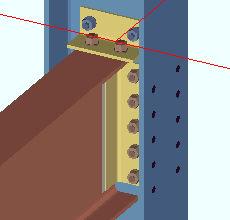
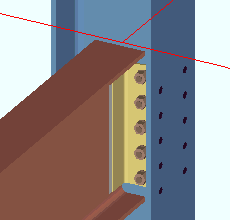
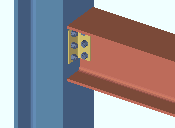
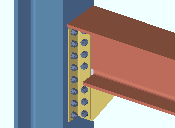
The Beam Edit window (or Beam Edit -- Multiple or Beam Review )
VIDEO 
Shear thru plates can be designed with an axial load. Form buttons are used to " Copy " settings from the right end of one Beam Edit window and " Paste " them to the left end of the Beam Edit window on the opposite end of the shear thru plate connection.
|
|||||
|
|
||||
Section size: The beam's main material (e.g., ' W12x45 ' ). Only materials listed in the local shape file can be specified here.
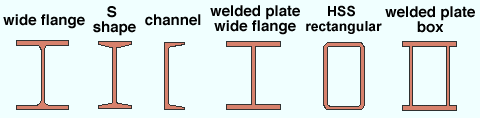
| Valid Material Types for Beam Connections " Input connection type " connections can be generated when the beam's " Section size " is one of the following shapes: |
|
|
|
| wide flange ,
channel , welded plate W , S shape |
Connection design can create the full range of " Input connection types " and can automatically connect braces, beams and columns to a beam whose " Section size " is any of these types. " |
|
HSS/TS (tube) |
Connection design can create clip angles (perp to W or tube beam/column), shear connections ( to tube or channel beams or perp to W or tube column) and end plates (perp to W or tube beam/column). Seats for tube beams are designed, even though field bolting a seat to a tube section can be problematic. Braces, beams and columns can automatically connect to tube beams.Connection design can create bent plates ( to W or S column) , but only with a paddle plates . |
| welded plate box |
If this beam end's " Input connection type " is ' Plain end ', connection design automatically sets back the beam and generates appropriate " |
|
" |
Connection design can create the full range of " Input connection types ," but cannot apply " |
To enter a section size: You can type in the section size that you want, or you can press the "file cabinet" browse button (
) and double-click any section that is on the list of available materials in the local shape file . Validation only lets you enter a material that is listed in the local shape file. Also, if you enter a section size that is set to not available , validation opens a yes-no dialog with the warning, " The section size is not available from suppliers. Are you sure you want to use it? "
C15x50
C15x40
C15x30
C12x30
C12x25
C12x20.7

Since only " Channel " is checked, only channel sections are listed. This selection dialog opens when you press the
button.
Invalid material types: If you enter a " Section size " that is not one of the "Valid Material Types for Beam Connections" listed in the above chart, you will get the following end connection failure message :
| Invalid material type for this member |
Note: Beam member lines (stick form worklines) are drawn across the top flange center line of a wide flange , welded plate wide flange or tube beam. For a channel beam, the work line is at the heel of the top flange of the channel.
To add/edit section sizes: Shapes Properties .
Required file for editing: The " Shape file " path must be set to the local shape file (press " Local ").
To copy section sizes from another shape file: Copy Shapes .Status Display: Member status > Member section size
Report Writer: Member.MaterialFile.SectionSize
Advanced Selection: m.SectionSize
Parametric module: m.SectionSize
Piecemark or System piecemark or User piecemark or Frozen piecemark :
Sequence :
Note this scenario: You are editing one beam, which shares its piecemark with other beams. You change its sequence and other settings. If you press " Yes " when prompted " Do you want to change all... ," the changed sequence applies only to the one beam you are editing, but the other settings are applied to all beams with the same piecemark.
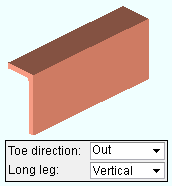
Long side: Vertical or Horizontal. This " ![]() General settings " option applies when the beam's " Section size " is a HSS/TS section.
General settings " option applies when the beam's " Section size " is a HSS/TS section.
|
|
' Vertical ' makes the long side vertical.
' Horizontal ' makes the long side horizontal.
Advanced Selection: m.LongLegOfAngleIsVertical
Parametric module: m.LongLegOfAngleIsVertical
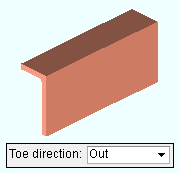
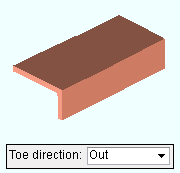
Toe direction: In or Out . This " ![]() General settings " option applies when the beam's " Section size " is channel or single angle material.
General settings " option applies when the beam's " Section size " is channel or single angle material.
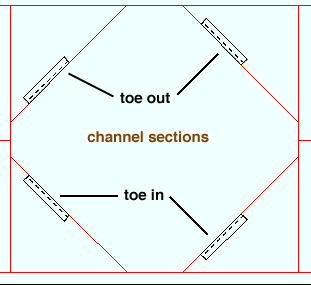
' In ' points the toe of the angle (toes of the channel) down in a plan view (toward the right if the workline of the beam is vertical in a plan view). It points the leg (or toes) toward you if you are facing the near side of the material in an elevation view.
' Out ' points the leg (or toes) up in a plan view (toward the left if the workline of the beam is vertical in a plan view). It points the leg of the angle (toes of the channel) away from you if you are facing the near side of the material in an elevation view.
A special case: Suppose that you change the " Toe direction " and other settings on a beam that shares its piecemark with other members. If you press " Yes " when prompted to " Change all... ," the changed toe direction applies to this beam only, while the other settings are applied to all of the other beams with this same piecemark.
Report Writer: Member.Settings.ToeIO
Advanced Selection: m.ToeIO
Parametric module: m.ToeIO
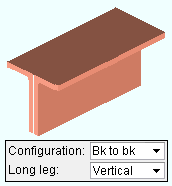
Configuration: Star or Back to back . This " ![]() General settings " option becomes available when the box is checked for "
General settings " option becomes available when the box is checked for " ![]() Double material ."
Double material ."
|
|
If ' Star ' is selected, the outside corner of each of the two angles is laid out along the member line of the beam. For a non-sloping beam with a " Rotation " of ' 0 ', the top face of lower angle is at the " End elevation " of the beam, while the bottom face of the upper angle is at the " End elevation " of the beam.
If ' Back to back ' is selected, the two angles are laid out so that one leg of each angle is back-to-back. For a non-sloping beam with a " Rotation " of ' 0 ', the top faces of the angles are at the " End elevation " of the beam.
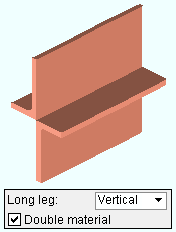
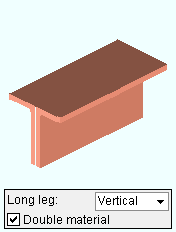
Long leg: Vertical or Horizontal . This " ![]() General settings " option applies when the beam's " Section size " is angle material.
General settings " option applies when the beam's " Section size " is angle material.
|
|
If ' Vertical ' is makes the long leg of the angle vertical when ' 0 ' is the " Beam rotation ."
If ' Horizontal ' makes the long leg of the angle horizontal when ' 0 ' is the " Beam rotation ."
Report Writer: Member.Settings.LongLegOfAngleIsVertical
Advanced Selection: m.LongLegOfAngleIsVertical
Parametric module: m.LongLegOfAngleIsVertical
Double material: ![]() or
or ![]() . This "
. This " ![]() General settings " option applies when angle or channel material has been entered as the beam's " Section size ." For a double-channel beam, connection design can create connections similar to those that it can create for a wide-flange beam.
General settings " option applies when angle or channel material has been entered as the beam's " Section size ." For a double-channel beam, connection design can create connections similar to those that it can create for a wide-flange beam.
|
|
If this box is checked (
), two angles (or two channels) are used as the beam main material. The two angles may be oriented either ' Back to back ' or in a ' Star ' " Configuration ." Channels are always back to back.
If the box is not checked (
), a single angle (or channel) is used as the beam main material.
