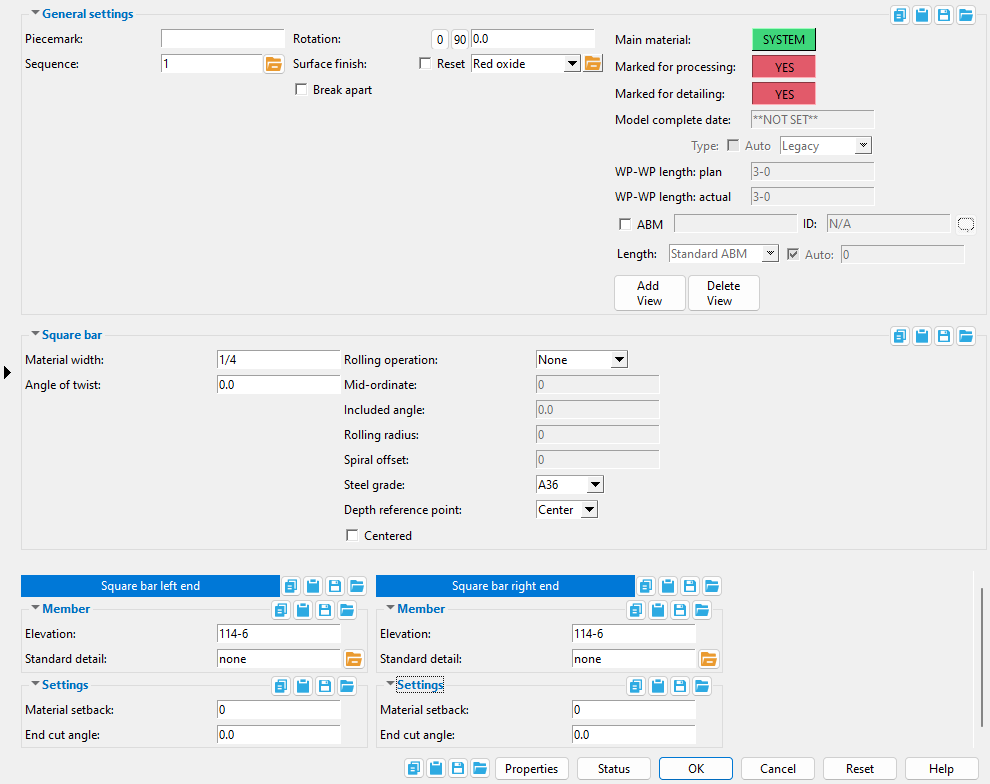
Square Bar Edit window
( Modeling > F2 > "  Misc steel " > " Square Bar ")
Misc steel " > " Square Bar ")
Selecting " Square Bar " as the " 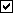 Miscellaneous steel " type adds a custom member with square bar material to a 3D model.
Miscellaneous steel " type adds a custom member with square bar material to a 3D model.
The Square Bar custom member is a superior alternative to " Miscellaneous -- Square Bar ."
The edit window of this member features material and member options on the same window.
Its " General settings " include " Break apart " and " Rotation ," which are not available for the legacy miscellaneous member.
Member operations such as many of those found on the Model > Member menu in Modeling can be performed on this member, and you can add custom components to it.


The " OK " button is disabled (grayed out) to indicate a validation error. Hover the " OK " button with your mouse pointer to get a listing of settings you need to change on this window. When all settings are valid, the " OK " button is enabled. 

Red-colored highlighting identifies an entry that is invalid. You need to change that setting, or you will not be able to close this window using " OK ."
Also see :
- Square bar (topic)
- Miscellaneous member types (the complete list)
- Custom members (a square bar miscellaneous member is a custom member)
- Square Bar Material (window can set Square Bar Edit's " Main Material " to ' USER ')
- Miscellaneous members versus legacy miscellaneous members (topic)
- Surfaces Connection (a custom component you can add to a miscellaneous member)
page 1 | contents | add (F2) | top
Add square bar :
1 . A square bar miscellaneous member can be properly located and rotated even in an isometric view. Before adding the member, be aware of the following:
2 . To add a square bar miscellaneous member (in Modeling ):
Alternative 1 : Press F2 > check the box for "
Miscellaneous steel " > double-click " Square Bar ."
