SDS2 Concrete
On this page :
Terms and Definitions :
Cast in place beam is a member type whose concrete profile is defined in a template . Also defined in the template are continuous longitudinal reinforcing bars and transverse ties. A cast in place beam primarily resists loads applied laterally to the beam's longitudinal axis. Since concrete by itself is not very resistant to such loads, the template for a cast in place beam member should define a fairly robust reinforcing bar system. In Modeling , settings for a concrete beam are defined on its Concrete Beam Edit window. Concrete beam templates are listed on the Beam Templates setup window and defined in the Beam Template Editor . A cast in place beam has options identical to those of a concrete beam .
Cast in place column is a member type whose concrete profile is defined in a template . Also defined in the template are continuous vertical reinforcing bars. Transverse ties can be added to a concrete column using the custom component named Tie Zone or Spiral Zone . Like an SDS2 steel column member, a cast in place column is a structural member designed to carry compressive loads. In Modeling , settings for a concrete column are defined on its Concrete Column Edit window. Concrete column templates are listed on the Column Templates setup window and defined in the Column Template Editor . A cast in place column has options identical to those of a concrete column .
CMU is an acronym for concrete masonry unit. In SDS2 , such masonry units are used for constructing walls. Many commonly used masonry units, including non-concrete items such as common bricks, are listed on the CMU Templates window. Bond beams that can be used for a CMU opening are also listed on the CMU Templates window. The Add CMU Template window together with the CMU Template Editor can be used to add new CMU templates.
CMU course is a member type whose masonry units (CMU) are defined in a template . The member can be a single horizontal or sloping layer of masonry blocks. The length of a CMU course is defined by its two work points. Two different templates can be used, one for " Field block ," the other (optional) for " End block ." A CMU course can be horizontal or sloping. Settings for this member type can be found on the CMU Course Edit window.
CMU Opening is a custom component that can be used to add, for example, windows or doors to CMU walls . A steel lintel (header) or concrete bond beam can be added along with the opening. A Concrete Wall Opening custom component is available for adding openings to concrete walls.
CMU wall is a member type whose masonry units (CMU) are defined in a template . Two different templates can be used, one for " Field block ," the other (optional) for " End block ." :The dimensions and layout of a CMU wall are initially defined by its layout points and on its member edit window, the CMU Wall Edit window. The member line of a CMU wall runs along the bottom of the wall. CMU walls are vertical, and they are typically added in a plan view , though it is not required that all layout points be at the same elevation or in the same plane. It is permissible to define an open or closed shape with the layout points. A window or door can be added to a CMU wall by using the CMU Opening custom component. The Rebar System component can add rebar to a CMU wall.
Concrete beam is a member type whose concrete profile is defined in a template . Also defined in the template are continuous longitudinal reinforcing bars and transverse ties. A concrete beam primarily resists loads applied laterally to the beam's longitudinal axis. Since concrete by itself is not very resistant to such loads, the template for a concrete beam member should define a fairly robust reinforcing bar system. In Modeling , settings for a concrete beam are defined on its Concrete Beam Edit window. Concrete beam templates are listed on the Beam Templates setup window and defined in the Beam Template Editor .
Concrete column is a member type whose concrete profile is defined in a template . Also defined in the template are continuous vertical reinforcing bars. Transverse ties can be added to a concrete column using the custom component named Tie Zone or Spiral Zone . Like an SDS2 steel column member, a concrete column is a structural member designed to carry compressive loads. In Modeling , settings for a concrete column are defined on its Concrete Column Edit window. Concrete column templates are listed on the Column Templates setup window and defined in the Column Template Editor .
Concrete elevation wall is a custom member type that is available in SDS2 Modeling and SDS2 Ultimate. The dimensions and layout of an elevation wall are defined by its layout points and on the Elevation Wall Edit window. Concrete elevation walls must be laid out in an elevation view . The layout points all need to be in the same plane and must form a closed shape. Openings can be added to a concrete elevation wall using the Concrete Wall Opening , and a rebar system can be added using the Rebar System custom component. Even if you don't have a license, you can add an opening to a concrete elevation wall using the Void Space Layout custom component.