Report Writer: Member.Settings.DoubleMaterial
Advanced Selection: m.DoubleMaterial
Parametric module: m.DoubleMaterial
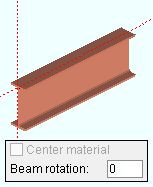
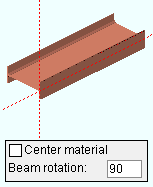
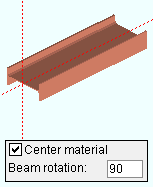
Center material: ![]() or
or ![]() . This "
. This " ![]() General settings " option applies when ' 90 ' when ' -90 ' is the " Beam rotation ."
General settings " option applies when ' 90 ' when ' -90 ' is the " Beam rotation ."
|
|
|
If this box is checked (
), the beam's main material (its " Section size ") is centered with respect to the beam member line .
If the box is not checked (
), the top flange of the beam's main material aligns with the beam workline.
Report Writer: Member.CenterMaterial
Advanced Selection: m.CenterMaterial
Parametric module: m.CenterMaterial
Welded section is single material: ![]() or
or ![]() . This "
. This " ![]() General settings " option applies when the beam's " Section size " is a welded plate wide flange or a welded plate box .
General settings " option applies when the beam's " Section size " is a welded plate wide flange or a welded plate box .
|
|
If this box is checked (
) when you detail the beam, the beam's bill of material will list the welded plate wide flange or welded plate box section as a single section size. You can generate a separate submaterial detail for the section (but not for the plates that make up the section). On a member such as a rolled section miscellaneous member or a legacy miscellaneous member , which does not have the " Welded section is single material " option, welded plate sections are always treated as single material.
If the box is not checked (
) when you detail the beam, the beam's bill of material will list the welded plate wide flange section as three plates (four plates for a welded plate box). You can generate separate submaterial details for the plates.
CNC for DSTV: Download plates (too) of welded sections
Report Writer: Member.Settings.WeldedSectionIsSingleMaterial
If this box is checked (
), connection design treats the beam as structurally connected to a concrete slab that is the " Slab width " entered below. Connection design looks to the Composite Reaction Factor Schedule for a reaction factor. If the reaction factor is ' 1 ', then connection design uses Beam Composite Design information to calculate the " Shear load ." If the reaction factor is a number other than ' 1 ', connection design multiplies that factor times the calculated beam reaction for a noncomposite beam to calculate the " Shear load ."
If the box is not checked (
), connection design does not treat the beam as a composite section when calculating the " Shear load ."
Also see: Home > Project Settings > Job > Design Settings > " Concrete strength " and " Concrete thickness " are used for composite design.
Status Display: Member status > Composite
Report Writer: Member.Conditions.Composite
Advanced Selection: m.Composite
Parametric module: m.Composite
Slab width: A distance (in the primary dimension " Units " or other units ) measured parallel with the beam's Z axis that represents the width of the concrete slab that is supported by the beam. For many cases, this is simply the beam spacing.
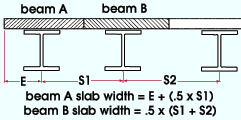
What distance to enter: For a beam that is not an edge beam, enter the distance between the center lines the adjacent beams and divide by two. For an edge beam, enter the smaller of either the distance from the edge of the slab plus half the distance to the adjacent beam, or the distance to the adjacent beam.
Note: If the beam span/4 is smaller than the beam spacing, enter beam span/4 as the " Slab width ." See the ASD 9th Edition Chapter I, Section I1, p 5-56 or the AISC Steel Construction Manual, Thirteenth Edition Section I3.1, p 16.1-83.
Report Writer: Member.CompositeBeamSlabSpacing
Number of studs: The stud count for this beam. Before you can enter a " Number of studs ," you need to check the box for " ![]() Composite design ." If you so choose, you can then uncheck the box for "
Composite design ." If you so choose, you can then uncheck the box for " ![]() Composite design ," and the number of shear studs you entered will still be retained.
Composite design ," and the number of shear studs you entered will still be retained.
|
In this example of an erection view drawing, the number ' 10 ' was entered as the " Number of studs " for the beams that are shown horizontal. Since " Show number of studs on member " was turned on, Detail Erection Views automatically appended the annotation ( S = 10) to the section sizes of the beams. |
Effect on erection view detailing: If you enter a " Number of studs " then did a Detail Erection Views with "
Show number of studs on member " turned on, the section size for this same beam will have appended to it (in parentheses) the number of studs that are entered.
No effect on connection design: Unlike the " Slab width ," this count does not affect connection design in any way. In other words, it does not affect how the automatic " Shear load " is calculated. It does not affect any information that is presented in the Connection Design Calculations Report or the Expanded Connection Design Calculations .
Report Writer: Member.StudCount
Parametric module: m.StudCount
Beam rotation: The positive or negative number of degrees of rotation ( 180 to -180 ) from web vertical. If you are looking along the beam member line toward the left end of the beam, a positive entry rotates the beam counterclockwise around its workline that number of degrees.
|
|
' 0 ' (zero) degrees sets the web of the beam to be vertical. The selection made to the " Web rotation " field may override an entry of ' 0 ' made here if the box for " Hold rotations " is not checked and the beam frames between sloping beams.
A ' number between +/-180 degrees ' is applied only if the box for " Hold rotations " is checked. When the box for " Hold rotations " is not checked and a number other than ' 0 ' or ' 180 ' is reported here, then that number is the " Web rotation " for a ' Hip and valley ' or ' Web normal ' situation.
' 90 ' degrees rotates the web of the beam so that it is horizontal and makes the " Web rotation " not applicable. Connection design can only apply clip angles (to a column web or flange) on a beam that has been rotated 90 degrees. User base/cap plates can be added to a column framing to a beam with a horizontal web as described here . No matter what the beam end's " Input connection type ," connection design copes the member main material and sets it back to prevent material interferences with the member the beam frames to. You can " Center material " when ' 90 ' is entered.
Report Writer: Member.Rotation
Hold rotations: ![]() or
or ![]() . This box is checked automatically when you change the " Beam rotation ." The box may also be checked automatically when Import Model was used to bring members into the 3D model.
. This box is checked automatically when you change the " Beam rotation ." The box may also be checked automatically when Import Model was used to bring members into the 3D model.
If this box is checked (
), " Web rotation " is disabled and the " Beam rotation " that is entered (above) is applied.
If the box is not checked (
), the beam's rotation is set per the " Web rotation " (' Web vertical ' or ' Hip and valley ' or ' Web normal ') or, when " Beam rotation " is ' 90 ', that value will apply.
Note: The Change option " Downloaded rotations to non-downloaded rotations " resets the box for " Hold rotations " on all edit windows to not checked. If you then press " OK ," you will not be able to reverse the process by checking this box again. The original downloaded web rotation will be lost.
Rolling operation: None or Camber annotation or Weak axis or Strong axis or Camber or Camber (Both) . The center of curvature for each of these choices (except ' None ' and ' Camber annotation ') is midway between the left and right end of the beam's main material. The work points of the beam are fixed, but the work line (stick form member line) becomes curved as a result of the rolling operation.
' None '
|
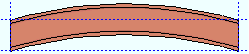
' Camber '
|
||||
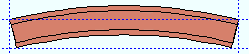
' Weak axis '
|
' Strong axis '
|
||||
|
|||||
' None ' makes the main material straight, not curved.
' Camber annotation ' also makes the main material straight, not curved. Enter a " Mid-ordinate " (other than 0) to add a shop note when the beam is detailed . A negative (-) " Mid-ordinate " indicates the camber is down. A positive " Mid-ordinate " indicates up. The same " Mid-ordinate " value is added to the " Remarks " column in the member bill of material if " Show camber on the bill of material " is checked at Home > Project Settings > Fabricator > Detailing > Member Detailing Settings > " Beams " section. You can " Show camber on members " on erection view drawings or display " Camber annotations " in 3D Modeling erection views.
' Weak axis ' or ' Strong axis ' produce circular rolling. The " Mid-ordinate " or " Included Angle " or " Rolling radius " sets the offset at mid-span and the direction (+ or -) of that offset.
' Camber ' produces parabolic bending along the strong axis of the rolled section with the ends fixed. The " Mid-ordinate " sets the offset at mid-span and the direction (+ or -) of that offset.
' Camber (Both) ' combines ' Camber annotation ' with ' Camber '. The beam is shown as curved in the 3D model and on the member detail. You also get the camber annotation on the beam detail.
