Writes a "Note" for the material that the user selects.
from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate, MtrlPropertySet
mtrl = MtrlLocate("Select a material", "Single")
MtrlPropertySet(mtrl, "Notes", "ABM page-line 14-2") obj.HoleList() or obj.hole_list() is a method that returns a list of holes ( hole_list objects -- see below ) in a material object. In the following script, len() is a built-in Python function that returns the number of items in a list. Since the list in this example is a list of holes, len(mtr.HoleList()) returns the number of holes in the material. Click here for another example of a Python script that uses obj.HoleList .
# Prints the hole count in the selected material.
from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate
mtrl = MtrlLocate("Select material with holes", "Single")
print(len(mtrl.HoleList()))
hole_listobject attributes includePoint1(global X, Y, Z coordinates),Point2(global X, Y Z coordinates),BoltDiameter(a distance),HoleType(Standard Round or etc),SlotLength(a distance),Material(a gen_mtrl object),BoltType(Auto or A325N or etc.),face(NS Face),ShouldBeValid(Yes or No),SlotRotation(number of degrees). Theobj.HoleList()method or theHoleLocate()function can be used to return a list of hole_list objects.# Prints attribute values for holes in a selected material. from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate m = MtrlLocate("Select a material", "Single") attrs = ['Point1', 'Point2', 'BoltDiameter', 'HoleType', 'SlotLength', 'Diameter'] for h in m.HoleList(): for a in attrs: print(a, ": ", getattr(h, a))
obj.MainMaterial or obj.main_mtrl returns "Yes" or "No". "Yes" indicates that the material is main material. ( read-only )
# Prints Yes if the selected material is main material.
from mtrl_list import MtrlLocate
mtrl = MtrlLocate("Select a material", "Single")
print(mtrl.MainMaterial) HoleLocate("prompt string") invokes Select Item(s) mouse bindings. Returns a list of hole_list objects if the user selects one or more holes and then right-clicks ( Menu ) and chooses " OK ." Returns None if the user right-clicks ( Menu ) and chooses " Cancel ." Click here for information on available hole_list object attributes.
|
|
|
Select Item(s) bindings |
# Prints the list of selected holes.
from mtrl_list import HoleLocate
hole_list = HoleLocate("Select holes")
print(hole_list)