Concrete pad footing is a custom member type that can be added in SDS2 Modeling and SDS2 Ultimate. In plan, the shape of a pad footing is rectangular. The footing typically supports a column and transfer's vertical loads to the ground. Adding a pad footing is done by locating a single point, which defines the center of the footing's top surface and presumably aligns with the center of the column that the pad footing supports. Adjustments to the pad footing's length, width, depth and elevation are provided on the Concrete Pad Footing Edit window. You can add reinforcement to the pad footing by using the Rebar System custom component.
Concrete wall is a custom member type that can be added in SDS2 Modeling and SDS2 Ultimate. The dimensions and layout of a concrete wall are defined by its layout points and on its member edit window, the Concrete Wall Edit window. Concrete walls are vertical, and they are typically laid out in a plan view , though it is not required that all layout points be at the same elevation or in the same plane. It is permissible to define an open or closed shape with the layout points. Openings can be added to a concrete wall using Concrete Wall Opening , and a rebar system can be added using Rebar System . The Void Space Layout custom component can also be used to add openings to walls.
Concrete wall opening is a custom component that can be used to add, for example, windows or doors to concrete walls or concrete elevation walls . The Concrete Wall Opening Edit window also includes options for adding reinforcement bars around the opening. A CMU Opening component is available for adding openings to CMU walls.
Concrete slabis a custom member type that can be added in SDS2 Modeling and SDS2 Ultimate. The dimensions and layout of a concrete slab are defined by its layout points and on its member edit window, the Concrete Slab Edit window. Concrete slabs are typically laid out in a plan view , though they can be laid out in non-plan views, so long as all layout points are in the same plane. users can add rebar to a slab using the Rebar System custom component. A concrete slab has a uniform thickness, but users can add thicker areas of concrete reinforcement that includes rebar beneath the slab by using the Thickened Slab custom component.
Continuous footing is a member type whose concrete profile is defined in a template . A continuous footing is part of a concrete foundation and is similar to a grade beam. The two concrete member types employ different sets of default templates since they should be used for different loading conditions. The default templates for a continuous footings have rebar at the bottom of the profile, whereas the default templates for grade beams have rebar at both the top and bottom and also include ties. Settings for continuous footings can be found on the Continuous Footing Edit window. Continuous footing templates are listed on the Continuous Footing Templates setup window and defined in the Continuous Footing Template Editor .
Embed plates are a custom member type that can be added in SDS2 Modeling and SDS2 Ultimate.
Grade beam is a member type that can be used for modeling concrete foundations. A grade beam is similar to a continuous footing. However, the two concrete member types employ different sets of default templates. The default templates for a grade beam have rebar at both the top and bottom of the profile and also include ties. A grade beam gets its name because it has load-bearing properties similar to a beam but is below grade. Settings for grade beams can be found on the Grade Beam Edit window. Grade beam templates are listed on the Grade Beam Templates window and defined in the Grade Beam Template Editor .
Left end ( origin ) is defined differently for different member types.

origin symbol identifies a member's left end when you hover its member line
Member Type Left End Grade Beam , Concrete Wall , Continuous Footing , CMU Wall , Tilt-up Panel These are layouts that may be defined using multiple layout points. (Two points are added to locate tilt-up panels.) The left end of the layout member is the first work point that was located when the member was added. Precast Double Tee , Precast Hollow Core , Precast Single Tee , Concrete Beam These are added by locating two points. The order in which you locate those two points does not matter. The elevation of the two points sets the top of concrete of the member. The member's left end is defined in the same way that the left end is defined for SDS2 members such as beams. Concrete Column , Pilaster The left end is the work point that is at the lowest elevation. That is, the work point with the smallest Z global axis coordinate. Embed Plate ,
Angle or Channel EmbedFor an embed plate member, the left end of the member depends on the member's " Plan rotation ." For an angle or channel embed, the left end is defined in the same way that the left end is defined for SDS2 members such as beams. Member lines can have their display turned on/off using " Member lines " in Display Options . Member lines can be a single line, multiple lines, an outline or a closed layout. EXPT snaps to a the ends of a member line segment. INCM snaps to the intersection of a construction line with a member line. BSMB works off of any line segment in a member line.