Status Display: Member status > Rolling operation
Report Writer: Member.RollingOperation
Advanced Selection: m.RollingOperation
Parametric module: m.RollingOperation
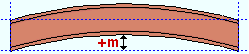
Mid-ordinate: The positive or negative (-) distance (in the primary dimension " Units " or other units ) that the beam's main material is offset at mid-span as a result of a " Rolling operation " of ' Camber ' or ' Camber (Both) ' or ' Strong axis ' or ' Weak axis '. The sign (+ or -) sets the direction of offset. A special case: The beam is modeled and detailed straight if ' Camber annotation ' is the " Rolling operation ."
Camber with a positive mid-ordinate ( +m )
 |
Camber with a negative mid-ordinate ( -m )
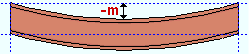 |
| Weak axis rolling with a positive mid-ordinate (rolling toward the near side)  |
Weak axis rolling with a negative mid-ordinate (rolling toward the far side)  |
Strong axis rolling with a positive mid-ordinate ( +m )
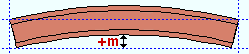 |
Strong axis rolling with a negative mid-ordinate ( -m )
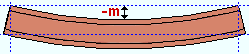 |
Status Display: Member status > Mid-ordinate
Report Writer: Member.Camber or Member.Conditions.HasCamber
Report Writer: Member.MidOrdinate
Advanced Selection: m.MidOrdinate
Parametric module: m.MidOrdinate
Included angle: The positive or negative (-) number of degrees that the beam's main material is curved as a result of a " Rolling operation " of ' Weak axis ' or ' Strong axis '. In the following example, ' Strong axis ' rolling is shown:
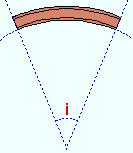
|
i = included angle. Extrapolate a circle from the inside curvature of the beam's main material, then draw a line along each end of the main material. The lines will meet at the center of the imaginary circle, and their included angle is the angle entered here. |
Note: The strong axis or weak axis rolling that takes place when an " Included angle " is entered is the same rolling that takes place when a " Mid-ordinate " is entered. The rolling is circular, and the work points of the beam do not change.
Status Display: Member status > Included angle
Report Writer: Member.IncludedAngle
Advanced Selection: m.IncludedAngle
Parametric module: m.IncludedAngle
Rolling radius: The positive or negative distance (in the primary dimension " Units " or other units -- up to +/- 120,000 inches) that the beam's edge is from the center of the radius of bending as a result of a " Rolling operation " of ' Weak axis ' or ' Strong axis '. The smaller the " Rolling radius " (+ or -), the greater the curvature.
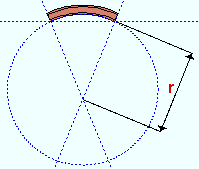
|
r = rolling radius. If you were to extrapolate a circle from the inside curvature of the beam's main material, the distance from any point on the inside curve of the top/bottom flange to the center of the circle is the distance entered here. |
Note: The strong axis or weak axis rolling that takes place when a " Rolling radius " is entered is the same circular rolling that takes place when a " Mid-ordinate " is entered. The rolling is circular, and the work points of the beam do not change.
Status Display: Member status > Rolling radius
Report Writer: Member.RollingRadius
Advanced Selection: m.RollingRadius
Parametric module: m.RollingRadius
Spiral offset: The positive or negative (-) distance (in the primary dimension " Units " or other units ) that the right end of the beam is to be offset from its right-end work point (wkpt 2 in the example). The left end work point of the beam remains fixed. This applies when the beam's " Rolling operation " is ' Weak axis ' or ' Strong axis '.

For both ' Weak axis ' and ' Strong axis ' rolling: The workline (stick form member line) and beam main material are adjusted to reflect the offset. The rolling remains circular.
For ' Weak axis ' rolling: A positive " Spiral offset " raises the elevation of the workline at its right-end point the exact distance that is entered. A negative " Spiral offset " lowers the elevation of the workline at its right-end point. For either sign (+ or -), the beam's right " End elevation " remains the same.
For ' Strong axis ' rolling: A positive " Spiral offset " offsets the workline at its right-end point the exact distance that is entered; the workline is offset in the direction of the near side of the beam. A negative " Spiral offset " offsets the workline in the direction of the far side of the beam.
Status Display: Member status > Spiral offset
Report Writer: Member.SpiralOffset
Swap member ends : ![]() or
or ![]() .
.
Break Apart : ![]() or
or ![]() .
.
------------------
Main material : ![]() or
or ![]() .
.
Marked for processing : . ![]() or
or ![]()
Marked for detailing : ![]() or
or ![]() .
.
Node-match job : ![]() or
or ![]() . ( read-only )
. ( read-only )
Model complete : ![]() or
or ![]() . ( read-only )
. ( read-only )
Model complete date : **NOT SET** or a month day year .
Lift assignment : not assigned or a crane placement name . (read-only)
------------------
WP to WP length, plan: read-only . The work point-to-work point distance (in the primary dimension " Units ") spanned by the beam's member line in a plan view, ignoring elevation. This " ![]() General settings " distance is calculated from the X and Y (but not Z) global coordinates of the beam's work points .
General settings " distance is calculated from the X and Y (but not Z) global coordinates of the beam's work points .
Note: If the beam is sloped out of the plan view elevation, the distance reported here will not be the actual work point-to-work point length, but rather the distance from column line to column line (grid line to grid line) as measured at a single elevation.
Report Writer: Member.WorkpointToWorkpointLevel
Advanced Selection: m.WorkpointToWorkpointLevel
Parametric module: m.WorkpointToWorkpointLevel
WP to WP length, actual: Read-only . The actual length of this beam's work line (in the primary dimension " Units "). This " ![]() General settings " distance is calculated from the X and Y and Z global coordinates of the beam's work points .
General settings " distance is calculated from the X and Y and Z global coordinates of the beam's work points .
Note: This distance minus the left- and right-end input or automatic " Material setback " is the actual length of the beam's main material. The maximum beam length for which you can reliably obtain system connections is 80 feet.
Tip: Using Move/Stretch Members or Move/Stretch Members, Include Material to lengthen or shorten a beam or changing a beam's " End elevation " on one end causes a different distance to be reported here.
Report Writer: Member.WorkpointToWorkpointSlope
Advanced Selection: m.WorkpointToWorkpointSlope
Parametric module: m.WorkpointToWorkpointSlope
| Special Buttons for Detailing | |||
|
|
|
|
|
| Press this button to open a window with a list of preset views that you can select. When you auto detail the beam, each preset view is drawn on the detail. | Press this button to open a list of views you can delete. If the beam has only a main view, you get a warning instead of a list of views since you cannot delete the main view. | This button opens the Annotations... window. Press " OK " on that window to detail the beam(s). Newly added views will be drawn on the detail. Deleted views will not be drawn. | Press this button to start up the Drawing Editor . You will automatically be shown the detail of the beam if the beam has been detailed and if the file is not currently open. |
The " Detail Member " button is enabled when you are multi-editing beams with different piecemarks, allowing you to auto detail those beams. The other buttons will be disabled ( grayed out ) for multi-edit operations, although you can " View detail " if the multiple beams being edited have the same mark. If the member is in Member Isolation , the " Add View " and " Delete VIew " buttons are also disabled.
Note 1: If you add or delete a view or detail this member using these buttons, the " Marked for detailing " button updates immediately.
Note 2: " Freeze drawing " in the Drawing Editor disables ( grays out ) the " Add View " " Delete View " and " Detail Member " buttons.
|
|||||
|
|
||||
Seismic moment frame member : Automatic or Yes or No . This option affects the design of ' Welded ' and ' Bolted ' beam-to-column-flange moment connections that are specified in the " ![]() Moment " leaf on either or both ends of this beam.
Moment " leaf on either or both ends of this beam.
| ' Yes ' or, possibly, ' Automatic ' | ' No ' or, possibly, ' Automatic ' |
| • The choice made to " Seismic moment frame type " (' OMF ' or ' IMF ' or ' SMF ') governs seismic moment connection design. |
• Moment connections can still be designed per choices made in the " |
| • When " Moment type " is ' Welded ' or ' Bolted ', the " Panel zone moment load " governs the design of seismic moment connection web doublers. | • Moment web doublers are designed without regard to the " Panel zone moment load ." |
|
• When " Moment type " is ' Non-moment ', a seismic moment connection cannot be designed. The " |
• When " Moment type " is ' Non-moment ', no moment connection can be designed. The " |
|
• When " Moment type " is ' Welded ', " Re-entrant cut " and " Groove angle " are disabled in the " |
• When " Moment type " is ' Welded ', " Re-entrant cut " and " Groove angle " are enabled . An ' Alternate 3 ' or ' Alternate 1 ' moment connection is designed. |
|
• The " |
• The " |
' Automatic ' specifies that connection design apply a setup choice ( Home > Project Settings > Job > Design Settings > " Seismic moment connection design " >
or
). If that box is checked and this end connection's " Moment type " is ' Welded ' or ' Bolted ', connection design creates a seismic moment connection. If it is not checked, connection design does not create a seismic welded moment connection.
