The Square Bar Material window ( Modeling ) (read-only)
- To open this window:
- Review Material ( Modeling )
- "Edit" on context menu, select material mark ( Modeling )
- Double-click on material -- not main material ( Modeling )
- Review 2D Items ( Drawing Editor )
Also see :
- General Information window (opened from this window)
- Submaterial piecemark (each unique material identified by)
- Submaterial detail (2D drawing of a material)
- Square bar material (type of material this window specifies)
page 1 | contents | material review | material types
------ General settings ------
Piecemark: The submaterial piecemarks ( up to 61 characters ) for the square bar whose settings are being reviewed.
Also see: Square bar system piecemarks begin with the material mark prefix for " Square bar. " For the current quantity of square bars that have been assigned this piecemark, refer to the " Current quantity " listed on this material's General Information window.
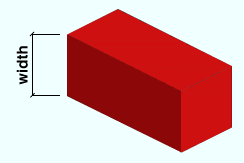
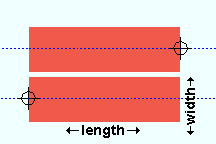
Material width: The width (in the primary dimension " Units " or in other units ) of the bar stock being reviewed. This dimension may be measured along the square bar's Y or Z material axis since all four edges of a square bar shown in cross section are equal.
Material length: The distance (in the primary dimension " Units " or in other units ) from the furthest point on the material's left end to the furthest point on the material's right end. This distance is measured parallel with the material's longitudinal axis ( X material axis ).
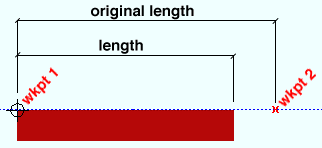
Note: If the left & right " End cut angle " are both ' 0 ' (zero), " Material length " is the " Work point distance " minus the left & right " Material setback ."
Work point distance: The distance (in the primary dimension " Units " or in other units ) between the work points of this square bar.
Note: The longitudinal axis of the square bar is defined by its two work points. In the material coordinate system, this axis is the X material axis .
Angle of twist: 0 (zero) degrees or the positive or negative (-) number of degrees of twist about the longitudinal axis ( X material axis ) of the square bar.

' 0 ' (zero) means the material is straight (not twisted).
A ' number of degrees ' means the right end of the material is rotated the number of degrees entered while the left end is fixed. Assuming you are looking from the right end toward the left end of the material, a positive entry rotates the material counterclockwise.
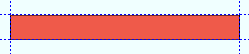
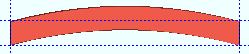
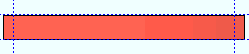
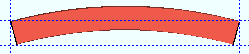
Rolling operation: None or Camber or Weak axis or Strong axis . The center of curvature for each of these choices (except ' None ') is midway between the left and right ends of the material.
' None '
|
' Camber '
|
' Weak axis '
|
' Strong axis '
|
' None ' means the square bar is straight (not curved).
' Camber ' produces indicates bending along the strong axis of the square bar with the ends fixed. The " Mid-ordinate " sets the offset at mid-span and the direction (+ or -) of that offset.
' Strong axis ' or ' Weak axis ' rolling indicates bending that is circular. The two ends of the square bar are not fixed; that is, if the ends were vertical before the operation, they may not be vertical afterwards. The " Mid-ordinate " or " Included Angle " or " Rolling radius " sets the offset at mid-span and the direction (+ or -) of that offset. A " Spiral offset " can also be set.
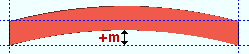
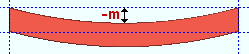
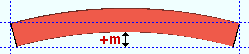
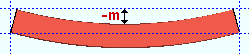
Mid-ordinate: The positive or negative distance (in the primary dimension " Units " or other units ) that the square bar is offset at mid-span as a result of a " Rolling operation " of ' Camber ' or ' Strong axis ' or ' Weak axis '. The sign (+ or -) sets the direction of offset.