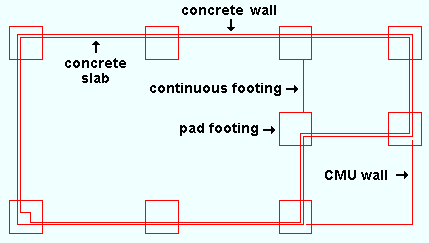
Member Type Member Line Grade Beam , Concrete Wall , Continuous Footing , CMU Wall Open layout: A layout that may be defined using multiple layout points. The member line consists of multiple line segments, which connect the layout points. Precast Double Tee , Precast Hollow Core , Precast Single Tee , CMU course , Concrete Beam , Concrete Column , Pilaster , Embed. A single line: These are added by locating two points. A single member line connects these two points. A concrete column's work point elevations match its left/right " End elevation ." Elevation Wall , Concrete Slab Closed layout: A layout that may be defined using multiple layout points to form a closed shape. The member line consists of multiple line segments, which connect the layout points and delineate the perimeter. Concrete Pad Footing A rectangle: A concrete pad can be added by locating a single point. The rectangular member line depicts the outline of the pad footing in plan.


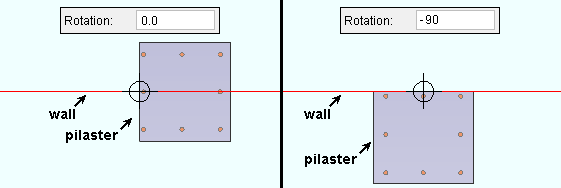
origin symbol identifies a member's left end when you hover its member line Pilaster is a member type whose concrete profile is defined in a template . The work point of a pilaster is located at the middel of one edge of the pilaster's profile. This, together with a " Rotation " option, makes it easy to position the pillaster so that it is face-to-face with a concrete wall.
Precast concrete is widely used in all sorts of buildings, such as parking garages, apartment buildings, motels and nursing homes. Precast concrete members are reinforced and poured in a precast production plant using reusable forms, then cured in the plant's controlled environment. They are then transported from the precast plant to the construction site and lifted into place. Site-poured concrete, on the other hand, is reinforced and poured at the construction site. Most of the members and components that are available in SDS2 are for modeling site-poured concrete and site-poured concrete reinforcement. Three member types -- precast double tee , precast single tee and precast hollow core -- are available to model precast concrete structures.
Precast double tee is a precast concrete member whose concrete profile is defined, in its entirety, on the Precast Double Tee Edit window. The span of a precast double tee is defined by locating two work points when the member is added.
Precast single tee is a precast concrete member whose concrete profile is defined, in its entirety, on the Precast Single Tee Edit window. The span of a precast single tee is defined by locating two work points when the member is added.
Precast hollow core is a precast concrete member whose concrete profile is defined, in its entirety, on the Precast Hollow Core Edit window. The span of a precast hollow core is defined by locating two work points when the member is added.
Rebar is a steel reinforcing bar or a pattern of such bars. When embedded in concrete, rebar provides tensile strength, that is, resistance to tension. In SDS2 , rebar is identified by attributes such as its bar size ( Rebar Definitions ), steel grade ( Reinforcing Bar Grades ), the reinforcing bar coating ( Rebar Coatings ), its specification ( Rebar Specifications ), its function ( Rebar Usage Descriptions ), and its shape ( Standard Rebar Bends ).
Rebar Area Layout is a custom component that was created specifically for concrete slabs , concrete walls , elevation walls , CMU walls and pad footings . The tool works like Rebar System , except that you locate points to designate the layout. Rebar System provides rebar matt coverage to the concrete member's perimeter. Rebar Area Layout provides mat coverage that coincides with a layout that you specify by locating points.
Rebar Run is a custom component that lets you define a run of rebar by locating two points.
Rebar System is a custom component that gives you industry standard rebar placement for concrete slabs , concrete walls , elevation walls , CMU walls and pad footings .
Repeated Rebar is a custom component. It lets you repeat a standard shape or custom layout into or out of the screen at a specified spacing. Use this tool when you are unable to define rebar in a concrete member's template or the Rebar System tool does not give you what you want. Defining rebar in a concrete member's template or using the Rebar System tool are more efficient ways to reinforce concrete.