' Yes ' instructs connection design to attempt to design a seismic moment connection based on the selected " Seismic moment frame type " (' OMF ' or ' IMF ' or ' SMF '). To get a connection, " Moment type " needs to be ' Bolted ' or ' Welded '. For a " Connection design method " that uses the AISC 13th or 14th edition, the seismic "
Auto " " Moment load " is calculated using AISC Seismic Design 2nd Edition, Section F2.3. For a method that uses the AISC 15th Edition, the auto seismic loading is calculated per AISC Seismic Design 3rd Edition, Section F2.3.
' No ' instructs connection design to design non-seismic welded and bolted moment connections based on choices made in the "
Moment " leaf.
Note: Seismic welded moment connections are designed based on the " Seismic Access Hole " designation (' A ' or ' B ' or ' C ' or etc.) that is entered in the local shape file for the " Section size " of the beam. Connection design references Home > Project Settings > Job > Seismic Weld Access Holes to determine the size and shape of the access hole. If the local shape file's " Seismic Access Hole " designation is ' None ' for the beam's " Section size ," then connection design does not reference the Seismic Weld Access Holes setup window, but instead uses the setup values defined for moment connections at Home > Project Settings > Job > Weld Design Settings . A back-up bar may optionally be included as part of the seismic connection, per the setup instructions entered at Home > Project Settings > Job > Moment Plate Design Settings > the " Back-up Bars on Welded Connections " tab > " Create solids for seismic connections ."
Seismic moment frame type : Automatic or OMF or IMF or SMF . This applies when " Seismic moment frame member " is set to ' Yes ' or, possibly, to ' Automatic '. ' IMF ' and ' SMF ' seismic moment connections can be designed when the " Connection design method " is any LRFD edition. ' OMF ' seismic moment connections can be designed for LRFD and ASD editions.
' Automatic ' specifies that connection design apply a setup choice ( Home > Project Settings > Job > Design Settings > " Seismic moment frame type " > ' OMF ' or ' IMF ' or ' SMF ' ). For example, if that option in Design Settings is set to ' IMF ', then connection design will use IMF design for the seismic moment connection.
' OMF ' stands for "Ordinary Moment Frame." OMF connections are recommended for non-seismic or low seismic regions. When the " Connection design method " is ' LRFD 15 ' or ' ASD 15 ', only welded moment shear tab connections can be designed.
' IMF ' stands for "Intermediate Moment Frame." IMF connections are designed to be installed in moderate seismic regions.
' SMF ' stands for "Special Moment Frame." SMF connections are designed to resist flexural, axial, and shearing actions that result as a building sways through multiple inelastic displacement cycles due to a strong earthquake.
End connection failure message: IMF/SMF connections not supported for ASD
End connection failure message: Seismic moment connection is not prequalified
End connection failure message: Seismic moment connection only allowed to column flange
End connection failure message: Only welded flange OMF supported for 15th edition
End connection failure message: IMF/SMF flange bolt design valid only for A490/F2280 bolts
End connection failure message: IMF/SMF flange hole type must be standard round
End connection failure message: IMF/SMF maximum flange bolt diameter is 1 1/8 inch
End connection failure message: IMF/SMF connections must have matching load auto flags
Story height above node : The distance from the half-depth of this beam to the half-depth of the beam above. See figure 4-26(a) on page 4-123 of the 3rd Edition Seismic Manual.
After making the appropriate entry here, enter the " Story height below node " (below) and follow steps 1 - 4.
Story height below node : The distance from the half-depth of this beam to the half-depth of the beam below. After making an entry here and above, and after the connedtion passes, do the following:
1. Press the " Design Calcs " or " Expanded Calcs " button at the bottom of this window.
2. Based on the entry you make here and to " Story height above node " (above) and on the appropriate end's " Panel zone moment load ," connection design will calculate the story shear force, Vc , and report the result in the design calculations (either report). The result is output to the report instead of this edit window because, currently, there is no " Auto " check box for " Story load ."
3. Manually enter the story load shown in the report to "
Loads " > " Story shear " for the appropriate end of this beam.
4. Connection design will re-design the connection factoring in the " Story shear " that you entered.
Uniformly distributed gravity load (kips or kN) : A user-entered load in kips (kilonewtons for ' Metric '). Unlike the left- and right-end " ![]() Loads " found on this window, this uniformly distributed gravity load applies to the entire beam.
Loads " found on this window, this uniformly distributed gravity load applies to the entire beam.
The value entered here affects the "
Auto " calculation of the " Panel zone moment load " for the end(s) of this beam that have an ' IMF ' or ' SMF ' welded or bolted seismic moment connection.
The " Panel zone moment load " affects the design of seismic moment connection web doublers.
|
|
| End setting buttons : " Lock End " " Lock All Lockables "
" Save As User Defined Connection " " Copy " " Paste " " Save " " Load " |
| Determining a beam's left end : |
| Look at the location of its piecemark (B_2). |
|
Look at its reference point ( |
| The left end is related to global coordinates . |
| Left end of a member in a plan view . |
| Left end of members in an elevation view . |
disables ( grays out ) all options under [ Left end settings ] or [ Right end settings ] (as the case may be), thus preventing users from making changes to the connection.
" Copy " and " Save " form buttons remain active for the locked end. You can also still make changes to "
General settings " and the other end's settings.
The material, hole, bolt and weld edit windows for system connection materials associated with this end of the member became read-only.
Furthermore, Delete or Erase cannot remove any of this connection's materials, holes, bolts or welds. Cut Layout , Add Holes , and similar material altering operations cannot be performed on any of the connection's materials. Such operations can only be performed on the member main material.
The member main material's setbacks and end preparations will become read-only.
Locking a member's end does not inhibit most operations that you can normally perform on the member main material -- such as Cut Layout or Add Holes -- nor does it stop you from applying Custom Properties to the locked connection material.
allows the options under [ Left end settings ] or [ Right end settings ] to be edited.
Status Update: Lock left/right end
Status Display: Approval and modeling > Member left end locked
![]() /
/ ![]() " Lock All Lockables" / "Unlock All Lockables "
" Lock All Lockables" / "Unlock All Lockables "
|
||
| Tip: Pressing the " Unlock All " button clears the above message . |
sets all "
End preparations " and "
Connection design locks " under [ Left end settings ] or [ Right end settings ] (as the case may be) to a locked state, thus preventing the connection from being altered by connection design . You will still be able to make changes to the connection by unlocking (
) particular lockable fields (so that connection design can make entries to that field) or by you yourself making different entries to the locked fields.
unlocks all connection design locks (lockables) associated with the left or right end (as the case may be). This results in a connection that is fully designed by connection design, without any user entries to connection design locks.
![]() Save As User Defined Connection: This button is available when you are editing one member at a time. It is not available if you are editing multiple beams. It allows you to save as a User Defined Connection changes that you have made to connection design locks and to other [ Left end settings ] or [ Right end settings ]. You can overwrite a previously saved user defined connection or create an entirely new user defined connection.
Save As User Defined Connection: This button is available when you are editing one member at a time. It is not available if you are editing multiple beams. It allows you to save as a User Defined Connection changes that you have made to connection design locks and to other [ Left end settings ] or [ Right end settings ]. You can overwrite a previously saved user defined connection or create an entirely new user defined connection.
1. When you are done adjusting the connection's settings, click the Save As User Defined Connection button.2. The Select one User Defined Connection window opens. Click the New... button to create a new user defined connection using the current Connection specifications, connection design locks, and Moment options you have set.
Alternative 1: To save over an existing user defined connection and replace its settings with the current settings of the edit window, select it and click OK or double-click it. Click Yes or No on the prompt window asking if you want to overwrite the connection. The user defined connection is immediately saved. There are no further steps to take.
Alternative 2: Click the Cancel button to close the Select one User Defined Connection window.
3. The User defined connection name input window opens. Type in a name for the connection (61 characters max.) and click OK to save the new user defined connection.