Alternative 2 : Choose Model > Member > Prompt for Member Type > check the box for "
Miscellaneous steel " > double-click " Square Bar ."
3 . Locate - Repeat - Return mouse bindings become active, and you are prompted to locate the square bar's work points. Two work points are required to lay out a square bar.
|
|
|
bindings |
3a : Select the appropriate Locate option.
3b : Left-click ( Locate ) at two different on-screen positions to define the work line between those two points. The first work point you enter when you add the bent plant defines the left end of the member. The work points of a square bar align with the top of the bar or, if " Centered " is checked, with the center of the bar, and, depending on the choice made for its " Depth reference point ," on the ' NS ', ' FS ', or ' Center ' of the bar's thickness. The following illustration shows the difference between laying out work points from left to right versus right to left.
If you Model > Member > Isolate > ... a square bar miscellaneous member, you will find that the member's MAIN VIEW shows the member's origin symbol (
) to be to your left. This is true for any miscellaneous member -- even if the origin symbol for the member is to your right in a plan view. The MAIN VIEW in member isolation directly correlates to the main view of the miscellaneous member's detail.
Best practice when adding a miscellaneous member in a plan view is to input the member from left to right or from bottom to top. That way, when you add a grid line from left to right, the near side of the member, as determined by the location of its left end , will be the side looking toward the bottom or toward the right of the screen.
4 . After you are done laying out work points, the Square Bar Edit window opens. On it are settings of the square bar you are adding.
4a : Enter a " Material width " for the square bar.
4b : Choose whether you want the square bar to be " Centered " or not.
4c ( optional ): The " Left/right end settings " on this window let you specify cuts or material setbacks on the ends of the square bar. The left end is the end associated with the first point you located in step 3.
4d : Press the " OK " button to apply your settings and close this window.
Note: The default settings on this window are those of the last square bar miscellaneous member added or edited in this session of Modeling . Even if all you do is double-click a square bar member and press " OK " on its edit window, its settings become the defaults for the next-added square bar miscellaneous member. You therefore only need to make changes to those settings which are different for this member.
5 . If User and Site Options > Modeling > " Process after modeling operation " is ' Process and create solids ', the new plate will have automatically undergone all phases of Process and Create Solids and will show up in a solid form . If that option is ' Process ' or ' Do nothing ', then the member line of the square bar you just added shows up on screen in stick form , and you will have to Process > Process and Create Solids in order to have the member piecemarked and able to be displayed in a solid form. Do one (1) of the following:
|
|
|
bindings |
Alternative 1 : Move the mouse pointer (
) and middle-click ( Repeat ) to lay out a square bar just like the last one beginning at the point where the point location target (
) is at. The X, Y global axes location of the repeated bar will begin from the located repeat point (where the target is at). The plate's Z location and other settings will be that of the last-added or last-edited square bar.
Alternative 2 : Follow these instructions beginning with step 3 to add a square bar with different settings than the one you just laid out.
Alternative 3 : Right-click ( Return ) if you are done adding square bar.
page 1 | contents | add (F2) | top
------ Square bar ------
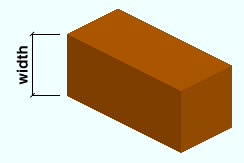
Material width: The width (in the primary dimension " Units " or other units ) of the bar stock being added/edited. This dimension may be measured along the square bar's Y or Z member axis since all four edges of a square bar shown in cross section are equal.
The following can be used to track the choice made here when " Main material " is ' SYSTEM ':
Report Writer: XXXXX . Width
Advanced Selection: Width
Parametric module: Width
Angle of twist: 0 (zero) degrees or the positive or negative (-) number of degrees of twist about the member line of the square bar.