Reveal is a custom component that applies decorative reveals to tilt-up panels .
Spiral Zone is a custom component for a concrete column or a concrete beam . It lets you to add spirals with different pitches at different zones along the length of the member. The " Pitch " is the distance between coils of the spiral. Each spiral zone that you add along the length of a concrete member is a distinct component, with its own distinct leaf on the concrete member's edit window.
Surface Specific Cover is a custom component that can be added to a surface on any concrete member.
Templates are used to define concrete profiles, longitudinal continuous reinforcing bars and transverse ties. They are also used to define concrete masonry blocks ( CMU ) and rebar ( Standard Rebar Bends ). Different sets of templates are defined for different member types. They are defined in setup windows found under the " Concrete Setup " tab in SDS2 Setup Job or Fabricator Options . All member types that can use a template must use a template since the template defines the cross-sectional shape of that member or the member's masonry units. SDS2 provides many useful templates and they allow users to modify those templates or define new templates of their own.
members or components that require a template: CMU Course , CMU Wall , Continuous Footing ,
Grade Beam , Concrete Beam , Concrete Column , Pilaster ,
Thickened Slab (a custom component)
members whose profiles are defined by entering concrete dimensions on their edit windows. These members don't use templates: Concrete Pad Footing , Precast Double Tee , Precast Hollow Core ,
Concrete Wall , Elevation Wall , Tilt-up Panel .Tilt-up Panel is a member, whose concrete profile is defined, in its entirety, on the Tilt-up Panel Edit window. The length of a tilt-up panel is defined by locating two work points when the member is added.
Void Space Cylinder (member) is a custom member type that can be added in SDS2 Modeling and SDS2 Ultimate. It can be used to model round shafts that impinge upon multiple steel or concrete members.
Void Space Cylinder (component) is a custom member type that can be added in SDS2 Modeling and SDS2 Ultimate. Being a component, it must be added to a member. That member can be any member type, including concrete members and steel members.
Void Space Layout (component) is a custom component that can be added in SDS2 Modeling and SDS2 Ultimate. Adding it to a member makes the void space layout a component of that member. It can be added to concrete members or steel members.
Void Space Layout (member) is a custom member that can be added in SDS2 Modeling and SDS2 Ultimate. Being a member, it can model, for example, shafts that span across multiple members.
Welded Wire Mesh Slab Reinforcement is a custom component for adding reinforcement to concrete slabs . The component models the application of "welded wire mesh" or "welded wire fabric," which are low-cost, easy-to-install alternatives to rebar for light loads and stable weathering conditions. For heavier loading conditions, a Rebar System provides concrete slab reinforcement that is superior to wire mesh.
Concrete Setup :
| Most of the following windows can be accessed from Home > Project Settings > Job > Rebar > or Home > Project Settings > Job > Rebar . |
Home > Job > Rebar > Rebar Schedule Placements .
Home > Fabricator > Concrete > Report Template Manager
Home > Fabricator > Concrete > Report Manager
Home > Job > Concrete > Concrete Strength .
Home > Job > Concrete > Concrete Finish .
Home > Job > Concrete > Concrete Cover Surfaces .
Home > Job > Rebar > Reinforcing Bar Grades .
Home > Job > Rebar > Rebar Definitions > Reinforcing Bar Definition .
Home > Job > Rebar > Rebar Coatings > Rebar Coatings .
Home > Job > Rebar > Rebar Specifications > Rebar Specification . .
Home > Job > Rebar > Rebar Usage Descriptions .
Home > Job > Connections > Embed Schedule .
Home > Job > Concrete > CMU Templates > Add CMU Template > CMU Template Editor .
Home > Job > Concrete > Thickened Slab Templates > Thickened Slab Template Editor .
Home > Job > Concrete > Column Templates > Column Template Editor .
Home > Job > Concrete > Beam Templates > Beam Template Editor .
Home > Job > Concrete > Grade Beam Templates > Grade Beam Template Editor .
Home > Job > Concrete > Continuous Footing Templates > Continuous Footing Template Editor .