Camber with a positive mid-ordinate ( +m )
 |
Camber with a negative mid-ordinate ( -m )
 |
| Weak axis rolling with a positive mid-ordinate (rolling toward the near side)  |
Weak axis rolling with a negative mid-ordinate (rolling toward the far side) 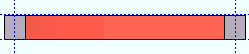 |
Strong axis rolling with a positive mid-ordinate ( +m )
 |
Strong axis rolling with a negative mid-ordinate ( -m )
 |
Included angle: The positive or negative (-) number of degrees that defines the angle of curvature when the " Rolling operation " is ' Strong axis ' or ' Weak axis '.
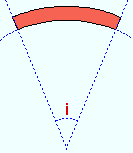
If the left end of the square bar is to your left: A ' negative (-) angle ' means the center of the square bar is lower on the screen than its two ends. A ' positive angle ' means the center of the square bar is higher on the screen than its two ends.
Rolling radius: A positive or negative (-) distance (in the primary dimension " Units " or other units -- up to +/- 120,000 inches) that defines the amount of curvature of the square bar when the " Rolling operation " is ' Strong Axis ' or ' Weak Axis '. The smaller the " Rolling radius " (+ or -), the greater the curvature.
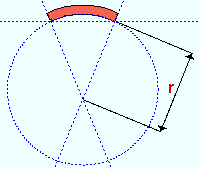
If the left end of the square bar is to your left: A ' negative (-) rolling radius ' means the center of the material is lower on the screen than its two ends. A ' positive rolling radius ' means the center of the material is higher on the screen than its two ends.
Spiral offset: The positive or negative (-) distance that the right end of the square bar is offset from its original work point. The left end of the square bar remains fixed. This applies when the " Rolling operation " is ' Weak axis ' or ' Strong axis '.

Steel grade: Any grade of steel ( A36 or A572 or etc.) from the Steel Grades for Plates & Bar Stock table in Job Options may be shown here as the steel grade for this square bar.
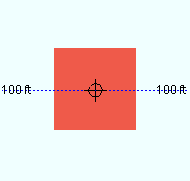
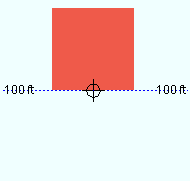
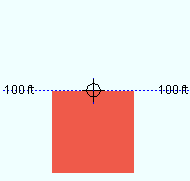
Depth reference point: Center or FS or NS . ' FS ' stands for far side, ' NS ' for near side. The setting that is selected here indicates the orientation of the Z axis of the bar's " Material width " with respect to its workline.
|
|||
| A section view of the same square bar, but with different depth reference points. The view looks perpendicular to the plan view (at 100 ft) in which the square bar was added. |
' Center ' indicates that the Z axis of this square bar's " Material width " is centered with respect to the bar's work points.
' FS ' indicates that the far-side surface of the square bar is in the same plane as the bar's work points.
' NS ' indicates that the near-side surface of the square bar is in the same plane as the the bar's work points.
Note: The square bar's " Reference elevation ," which is reported on the General Information window, is the elevation of the left-end work point of the square bar. Assuming that both work points of the square bar are at that same elevation, the " Depth reference point " tells you whether the square bar material is centered at that elevation, or above that elevation, or below that elevation.
Surface finish: None or Sandblasted or Red oxide or Yellow zinc or Gray oxide or Blued steel or Galvanized or Duplex Coating or Undefined 1 or Undefined 2 or Undefined 3 or Red oxide 2 or Any user added surface finish. This affects the colors of 'Solid ' members on erection views in the Drawing Editor . This also sets the color when "Output material color " is set to 'Surface finish ' for a VRML Export or a DWG/DXF Export . The "Color " ( not "Surface finish ") sets the color of this material in Modeling .
| sand blasted | red oxide | yellow zinc | user surface finish 1 |
| gray oxide | blued steel | galvanized | user surface finish 2 |
To assign a different surface finish, you can drop-down the current surface finish and select the one you want, or you can press the "file cabinet" browse button (
) and double-click any surface finish that is on the list.