Alternative: Click the Cancel button to close the User defined connection name input window and return to the Select one User Defined Connection window.
![]() " Copy " " Paste " " Save " " Load "
" Copy " " Paste " " Save " " Load "
These may be referred to as "form buttons."
You can use these buttons to save and copy connections. The buttons operate on all fields under all leaves that are under the [ Left end settings ] or [ Right end settings ] heading.
For more information, see "Copy" "Paste" "Save" "Load" .
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
||||||||
Connection: Force and/or Graphical or a System connection . This " ![]() Information " option and its related messages apply when this beam end's " Input connection type " is a choice other than ' Plain end '.
Information " option and its related messages apply when this beam end's " Input connection type " is a choice other than ' Plain end '.
' Force ' applies when the connection has failed , which results in your not getting any connection materials in the 3D model.


forced 

system
VIDEO 
When a connection has failed , you don't get any connection materials. Forcing the connection gets you connection materials. The Connection Design Calculations report includes a warning when a connection has been forced.
VIDEO 
a ' Clip angle ' to a concrete wall fails with the message " Valid schedule entry required for steel to concrete wall connections ." The beam " Connection " is set to " Force ," resulting in a clip angle being generated in the model.
Forced rotated connections can be generated using the " Relative rotaton " connection design lock. lock leaf " Relative rotation " NS Clip / FS Clip " Relative rotation " Bent Plate " Relative rotation " Web Plate (for a beam splice) " Relative rotation " Shear Tab (on supported, to no supporting member) To get connection materials so that you can assess the connection and make needed changes, check the box for "
Force ". The Connection Design Calculations report (and Expanded Connection Design Calculations ) will include a warning that the connection has been forced. Example: Suppose you get the end connection failure message " Physical limitations exceeded " instead of a connection. Checking the box for "
Force " is a possible way to get a solids model of the connection. Although the forced connection will probably have obvious flaws and not be of much use, it may help you to better understand why the problem occurred and how you can fix it.
' Graphical ' may have been automatically set to "
Graphical " as a result of a user employing modeling operations to modify the system connection on this end of the member, thus making it graphical .


graphical 

system A graphical connection will not be changed by connection design . On this window, you will not be able to change any of that connection's "
Connection design locks " or "
End preparations ." The Connection Design Calculations report (and Expanded Connection Design Calculations ) will include the warning " GRAPHICAL CONNECTION -- STRENGTH CALCULATIONS NOT GENERATED ." If "
Graphical " is checked and you switch it to "
Graphical " then press " OK " (so that Create Solids is performed), user-added modifications to that connection will be overwritten or erased. For example, user-added holes will disappear. On the General Information window for each of the connection materials, you will see that switching from "
Graphical " to "
Graphical " caused the connection materials that were regenerated to be changed from " User modified connection material " to " System created connection material ."
Search and Change:
- Graphical Connections (a search)
- Change Graphically Altered to System Connections
- Change System to Graphically Altered Connections
- Change Force to System Connections
Status Display: Search > Graphical connections
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.Settings.ForceConnection
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.IsGraphicalConnectionAdvanced Selection: m.Ends[0].ForceConnection
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].IsGraphicalConnectionParametric module: m.Ends[0].ForceConnection
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].IsGraphicalConnection
" Connection design locks set ," connection failed messages, other messages :
If you are in a multi-user environment, a member edit window could be opened at the same time somebody else is adding a member that connects to that member. As a result, Process within member edit will be locked from accessing information about that opened member, and the following message will be generated:
| On-the-fly process failed |
If you are editing multiple beams and those beams have different connection failed or connection-changed messages, a banner like the following is displayed:
Multiple failed and/or changed connection messages The following banner notifies you that the connection has at least one "
Connection design lock " or "
End preparations " setting that is locked (
):
Connection design locks set.
VIDEO 
Sections of a window (" leaves ") within which at least one locked variable resides are marked (in the navigation tree) with a locked icon ( ).
Search: Connection design locks set
Status Display: Search > Connection design locks setSetting the User and Site Options > Modeling > " Process within member edit " to ' Off ' gets you the following banner:
The option "Process within member edit" has been disabled.
Values on this screen may change after process.You may find a red connection failure banner like that shown below along with a
button for context-sensitive help about the message.
| Beam web shear capacity failed |
|
|
|
for help on the failure message that is shown |
launches your User and Site Options > General > " Help browser " and gives you context-sensitive help about an end connection failure message . If there is no failure message, this button will not be shown. A connection failure message may be generated, for example, due to "
Left/Right end limit state " analysis revealing that a connection cannot carry the load that the connection's member is subjected to. The various limit states associated with a connection are tested during connection design .
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.ConnectionHasFailed
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.Conditions.ConnectionFailError
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].ConnectionHasFailed
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].ConnectionHasFailedOr you may find a green " Connection changed ... " banner that indicates connection design has deviated from the "
Connection specifications " entered by the user in order to make the connection work.
| Conn changed. Possibly: Angle vs Plate |
Tip: Compare this beam end's " Input connection type " and " System designed connection " and "
Connection specifications " to assess what has changed.
Search: Connections Changed by System .
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].DesignHasChanged
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].DesignHasChangedYou will find a yellow " Frames to ... " banner on this end of the beam if this end of the beam frames to a member that has its " Model complete date " set. The message (possible inaccurate connection) may be added to the banner, or connection design may fail the connection on this end (the banner end) with the error message: Frames to a Model Complete member .
Frames to a Model Complete member
(possible inaccurate connection)Model complete type: Restrictive or Legacy
Setup: Home > Project Settings > Job > Member and Drawing Restrictions
Also see: Lock Ends Framing to Model Complete MembersYou will find a yellow " Frames opposite ... " banner if the beam frames to a beam web or column web, opposite to another beam that has its " Model complete date " set. Special caution should be taken if this beam has a bolted-to-web connection and the beam opposite also has a bolted-to-web connection. Clip angles, bent plates and end plates can all potentially be applied as bolted-to-web connections. A " Model complete date " on the opposing beam does not prevent connection design from designing a connection on this end of the beam, but you may get undesirable, inaccurate results since the model-complete member is not permitted to be physically altered.
Frames opposite a Model Complete member
(possible inaccurate connection)Model complete type: Restrictive or Legacy
Setup: Home > Project Settings > Job > Member and Drawing Restrictions
Also see: Lock Ends Framing to Model Complete Members
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
End elevation: The elevation (in the primary dimension " Units " or other units ) of the work point at this end of the beam. For a non-sloping beam, both the left and right end elevations are the same. The work points of a beam align with the top flange of the beam.
| A beam has two exact points , whose elevation you can change by changing the beam's left- and/or right-end " End elevation ." |

|
|
|
To determine the end elevation on a beam in the 3D model, use Construction Line Add or a similar tool, select EXPT as the Locate option, then snap the point location target to the work point at the end of the beam. The Z coordinate reported in the X-Y-Z display tells you the elevation at the snapped-to exact point.
Note 1: " Copy " " Paste " " Save " " Load " buttons do not operate on the " End elevation ."
Note 2: If you are editing one beam with a piecemark shared by at least one other beam and change its " End elevation " on one or both ends, you will get a notification dialog after you press " OK " to close this window. The dialog will remind you that you have the option to change the elevations of all beams with the same mark. If you choose to change the elevations of all beams with the same mark, the ends of the members will be moved in the same manner and by the same relative amount (not necessarily to the same elevation).
Note 3: If the beam setup option " Show end elevations on details " is on, then changing the " End elevation " causes the beam to be " Marked for detailing ."
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.LocationZ
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].Location.z
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].Location.z
Web rotation: Automatic or Web vertical or Hip and valley or Web normal . This " ![]() Member " option applies when the box for " Hold rotations " is not checked. When the box for " Hold rotations " is checked or " Beam rotation " is ' 90 ', the number of degrees entered to " Beam rotation " applies. Be sure to set this option correctly for both ends; otherwise the beam may become twisted. For a beam to a perfectly vertical column, select ' Web vertical '. For a beam that is perpendicular to a perfectly horizontal beam, selecting any of the four choices gives you the same results.
Member " option applies when the box for " Hold rotations " is not checked. When the box for " Hold rotations " is checked or " Beam rotation " is ' 90 ', the number of degrees entered to " Beam rotation " applies. Be sure to set this option correctly for both ends; otherwise the beam may become twisted. For a beam to a perfectly vertical column, select ' Web vertical '. For a beam that is perpendicular to a perfectly horizontal beam, selecting any of the four choices gives you the same results.