Home > Job > Concrete > Pilaster Templates > Pilaster Template Editor .
Home > Job > Rebar > Standard Rebar Bends > Rebar Shape Template Editor > and/or 3D Multi-dimension Segment and/or Segment and/or Seismic Stirrup Hook and/or Stirrup Hook and/or End Hook Planar Multi-dimension Segment and/or Bend and/or Arc and/or Circular Hoop and/or Spiral .
Members :
| members are custom members . |
The CMU Course Edit window.
The CMU Wall Edit window.
The Concrete Pad Footing Edit window.
The Concrete Slab Edit window.
The Continuous Footing Edit window.
The Embed Plate Edit window.
The Precast Double Tee Edit window
The Precast Hollow Core Edit window
The Precast Single Tee Edit window
The Concrete Wall Edit window.
The Elevation Wall Edit window
The Grade Beam Edit window.
The Concrete Beam Edit window.
The Concrete Column Edit window.
The Pilaster Edit window.
The Tilt-up Panel Edit window.
Components :
| components are custom components . |
Material :
The Concrete Material window
The CMU Edit window
The Edit Rebar Shape window
The Welded Wire Mesh Edit window
General settings :
Template: A template file name that has been defined in Concrete Setup . The template defines the member's concrete profile along with longitudinal reinforcing bars and their transverse ties.
| If you are on this window: | The template is selected from: |
| Grade Beam Edit | Grade Beam Templates |
| CMU Wall Edit
and CMU Course Edit |
CMU Templates |
| Concrete Column Edit
and Cast in Place Column Edit |
Column Templates |
| Concrete Beam Edit | Beam Templates |
| Continuous Footing Edit | Continuous Footing Templates |
| Pilaster Edit | Pilaster Templates |
| Thickened Slab Edit | Thickened Slab Templates |
To enter a template, press the "file cabinet" browse button (
) and double-click any template that is listed. The above table tells you which templates are listed for which member types.
Piecemark: Blank or a system piecemark or a user-entered string (of up to 61 characters ) which identifies this member as having an unique design distinct from other members that have been assigned different piecemarks.
Blank indicates that SDS2 piecemarking will assign a system piecemark to the member when you press " OK " to close the member edit window. " PIecemark " is, by default, left blank when you first add a new member.
A system piecemark ( system piecemark ) is assigned automatically if " Piecemark " is blank when you press " OK ."
A user-entered string is a user piecemark . SDS2 piecemarking will not assign new members that user piecemark, nor will piecemarking remove that user piecemark from members to which it has been assigned. It is your responsibility to ensure that the same user piecemark is not used for another distinctly different member.
Tip: If you have assigned a user piecemark to a member, clearing that piecemark and leaving " Piecemark " blank will result in piecemarking assigning a system piecemark to the member when you press " OK ."
Note: A member may be a layout that consists of multiple segments. For example, a concrete wall , a grade beam and a continuous footing are all layouts that are composed of multiple segments which together are assigned the same member " Piecemark ."
Display Options: Member piecemarks
Status Display: General status options > Piecemark
Advanced Selection: m.Piecemark
Advanced Selection: m.SystemPiecemark
Sequence: Any sequence name from the Sequence Names setup list can be entered here.
Defaults: The sequence assigned by default to the first concrete member of the same type (concrete pad footing, concrete slab, etc.) that is added after you first start up Modeling is the sequence listed in line 1 of the Sequence Names list. For each subsequently added member of that type during the same session in Modeling , the default sequence becomes the sequence assigned to the last-added or last-edited member.
To assign a different sequence, you can type in any sequence name that is on the Sequence Names list, or you can press the "file cabinet" browse button (
) and double-click any sequence name that is on the list.
Why assign sequences: Sequences may be assigned to members as a means of grouping such members together. This makes it convenient, for example, to turn off their display using the " Sequence " or " Zone " options in Status Display . For concrete members that are actually shipped to the construction site, the " Sequence " you assign to that member may correspond to the erection sequence.
Sequences and zones: When a member is assigned a sequence, it is also assigned to a zone. Many sequences may be assigned to one zone, but different zones cannot be assigned the same sequence. As a consequence of this, each physical member is in one sequence and in one zone. The Zone and Sequence setup window tells you which sequences are under which zones.