Auto ![]() or
or ![]() .
.
If this box is checked (
), the material surface finish follows what is set on the member level.
If the box is not checked (
), the material surface finish can be changed to whatever is available in the list of surface finishes. If the surface finish changes from what the member level has set, the auto checkbox will be unchecked automatically. When the auto check box is unchecked, the member edit window shows an information tag which notifies the user that an attached material is not following what was set on the member level.
Note 1: Submaterial piecemarks can be split apart by surface finish. All surface finishes that do not have the 'Break Marks Material' checked on can be applied to any like material with out the material splitting. If the 'Break Marks Material' is checked on then only like materials with that specific surface finish can have the same piecemark, and because the submaterial marks differ so would the member's piecemark.
Note 2:When exporting a KISS file using "model" as the "Data source " surface finish data on the materials are compiled into the KISS download as follows, with a few exceptions (G=galvanized, N= none or sandblasted, P= others). Those exceptions are:
If the box for "Finish" routing in KISS export setup is set to a user routing
If the user has adjusted the Abbreviation for any of the default provided surface finishes
If you are using a user added surface finish
In these cases you will get what is provided in either the User routing, or the abbreviation field. For other exports it will always provide the abbreviation in the 'surface finishes' settings page.
Tip 1: "Surface area" is reported on the General Information window -- and this can be used to estimate the amount of coating required and its cost.
Tip 2: Changing "Steel grade " "Color " and "Surface finish " do not cause the plate to be regenerated. This means that, if you change those settings only, material fit operations such as a Fit Exact may, optionally, be preserved.
Report Writer:MemberMaterial.Material.SurfaceFinish
Setup:Surface Finish Settings
Color: The color of the square bar when it is displayed in solids form . Different colors may be assigned to materials that have the same submaterial piecemark . The color swatch next to the list box ( ![]() ) displays the color that is selected.
) displays the color that is selected.
Setup: The default colors for member main materials and submaterials is set up on the Modeling Colors setup window.
 |
 |
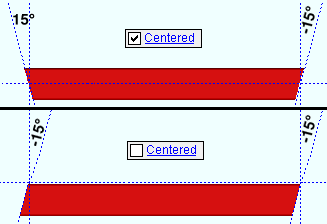
If this box is checked (
), the Y axis of the " Material width " (its near-side width) is centered with respect to the square bar's workline. When looking at the near side, you see the square bar's length and width, but not its depth.
If the box is not checked (
), the square bar's " Material width " is positioned above or below its workline, which runs along its " Material length ."
Note: The " Centered " option does not affect the workline's location within the global coordinate system ; it sets the square bar's position with respect to the workline.
page 1 | contents | material review | material types | top
------ Left/right end settings ------
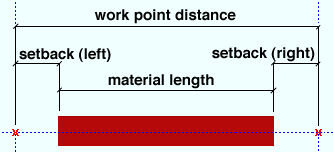
Material setback: The positive or negative (-) distance in the primary dimensioning " Units " that the left/right end of the square bar is displaced from its work point. A negative material setback makes the square bar longer; a positive material setback makes it shorter.

Note: If the left & right " End cut angle " is ' 0 ' (zero), the " Material Setback " distance entered to the right and left ends of the square bar is subtracted from the " Work point distance " to give you the actual " Material length ."
End cut angle: Any angle from 89 to -89 degrees. If you are viewing the near side of the square bar, a positive angle is measured counterclockwise from a perpendicular bisector to the workline. A negative angle is measured clockwise from a perpendicular bisector to the workline.
page 1 | contents | material review | material types | top
To close this window :
" General Information " opens the General Information window, which you can use to review additional information about the selected material.
Press " Close " on the General Information window to close that window and reactivate this window.
"OK" (or the Enter key) closes this window.
page 1 | contents | material review | material types | top