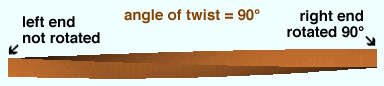
' 0 ' (zero) results in the member's main material not being twisted.
Entering a ' number of degrees ' causes the left end of the member's main material to remain fixed, while its right end is rotated the number of degrees entered. Validation accepts entries between -3600 and 3600 degrees and can generate twists to .06 degree. Assuming that you are looking from the right end toward the left end of the member, a positive entry rotates the main material counterclockwise.
The following can be used to track the choice made here when " Main material " is ' SYSTEM ':
Report Writer: XXXXX . MaterialTwistAngle
Advanced Selection: MaterialTwistAngle
Parametric module: MaterialTwistAngle
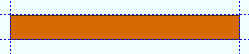
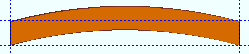
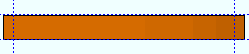
Rolling operation: None or Camber or Weak axis or Strong axis . The center of curvature for each of these choices (except ' None ') is midway between the left and right ends of the member.
None
|
Camber
|
Weak axis
|
Strong axis
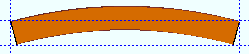
|
' None ' makes the square bar straight (not curved).
' Camber ' produces parabolic bending along the strong axis of the square bar with the ends fixed. The " Mid-ordinate " sets the offset at mid-span and the direction (+ or -) of that offset.
' Strong axis ' or ' Weak axis ' rolling produces bending that is circular. The two ends of the square bar are not fixed; that is, if the ends were vertical before the operation, they may not be vertical afterwards. The " Mid-ordinate " or " Included Angle " or " Rolling radius " sets the offset at mid-span and the direction (+ or -) of that offset. A " Spiral offset " can also be set.
The following can report the choice made here when " Main material " is ' SYSTEM ':
Report Writer: XXXXX . RollTypeDescription
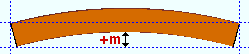
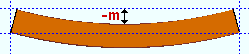
Mid-ordinate: The positive or negative distance (in the primary dimension " Units " or other units ) that the square bar is offset at mid-span as a result of a " Rolling operation " of ' Camber ' or ' Strong axis ' or ' Weak axis '. The sign (+ or -) sets the direction of offset.
Camber with a positive mid-ordinate ( +m )
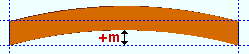 |
Camber with a negative mid-ordinate ( -m )
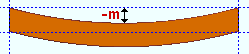 |
| Weak axis rolling with a positive mid-ordinate ( rolling toward the near side )  |
Weak axis rolling with a negative mid-ordinate ( rolling toward the far side ) 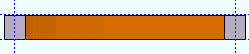 |
Strong axis rolling with a positive mid-ordinate ( +m )
 |
Strong axis rolling with a negative mid-ordinate ( -m )
 |
The following can report the choice made here when " Main material " is ' SYSTEM ':
Report Writer: XXXXX . MidOrdinate
Included angle: The positive or negative (-) number of degrees that defines the angle of curvature when the " Rolling operation " is ' Strong axis ' or ' Weak axis '.
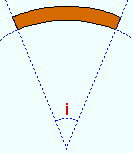
|
i = included angle. Extrapolate a circle from the inside curvature of the member, then draw a line along each end of the material. The lines will meet at the center of the imaginary circle, and their included angle is the angle entered here. |
If the left end (work point 1) of the square bar is to your left: A ' negative (-) angle ' lowers the center of the square bar's curvature on your computer screen. A ' positive angle ' makes the square of the member's curvature lower on your computer screen than its two ends.
The following can be used to track the choice made here when " Main material " is ' SYSTEM ':
Report Writer: XXXXX . IncludedAngle
Advanced Selection: IncludedAngle
Parametric module: IncludedAngle
Rolling radius: A positive or negative (-) distance (to +/- 120,000 inches in the primary dimension " Units " or other units ) that defines the amount of curvature of the square bar when the " Rolling operation " is ' Strong Axis ' or ' Weak Axis '. The smaller the " Rolling radius " (+ or -), the greater the curvature.