Warning: If the setup option " Break member piecemarks apart by " in Member and Material Piecemarking is set to ' Sequence ' or ' Zone ', some members may be assigned new piecemarks as you change their sequences. The same is true if the box is checked for " Break submaterial marks apart by sequence " or " Break submaterial marks apart by zone ."
Setup: Zone and Sequence window
Topic: Dividing a model into sequences/zones
Tools: Sequence by Area , Set Sequence , Update Attributes
Status Display: General status options > sequence and Zone
Status Report by XXX: Sequence and Zone
Report Writer: Member.ErectionSequence
Report Writer: Member.ErectionZone (the " Sequence " sets the zone)
Advanced Selection: m.ErectionSequence
Advanced Selection: m.ErectionZone (the " Sequence " sets the zone)
Parametric module: m.ErectionSequence
Parametric module: m.ErectionZone (the " Sequence " sets the zone)
Graphical: members are custom members . components are custom components . When custom members were first introduced to SDS2, overlapping duplicate materials could be generated on custom members due to users graphically modifying the custom-member material, then making changes on the custom-member edit window. By marking graphically altered materials as graphical and deleting such materials whenever custom-member-generated materials are regenerated, overlapping duplicate materials are not generated.
| What makes a custom member or component graphical ? A custom member or custom component is set to " |
If "
Graphical " is checked , then changes made on the custom member's edit window or to a custom component will not be applied, thus preserving all graphical changes that were made to the custom member's or component's materials. This means that when you press " OK " on the edit window, or when you Process a custom member or a custom component, no new materials will be generated.
If "
Graphical " is not checked , then after you press " OK " to close the custom member/component's edit window, all of the member/component's materials will be deleted, and new materials will be generated per settings on the edit window. Any graphical changes that you made to materials will be lost.
Warning : Any graphical changes that you make to materials will be preserved only so long as the custom member is set to "
Graphical ." For this reason, you should make changes on the custom-member edit window before you begin to graphically alter the custom-member material. Otherwise, any graphical changes that you make will be lost.
Strength: The compressive strength of the concrete. Residential requirements are commonly from 2500 psi (17 MPa). Commercial requirements may be to 4000 psi (28 MPa). Special applications may call for strengths exceeding 10,000 psi (70 MPa).
The list box choices for " Strength " that you can choose from are the strengths that are listed on the Concrete Strength setup window. If the primary dimension " Units " are set to ' Metric ' for your current Fabricator, then the strength values that are listed in MegaPascals (MPa). Otherwise, they are in pounds per square inch (psi).
The " Strength " that you specify for a concrete member is not used for any load calculations or connection design. " Strength " is simply an attribute that you can assign and track to differentiate among concrete installations.
Finish: None or Smooth or Broomed or Stamped or Stained or Epoxy or Sealed or etc.
The list box choices for " Finish " that you can choose from are the finishes that are listed on the Concrete Finish setup window.
Model complete date: **NOT SET** or a month day year (see entering dates ).
' **NOT SET** ' removes the designation of " Model complete " from this member, thus allowing the member to be physically altered. Type in 0 to enter ' **NOT SET** ' -- see entering dates .
If a ' month day year ' is entered, settings on this window are grayed out and cannot be changed. The affected member is prevented from being altered during the solids creation phase of Process and Create Solids .
Volume (cubic yards): Read only . The concrete volume is recalculated after you press " OK ." When you re-open this window, the newly corrected volume will be reported, in cubic yards. To convert cubic yards to cubic feet, multiply by 27 (3 x 3 x 3).