For a beam to a sloping column:
' Web vertical ' makes the web of the beam vertical to the world.
' Web normal ' rotates the beam so that its web aligns with the member line of the column.
For a skewed or nonskewed beam to a sloping beam:
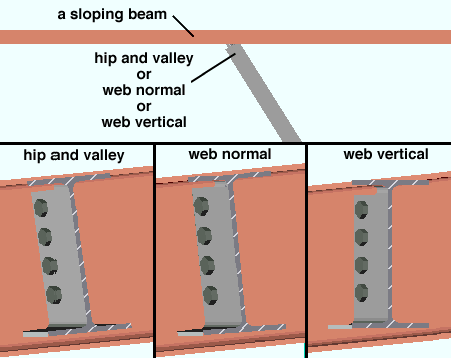
' Automatic ' lets connection design choose the web rotation for you.
' Web vertical ' makes the web of the beam vertical to the world.
' Hip and valley ' rotates the web of the beam to keep its flange in the same plane as the flange of the sloping beam it is framing to.
' Web normal ' rotates the web of the beam as needed to keep the connection on the beam perpendicular to the flange of the sloping beam it is framing to.
Example: You frame a beam to a sloping beam to form a roof support. The other end of the beam has a plain end and frames to concrete. For the framing end, you select ' Web normal '. For the opposite end, you select ' Automatic ' in order to keep the beam from being twisted.
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MemberRotationTypeDescription
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].MemberRotationType
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].MemberRotationType
Standard detail: None or a standard detail name . To apply a standard detail, you can type in the name of the drawing (if you know it), or you can press the "file cabinet" browse button ( ![]() ) and double-click any job standard detail or global standard detail that is on the list.
) and double-click any job standard detail or global standard detail that is on the list.
|
If ' none ' is entered here, then no standard detail is applied on this end of the beam when the beam is automatically detailed .
If a ' standard detail name ' is entered here, the next time you automatically detail the beam, the reference point of the standard detail aligns with the input work point on this end of the beam, and the standard detail's bill of material combines with the beam's bill of material. The detail is placed on a layer that is named after the standard detail plus a " _L " or " _R " suffix.
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.StandardDetailFileType
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.StandardDetailFileNumber
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.StandardDetailFileNameAdvanced Selection: m.Ends[0].StandardDetailFileNumber
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].StandardDetailFileTypeParametric module: m.Ends[0].StandardDetailFileNumber
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].StandardDetailFileType
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
||||||||
Input connection type: Auto standard or User defined or Plain end or Bearing or Clip angle (" ![]() Moment " options can also be added) or Bent plate ("
Moment " options can also be added) or Bent plate (" ![]() Moment " options can also be added) or End Plate ("
Moment " options can also be added) or End Plate (" ![]() Moment " options override "
Moment " options override " ![]() Connection specifications ) or Shear ("
Connection specifications ) or Shear (" ![]() Moment " options can also be added) or Seated (N/A for tube beams) or Splice plate (N/A for HSS beams, "
Moment " options can also be added) or Seated (N/A for tube beams) or Splice plate (N/A for HSS beams, " ![]() Moment " options can apply to W beams) or Fully welded moment (automatically sets " Moment type " to ' Welded ').
Moment " options can apply to W beams) or Fully welded moment (automatically sets " Moment type " to ' Welded ').
|
| Input connection | Comments |
| ' Auto standard ' | A system connection that is designed per the beam's framing situation . Auto standard connections have a number of advantages . |
| ' User defined ' | Enter the connection's name to " User defined connection " (below). |
| ' Plain end ' | For when you do not want a system connection on this end of the beam. Even though a connection is not automatically designed, connection design still automatically copes and sets back a ' Plain end ' beam to a beam or column. See " Plain end " at Home > Project Settings > Job > Field Clearances . |
| ' Bearing ' |
An " Embed schedule entry " needs to be made in order for you to get a bearing plate / angle / channel to a concrete wall or panel . Locks in the " |
| ' Clip angle ' or ' Bent plate ' or ' End plate ' or ' Shear ' or ' Seated ' or ' Splice plate ' |
" |
| ' Clip angle ' or ' Bent plate ' or ' End plate ' or ' Shear ' or ' Splice plate ' |
" |
| ' Clip angle ' or ' Bent plate ' or ' End plate ' | Connections of these types can be created even when the end of the beam does not frame to another member. |
| ' Bearing ' or ' Clip angle ' or ' Bent plate ' or ' Shear ' or ' Seated ' or ' Plain end ' |
For a beam that frames to concrete, an " Embed schedule entry " must made in order to create a connection, though in some cases you may be able to ' |
|
' Fully welded moment '
|
The " Moment type " is automatically set to ' Welded " and connection design does not use a clip angle or shear plate or bent plate as part of the connection. The web of the wide flange or similarly shaped beam welds directly to the column. Some " Sloped fully weled moment connections can be designed, and an axial load (compression or tension) can be applied to such a connection. Click here ( |
When you change this beam end's " Input connection type ," previously set-for-this-end "
Connection Specifications " and connection design locks are replaced with new, default settings.
Process within member edit takes place immediately, at the time that a " Input connection type " is entered.
"
Connection Specifications " and connection design locks provide settings for finer control of a connection's design.
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.InputConnection.TypeDescription
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].Input.TypeDescription
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].Input.TypeDescription
Also see: The Connection Guide
User defined connection: The file name of the user defined connection in your current Job that you want applied when this beam end's " Input connection type " is ' User defined '.
To make an entry: You can type in the name of the user defined connection that you want (if you know it), or you can press the "file cabinet" browse button (
) and double-click any user defined connection that is on the list.
Tip: The " Moment load " on a beam's end is enabled (editable) when the " User defined connection " entered here, for that same end, is a moment connection.
Status Display: Connection type > Specific user defined connection
Report Writer: Member.Conditions.HasAUserDefinedConnection
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].FinalConnectionIsUserDefined
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].FinalConnectionIsUserDefined
Embed schedule entry: None or a standard piecemark name from the " Piecemark " column in the Embed Schedule . A schedule entry can be made when this beam end's " Input connection type " is ' Clip angle ' or ' Shear ' or ' Bent plate ' or ' Seated ' or ' Plain end ' or ' Bearing ' and the beam frames to a concrete wall or tilt-up panel. If those requirements are not met, this option is disabled ( grayed out ). ' None ' may be entered by default, or you can manually enter ' None ' by deleting the text that is entered.
|
|
|
|
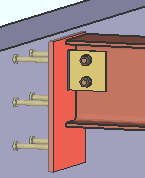
|
An embed plate from the Embed Schedule . In this example, the " Input connection type " is ' Shear '. A similar connection is created when the " Input connection type " is ' Clip angle ' or ' Bent plate '. For ' Seated ', the embed plate is also vertical, but placed lower down with respect to the beam. For ' Plain end ," there is no connection to the embed plate. |
|
An embedded bearing angle from the Embed Schedule . The " Input connection type " is ' Bearing '. By default, SDS2 connection routines automatically match the length of the angle to the width of the pocket that is created in the concrete wall. Home > Project Settings > Job > Field Clearances > " Steel to concrete " clearances apply to the pocket. |
|
An embedded bearing channel from the Embed Schedule . The " Input connection type "is ' Bearing '. The length of the channel matches the width of the pocket. The " Side " erection clearance in the " |
Please note: An embed plate or bearing plate/angle that is added on this window by making an " Embed schedule entry " or by selecting ' Auto standard ' or ' User defined ' as this beam end's " Input connection type " does not become a component that you can edit on this window. The embed becomes its own member and is shown as its own independent member in the Model Tree . You can edit that embed plate in the same ways that you can edit any other custom member -- for example, you can double-click it to open its Embed Edit window.