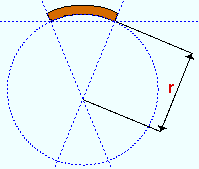
|
r = rolling radius. If you were to extrapolate a circle from the inside curvature of the member, the distance from any point on the inside curve of the top/bottom flange to the center of the circle is the distance entered here. |
If the left end (work point 1) of the square bar is to your left: A ' positive rolling radius ' raises the center of the member's main material on your computer screen. A ' negative (-) rolling radius ' makes the center of the main material lower on your computer screen than its two ends.
The following can be used to track the choice made here when " Main material " is ' SYSTEM ':
Report Writer: XXXXX . RollingRadius
Advanced Selection: RollingRadius
Parametric module: RollingRadius
Spiral offset: The positive or negative (-) distance that you want the right end of the square bar to be offset from work point 2. The left end (work point 1) of the square bar remains fixed. This applies when the " Rolling operation " is ' Weak axis ' or ' Strong axis ', and a non-zero entry has been made to the " Mid-ordinate ," " Included angle ," or the " Rolling Radius " fields.

For a square bar whose member line is in the plane of a plan view: A ' positive distance ' raises the elevation of the right end. A ' negative (-) distance ' lowers the elevation of the right end.
The following can be used to track the choice made here when " Main material " is ' SYSTEM ':
Report Writer: XXXXX . SpiralOffset
Advanced Selection: SpiralOffset
Parametric module: SpiralOffset
Steel grade: A36 or A572 or etc. This is the grade of steel for the square bar whose settings are defined on this window.
Setup: If the steel grade you want is not on the list box (
) for this field, you can use Home > Project Settings > Job > Round and Square Bar Grades to add it to the list.
Tip: Changing the " Steel grade " does not cause the square bar to be regenerated. This means that, if you change this setting only, material operations such as a Cut on Plane may, optionally, be preserved.
The following can be used to track the choice made here when " Main material " is ' SYSTEM ':
Report Writer: MemberMaterial.Material.SubMaterial.MaterialGradeDescription
Advanced Selection: MaterialGrade
Parametric module: MaterialGrade
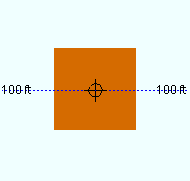
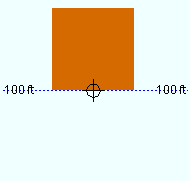
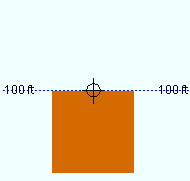
Depth reference point: Center or FS or NS . ' FS ' stands for far side, ' NS ' for near side. This option orients the Z axis of the bar's " Material width " with respect to its member line. Assuming that the square bar has not been rotated, its Z axis is parallel to the depth of the view in which the bar was added -- that is, its Z axis is perpendicular to the plane of that view.
|
|||
| A section view of the same square bar, but with different depth reference points. The view looks perpendicular to the plan view (at 100 ft) in which the square bar was added. |
' Center ' aligns the Z axis of this square bar's " Material width " so that it is centered with respect to the bar's work points.
' FS ' aligns the square bar so that its far-side surface includes the bar's member line. When the bar was added in a plan view at the default " Rotation " (' -90 '), the far side is the face that is away from you when you are in that view and when the bar was not subsequently rotated. You might select this setting, for example, when your work plane is the Surface of a material, you have located two points on that surface to add this square bar, and you want this bar's far side to be flush to that surface.
Choose ' NS ' if you added the square bar in a plan view and want its near side to be at the elevation of the bar's work points. The near side is the face of the square bar that faces you when you are in the view in which the bar was added, assuming the bar was added in a plan view at the default " Rotation " (' -90 ' in a plan view) and was not subsequently rotated.
Piecemarking: Piecemarking will assign different member piecemarks to two square bars with a different " Depth reference point ." Their material may have the same submaterial " Piecemark ". The square bars will have different submaterial mark index numbers .