| Member Type | Items Related to Concrete Volume |
| Concrete Pad Footing | " Depth " " Width " " Length " |
| Concrete Slab | " Perimeter length " " Diagram " " Depth " " Surface area " |
| Continuous Footing | " Total length " " Diagram " " Template " " Reference " |
| Precast Double Tee | The span of the precast double tee is its wkpt to wkpt distance. Also relevant to volume calculations are " Flange thickness " " Depth " " Stem top width " " Stem bottom width " etc. |
| Precast Hollow Core | The span of the precast hollow core is its wkpt to wkpt distance. Also relevant to the volume calculation are " Width " " Depth " " Hollow diameter " " Hollow spacing " etc. |
| Precast Single Tee | The span of the precast single tee is its wkpt to wkpt distance. Also relevant to volume calculations are " Flange thickness " " Depth " " Stem top width " " Stem bottom width " etc. |
| Concrete Wall |
" Total length " " Height " " Thickness "
" Reference " " Diagram " |
| Elevation Wall | " Perimeter length " " Diagram " " Depth " " Surface area " |
| Grade Beam | " Total length " " Template " " Reference " |
| Concrete Beam | " Total length " " Template " " Left/right material setback " " Notch end " |
| Concrete Column | " Total length " " Template " " Left/right material setback " |
Volume (cubic feet): Read only . The concrete volume is recalculated after you press " OK ." When you re-open this window, the newly corrected volume will be reported, in cubic yards. To convert cubic feet to cubic yards, divide by 27.
| Member Type | Items Related to Concrete Volume |
| Concrete Pad Footing | " Depth " " Width " " Length " |
| Concrete Slab | " Perimeter length " " Diagram " " Depth " " Surface area " |
| Continuous Footing | " Total length " " Diagram " " Template " " Reference " |
| Precast Double Tee | The span of the precast double tee is its wkpt to wkpt distance. Also relevant to volume calculations are " Flange thickness " " Depth " " Stem top width " " Stem bottom width " etc. |
| Precast Hollow Core | The span of the precast hollow core is its wkpt to wkpt distance. Also relevant to the volume calculation are " Width " " Depth " " Hollow diameter " " Hollow spacing " etc. |
| Precast Single Tee | The span of the precast single tee is its wkpt to wkpt distance. Also relevant to volume calculations are " Flange thickness " " Depth " " Stem top width " " Stem bottom width " etc. |
| Concrete Wall |
" Total length " " Height " " Thickness "
" Reference " " Diagram " |
| Elevation Wall | " Perimeter length " " Diagram " " Depth " " Surface area " |
| Grade Beam | " Total length " " Template " " Reference " |
| Concrete Beam | " Total length " " Template " " Left/right material setback " " Notch end " |
| Concrete Column | " Total length " " Template " " Left/right material setback " |
Perimeter length: Read only . The distance that is reported here is calculated automatically and reported in the primary dimension " Units ." It is the total length of the perimeter of the top surface of a concrete slab . The member line of a concrete slab shows this perimeter.
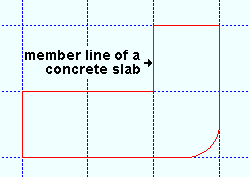
|
The perimeter of a concrete slab is shown when that slab is displayed in stick form . |
Total length: Read only . The distance that is reported here (in the primary dimension " Units ") is the length of the longest edge of a wall or member. This length is not necessarily the length of the member line . See the table below,
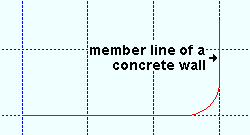
|
The member line of a concrete wall depicts the outline of that wall when that wall is displayed in stick form . The " Total length " of the wall is the length of its longest edge and therefore also depends on the wall's " Reference ." |
| Concrete Member | Items Related to Total Length |
| Continuous Footing | " Diagram " " Template " " Reference " |
| Concrete Wall | " Thickness " " Reference " " Diagram " |
| Grade Beam | " Template " " Reference " |
| Concrete Beam | " Template " " Left/right material setback " |
| Concrete Column | " Template " " Left/right material setback " |
| CMU Wall | " Field block " " Reference " See the note. |
Note: On the CMU Wall Edit window, " Total length " is called " Total wall length ." A CMU Wall may extend past or not quite to the extents of its member line due to choices made to " Starting edge " and " Ending edge ." The choices made to those options, however, do not affect the " Total wall length ."