Connection Guide: Shear connection to an embed in a concrete wall
Connection Guide: Clip angle to an embed in a concrete wall
Connection Guide: Beam seat to an embed in a concrete wall
Connection Guide: Beam to concrete bearing connectionsEmbed window, Modeling : Embed schedule entry
Auto Standard Connections: Embed schedule entry
User Defined Connections: Embed schedule entry
System designed connection: This " ![]() Connection type " field is a read-only . It tells you the type of connection that connection design created on this end of the beam (e.g., ' Clip angle ' or ' Bent plate ' or etc.). If a non-auto standard connection has failed , resulting in no solids model being created, the connection type that connection design attempted to design will still be reported here. The connection type reported here may be different than this beam end's " Input connection type " in the following situations:
Connection type " field is a read-only . It tells you the type of connection that connection design created on this end of the beam (e.g., ' Clip angle ' or ' Bent plate ' or etc.). If a non-auto standard connection has failed , resulting in no solids model being created, the connection type that connection design attempted to design will still be reported here. The connection type reported here may be different than this beam end's " Input connection type " in the following situations:
If ' User defined ' or ' Auto standard ' is this beam end's " Input connection type ," the specific designed connection type is reported here. Press the " Design Calc " or " Expanded Calc " button for more information about that connection.
If an auto standard connection has failed , the connection type reported here is ' Plain end '.
If the specified " Input connection type " will not work, connection design may change the connection to something that will work. For example, if the ' End plate ' is specified as the " Input connection type " and the beam frames to a W8 column web, connection design will -- instead of failing the connection -- attempt to design a single-plate shear connection. A green banner notifies you that connection design has made such a change.
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.DesignedConnection.TypeDescription
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.DesignedConnection.MomentTypeDescription
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].Designed.TypeDescription
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].Designed.TypeDescription
NM bolt type to supported: Auto or A325N or A325SC or A325X or etc. NM stands for "non-moment." This " ![]() Connection type " option sets the type of non-moment bolt for fastening the connection material to this end of this beam (the supported member). If the connection is a bolted moment connection, you can additionally apply a moment " Bolt type " for bolting the flange plates ( Exception: moment end plates take moment bolts only). For certain connection types, you may apply a " NM bolt type to supporting " instead of or in addition to a " NM bolt type to supported ."
Connection type " option sets the type of non-moment bolt for fastening the connection material to this end of this beam (the supported member). If the connection is a bolted moment connection, you can additionally apply a moment " Bolt type " for bolting the flange plates ( Exception: moment end plates take moment bolts only). For certain connection types, you may apply a " NM bolt type to supporting " instead of or in addition to a " NM bolt type to supported ."
If " Auto " is checked (
), connection design uses the non-moment " Bolt type " for connections set at Home > Project Settings > Job > Bolt Settings for connections other than auto standard. For auto standard connections, connection design uses the " NM bolt type " set for that particular connection and framing condition.
If " Auto " is not checked (
), you can select a bolt type from the list box (
). Bolt types that are listed come from Home > Project Settings > Job > Bolt Settings .
Moment flange plates, flange angles & splice plates use the " Bolt type " for moment connections that can be found in the "
Moment " leaf.
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].ConnectionDesignBoltTypeDescription
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].NonMomentBoltTypeWasInput
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].ConnectionDesignBoltTypeDescription
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].NonMomentBoltTypeWasInput
NM bolt type to supporting: Same as " NM bolt type to supported ," except that this " ![]() Connection type " option applies to bolts that fasten the connection material to the supporting member. The supported member is this beam. The supporting member is the column or beam that this beam frames to. The table below explains, by connection type, when this option is disabled ( grayed out ) and when it is enabled (applicable):
Connection type " option applies to bolts that fasten the connection material to the supporting member. The supported member is this beam. The supporting member is the column or beam that this beam frames to. The table below explains, by connection type, when this option is disabled ( grayed out ) and when it is enabled (applicable):
| Input
connection type |
NM bolt type | |
| to supported | to supporting | |
| auto standard | enabled | enabled |
| user defined | enabled | enabled |
| clip angle | enabled | enabled |
| bent plate | enabled | enabled |
| end plate | dis abled | enabled for non-moment end plates only |
| shear plate | enabled | dis abled |
| shear tee | enabled | enabled |
| seated beam | enabled | enabled |
| splice plate | enabled | dis abled |
Moment end plates take moment bolts only. When this beam end's " Input connection type " is ' End Plate ' and the " Moment type " is ' Bolted ', only the " Bolt type " found in this window's "
Moment " leaf is used, and the " NM bolt type to supported " is disabled .
NM bolt diameter: Auto or a user-entered diameter (inches or mm) of the non-moment bolts in this connection. If the connection is a bolted moment connection, you can additionally apply a moment " Bolt diameter ," which will be applied to the flange plates ( Exception: moment end plates take moment bolts only).
| diameter |
|
If " Auto " is checked (
), connection design uses the non-moment " Bolt diameter " set at Home > Project Settings > Job > Bolt Settings for connections other than auto standard. For auto standard connections, connection design uses the " NM bolt diameter " set at Home > Project Settings > Job > Auto Standard Connections for the particular connection and framing condition.
If " Auto " is not checked (
), you can either type in the diameter of bolt, or select a bolt diameter from the combo box (
). The diameters that are listed in the combo box come from the " Available bolt diameters " list in Bolt Settings .
Note: For clip angles, shear plates, end plates, bent plates and splice plates, connection design may increment the user-input " NM bolt diameter " to a larger diameter (of the same units) if that diameter is checked (
) at Home > Project Settings > Job > Bolt Settings > " Available bolt diameters ."
Bolt diameter controls row spacing: " Bolt spacing "
End connection failure message: " Maximum is 1 1/4 in; 31 mm " (clip angles, seats, end plates)
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.MinimumNonMomentBoltDiameter
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].MinimumNonMomentBoltDiameter
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].MinimumNonMomentBoltDiameter
Use miscellaneous plates list: ![]() or
or ![]() .
.
If this box is checked (
), connection design looks to the appropriate section in Home > Project Settings > Fabricator > Standard Fabricator Connections > Plates to determine the plate thicknesses to be used for end plates , shear plates , beam web doublers , column web doubler plates for moment connections, column stiffeners for moment connections, flange plates for bolted or welded moment connections, plates used for extended tees , web extension plates for extended clip angles, bent plates , plate seats , stiffeners for angle seats and splice plates . First connection design calculates the thickness of the plate required to stand up to the load, then it chooses a plate from the list that is the calculated required thickness or the next thicker. If the plate from the list results in material interferences or too narrow a clearance or a thickness outside of AISC guidelines, connection design fails the connection and gives you the failure message, " Suitable plate thickness not found ."
If the box is not checked (
), connection design rounds the calculated required thickness of plates as based on the load to the next 1/16 inch (or 1/8 inch if the calculated required thickness is greater than 5/16 inch).
Related settings: The " Minimum thickness " in Standard Shear Plate Settings sets the minimum thickness for thru plates and moment shear plates and beam-to-beam splice plates . The minimum thickness for single-plate shear connections (shear tabs) is set using the Schedule of Minimums for Single-Plate Shear Connections . The " Design non-AISC single-plate shear connections " check box also affects shear plate thicknesses. " Minimum doubler plate thickness " affects column web doubler plates for moment connections.
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.UseMiscellaneousPlates
Use a safety erection seat: ![]() or
or ![]() . This "
. This " ![]() Connection type " option applies to ' Non-moment ' clip angle , bent plate , end plate and shear connections that are entered as the " Input connection type " or as " User defined " or " Auto standard ." The beam must have a flanged section size such as wide flange, S shape or welded plate W material and must be non-sloping and perpendicular to the supporting member. The designed connection will have the same capacity regardless of whether or not a safety seat is added.
Connection type " option applies to ' Non-moment ' clip angle , bent plate , end plate and shear connections that are entered as the " Input connection type " or as " User defined " or " Auto standard ." The beam must have a flanged section size such as wide flange, S shape or welded plate W material and must be non-sloping and perpendicular to the supporting member. The designed connection will have the same capacity regardless of whether or not a safety seat is added.
|
|
If this box is checked (
), connection design creates an angle seat on the ( top or bottom ) flange of the beam. The Connection Design Calculations Report and Expanded Connection Design Calculations Report note the size and orientation of the safety seat, but do not figure the safety seat into any limit state or load capacity calculations for the connection. To find an appropriate angle, connection design searches the Preferred Angle Sizes list first, then (if it can't find one), searches the local shape file . The safety seat design takes into account the " Field clearance " entered for this end of this beam.
If the box is not checked (
), a safety seat is not be added to the connection.
Connection design locks: Safety Seat
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.Settings.BeamSafetyErection Seat
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].BeamSafetyErectionSeat
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].BeamSafetyErectionSeat
Location of safety erection seat: Top or Bottom . This " ![]() Connection type " option applies when the box for "
Connection type " option applies when the box for " ![]() Use a safety erection seat " is checked.