Note: This option does not change the bar's elevation. It only changes the positioning of the bar with respect to its member line. You can change the " End Elevation " of either end of the square bar.
Centered: ![]() or
or ![]() . The choice made here positions the square bar's depth with respect to its member line.
. The choice made here positions the square bar's depth with respect to its member line.
If this box is checked (
), aligns center of the square bar's depth with respect to the bar's work points.
If the box is not checked (
), the square bar is positioned below its member line, which runs along distance spanned by the bar's member line.
page 1 | contents | add (F2) | top
|
|
|
------ Member ------
End elevation: The elevation (in the primary dimension " Units " or other units ) of the work point at this end of the square bar. For a non-sloping bar, both the left and right end elevations are the same. When you add the square bar, its work points are placed in your current view's reference elevation until you change their elevations here, on this window.
| A square bar has two exact points , whose elevation you can change by changing the member's left- and/or right-end " End elevation ." |

|
To discover the end elevation of a square bar in the 3D model, use Construction Line Add or a similar tool, select EXPT as the Locate option, then snap the point location target to the work point at the end of the member. The Z coordinate reported in the X-Y-Z display tells you the elevation at the snapped-to exact point.
Tip: You should use this option instead of rotating a square bar member's material to change its left- or right-end elevation. For complex situations, you can Model > Member > Move/Stretch one or the other of its work points.
Standard detail: None or a standard detail name . To apply a standard detail, you can type in the file name of the drawing (if you know it), or press the "file cabinet" browse button ( ![]() ) and double-click any job standard detail or global standard detail that is on the list.
) and double-click any job standard detail or global standard detail that is on the list.
If ' none ' is entered here, then no standard detail will be applied on this end of the miscellaneous member when it is automatically detailed .
If a ' standard detail name ' is entered here, the next time you auto detail this miscellaneous member, the reference point of the standard detail will align with the input work point on this end of the member, and the standard detail's bill of material will be combined with the member's bill of material. The detail is placed on a layer that is named after the standard detail plus a "_L" or "_R" suffix.
page 1 | contents | add (F2) | top
------ Settings ------
Material setback: The positive or negative (-) distance in the primary dimensioning " Units " that you want the left/right end of the square bar is displaced from its work point.
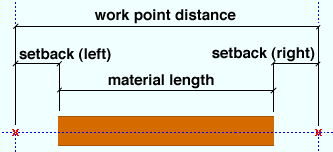
A ' positive material setback ' makes the square bar member shorter. The distance is subtracted from the distance spanned by the bar's member line to give you the length of the bar.
A ' negative (-) material setback ' makes the square bar longer. The distance is also subtracted from the distance spanned by the bar's member line to give you the length of the bar.
The following can be used to track the choice made here when " Main material " is ' SYSTEM ':
Report Writer: XXXXX . MaterialSetbackLeftEnd
Report Writer: XXXXX . MaterialSetbackRightEnd
Advanced Selection: MaterialSetback[0] or MaterialSetback[1]
Parametric module: MaterialSetback[0] or MaterialSetback[1]
End cut angle: Any angle from 89 to -89 degrees.
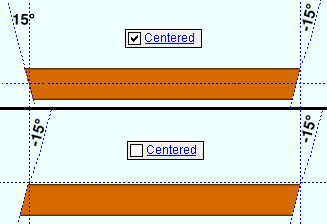
If the left end of the square bar is to your left on your computer screen and negative distances along its Y member axis are toward the bottom of the screen: ' 0 ' (zero) square cuts the end. A ' positive angle ' is measured counterclockwise from a perpendicular bisector to the member line. A ' negative (-) angle ' is measured clockwise from a perpendicular bisector to the member line.
The following can be used to track the choice made here when " Main material " is ' SYSTEM ':
Report Writer: XXXXX . WebCutLeftEnd
Report Writer: XXXXX . WebCutRightEnd
Advanced Selection: WebCutEnd[0] or WebCutEnd[1]
Parametric module: WebCutEnd[0] or WebCutEnd[1]