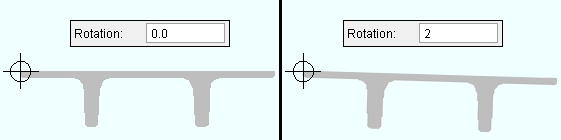
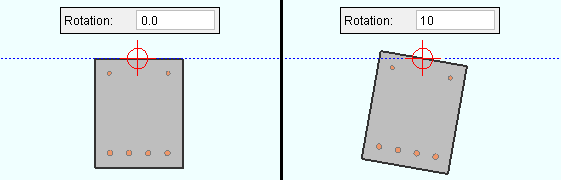
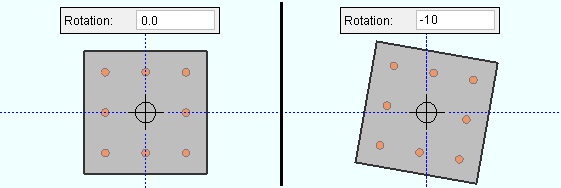
Rotation: A positive (+) or negative (-) number of degrees. The axis of rotation is the member line of the member. A precast double tee and a precast single tee and a precast hollow core are similarly placed with respect to its member line. A concrete beam's member line is centered along the length of that concrete beam's top surface. A concrete column's member line is centered with respect to its concrete profile.
|
|
If you are looking at the left end of a precast double tee or a precast single tee or a precast hollow core , .the member's origin ( |
|
| The member line axis of rotation for a concrete beam is centered at the top surface of that beam. The left end of a beam is determined by its global coordinates. |
|
| The left end of a concrete column is its bottom end. In a plan view , you are looking at the top end of a concrete column. A negative (-) rotation for a column rotates that concrete column clockwise in a plan view. |
|
| The work point of a pilaster is placed at the center of one edge of the member. This makes it easy to rotate it so that it interfaces with a concrete wall. |
If you are looking at a member's left end :
' 0 ' degrees orients concrete member flat, that is, so that it its top surface is horizontal in an elevation view. That same top surface will be flat in a plan view.
' A positive number ' of degrees rotates the member clockwise from its zero position.
' A negative number ' of degrees rotates the member counterclockwise from its zero position.
Surface area (sq. feet): Read only . The distance that is reported here is calculated automatically and reported in square feet. It is the total surface area of the top surface of a concrete slab .

|
The top surface of a concrete slab is the 2D area inside the perimeter of the concrete slab. The perimeter of the concrete slab is the member line that is shown when that slab is displayed in stick form . |
Bottom-row buttons, members :
![]() ( form buttons ) are named " Copy " " Paste " " Save " and " Load ."
( form buttons ) are named " Copy " " Paste " " Save " and " Load ."
On a member or component edit window, form buttons that are at the bottom of the window operate on all settings, across the entire edit window. This means, for example, that " Copy " will copy all settings on the window.
When form buttons are embedded in the headers for individual leaves on the edit window, the buttons apply only to the settings that are contained in that leaf.
Click here for more information about how form buttons work.
"Properties" opens the Edit Properties window, on which you can make entries to custom properties . If, at the time it was created, your current Job was set to use a legacy flavor, the window that opens is named Custom Properties , not Edit Properties .
The Edit Properties window can also be used to read "
Log " entries or review or type "
Notes ."
The " Properties " button is disabled ( grayed out ) when a new custom member is being added.
Tip: Model > Member > Properties is an alternative to this button. It opens the Edit Properties window without your first having to open a member edit window.
" Status " opens the Member Status Review window, which can give you additional information about the custom member, and which you can use to enter status information.
"OK" (or the Enter key) closes this window and saves the settings on it.
If the " OK " button is disabled ( grayed out ), you have made an invalid entry to this window


Red-colored highlighting identifies an entry that is invalid. You need to change that setting, or you will not be able to close this window using " OK ." Solids on "OK": This applies to custom members, not custom components. If the appropriate choice is made to User and Site Options > Modelng > " Automatically process after modeling operation ," then the member will automatically be regenerated ( Create Solids will take place) after your press " OK ." Otherwise, you will have to manually Process and Create Solids in order for changes you made on this window to be fully updated in the 3D model.
"Cancel" (or the Esc key) closes this window without changing (or adding) the member or component you are editing (or adding).
"Reset" undoes any changes made since you first opened this window. That is to say, " Reset " populates this window with the settings that were originally entered to it when you first opened the window. The window remains open.