Use a safety erection seat " is checked.
|
|
|
| Bottom |
' Top ' instructs connection design to bolt an erection angle to the top flange of this beam. If ' On column ' or ' Ship loose ' is selected in Connection Erectability Settings for " Show field bolted stability angles ," the angle is detailed on the column. If ' On beam ' is selected for " Show field bolted stability angles ," the angle is detailed on the beam.
' Bottom ' instructs connection design to bolt the seat to the bottom flange of the beam. The seat is detailed on the column.
Report Writer: BeamSafetyErectionSeatLocationDescription
Safety erection seat gap: Auto or a user-entered distance (inches or mm). This " ![]() Connection type " option applies when the " Location of safety erection seat " is set to ' Bottom '.
Connection type " option applies when the " Location of safety erection seat " is set to ' Bottom '.
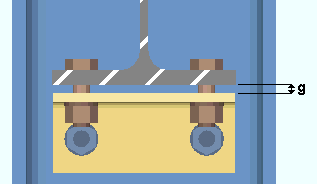
|
g = gap between the safety seat and the bottom flange of the beam. |
If " Auto " is checked (
), connection design uses the " Gap for safety seat on bottom flange " that is set at Home > Project Settings > Fabricator > Connection Erectability Settings . When adding a new beam for the first time in a Modeling session, "
Auto " is checked by default.
If " Auto " is not checked (
), you can type in the gap (in the primary dimension " Units " or other units ) that you want between the safety erection seat and the bottom flange of the beam.
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.Settings.AutoSafetyErectionSeatGap
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.SafetyErectionSeatGap
Attachment: Automatic or Bolted or Welded . This " ![]() Connection type " option applies when the box for "
Connection type " option applies when the box for " ![]() Use a safety erection seat " is checked.
Use a safety erection seat " is checked.
' Automatic ' specifies that connection design shop weld or shop bolt the safety erection seat to the supporting column based on a setup choice ( Home > Project Settings > Fabricator > Detailing > Connection Erectability Settings > " Safety erection seat connection to supporting ").
' Bolted ' instructs connection design to shop bolt the safety erection seat to the column. If ' Bolted ' is selected for a beam to an HSS/TS column, connection design does not fail the connection but instead gives you the same results as you would get if you had selected ' Welded '.
' Welded ' instructs connection design to shop weld the seat to the column.
Provide minimum cope depth: Automatic or Yes or No . This " ![]() Connection type " option applies to copes generated for beam-to-beam framing conditions when the connection is, for example, a clip angle, shear plate, bent plate or end plate.
Connection type " option applies to copes generated for beam-to-beam framing conditions when the connection is, for example, a clip angle, shear plate, bent plate or end plate.
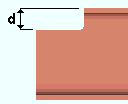
|
d = cope depth. |
' Automatic ' specifies that connection design create the connection on this end of the beam based on the choice made to Home > Project Settings > Fabricator > Member Detailing Settings > the " Beams " section > " Provide minimum cope depth ."
' Yes ' instructs connection design to ignore the k distance of the supporting member when calculating the depth of the cope. This will provide a cope of minimum depth.
' No ' configures connection design to cope the supported beam so that it clears the k distance of the supporting member.
Minimum setup connection: Automatic or Yes or No . For a minimum setup connection to be designed, the " ![]() Loads " on this window that can be auto must be set to "
Loads " on this window that can be auto must be set to " ![]() Auto", with loads that cannot be auto set to ' 0 ' (see validation ). After the connection is designed, the values reported for the "
Auto", with loads that cannot be auto set to ' 0 ' (see validation ). After the connection is designed, the values reported for the " ![]() Auto Shear load " and, if applicable, the "
Auto Shear load " and, if applicable, the " ![]() Auto Moment load ," will be the capacity of the connection instead of the allowable load. The Connection Design Calculations and Expanded Connection Design Calculations reports will also report the minimum setup connection's capacity.
Auto Moment load ," will be the capacity of the connection instead of the allowable load. The Connection Design Calculations and Expanded Connection Design Calculations reports will also report the minimum setup connection's capacity.
|
|
' Automatic ' instructs connection design to create the connection on this end of the beam based on the choice to " Minimum setup connection " at Home > Project Settings > Job > Design Settings .
' Yes ' instructs connection design to, instead of calculating the "
Loads " that are set to "
Auto " on this window, apply minimal values for those loads, and thus create a connection with the minimum number of bolt rows, the minimum plate thickness, etc. A green banner in the "
Loads " leaf of this window will notify you that the connection has been designed with the " Minimum setup connection capacity ." A minimum setup connection may not stand up to the loading conditions that the actual connection will be subjected to in the built structure. You can use connection design locks to build up the connection. Also, see the validation below.
' No ' instructs connection design the connection on this end of the beam to stand up to the governing auto "
Loads ." "
Auto " loads are calculated per choices made to " Base beam design reaction on " (for non-moment and moment connections) or " Base beam design moment on " (for moment connections) in Design Settings .
Tip: Instead of choosing ' Yes ' for " Minimum setup connection ," you can enter a minimal value such as 6 kips for each of the loads that govern the design of the connection -- for example, the " Shear load " on a non-moment clip angle. The resulting connection will effectively be the same as a minimal setup connection.
Validation: The loads entered to " Tension ," " Compression " and " Story shear " are validated when you press " OK ." If at least one of these are non-zero and a minimum setup connection is specified on the same end, a warning dialog opens before the Beam Edit window closes. The dialog gives you three ways to rectify the conflict: 1 ) You can select the first option, which automatically resets the " Minimum setup connection " to ' No '. 2 ) You can choose the second option, which automatically sets " Tension " " Compression " and " Story shear " to zero. 3 ) Or you can press " Cancel " to reactivate the Beam Edit window and fix the conflict yourself.
|
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.MinimumSetupConnectionDescription
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.DesignedConnection.IsMinimumConnection
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].Designed.IsMinimumConnection
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].MinimumSetupConnection
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].Designed.IsMinimumConnection
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].MinimumSetupConnection
Disable framing situation checks: ![]() or
or ![]() .
.
If this box is checked (
), the framing situation checks are turned off.
If the box is not checked (
), the framing situation checks are turned on.
Also see: Click here (bent plates), here (clip angles) and here (end plates) for some examples from the Connection Guide where framing situation checks are crucial.
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].MarkedToCheckFramingSituation
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].MarkedToCheckFramingSituation
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
||||||||
"
Connection specifications " is populated with options when this beam end's " Input connection type " is ' Clip angle ' or ' Bent plate ' or ' End plate ' or ' Shear ' or ' Seated ' or ' Splice plate ' or ' Fully welded moment '. There are no "
Connection specifications " options -- just an empty leaf -- when the " Input connection type " is ' Auto Standard ' or ' User Defined ' or ' Plain end '.
For more information, click on a link :
| Clip angle (" |
|
| Gage | Use expanded vertical bolt spacing |
| Attachment to supported | Welded extended tee |
| Attachment to supporting | Full depth extended tee |
| Side | Flange splice plates on |
| Attached to | Replace doubler with larger clip |
| Use erection bolts | Use paddle plate |
| Safety connection | Skew holes in angle |
| Extend past flange | Combine beam/vbrc clip angles |
| Create web doublers | Check supporting member for axial load |
| Stagger on | Embed plate location |
Bent plate
(" ![]() Moment " options can also be added)
Moment " options can also be added)
| Gage | Stagger on |
| Attachment to supported | Welded extended tee |
| Attachment to supporting | Full depth extended tee |
| Side | Bent plate grade |
| Attached to | Use paddle plate |
End plate
(" ![]() Moment " options can also be added)
Moment " options can also be added)
| Gage | Combine beam/vbr end plates |
| Safety connection | Welded extended tee |
| Expanded vertical bolt spacing | Full depth extended tee |
| Extend plate to beam flanges | Check supporting for axial load |
| Extension dimension | End plate grade |
Shear
(" ![]() Moment " options can also be added)
Moment " options can also be added)
| Material type ( |
Use expanded vertical bolt spacing |
| Attachment | Combine beam/vbr shear plates |
| Attached to | Try two bolt column shear tabs |
| Shear plate/tee side | Use paddle plate ( |
| Flange splice plates | Skew holes in plate |
| Support condition | Use back-up bar |
| Thru shear plate ( |
HSS column reinforcement ( |
| Weld split plate to thru plate | Use alternate eccentricity |
| Extend past flange | Check supporting for axial load |
| Extend stabilizer plates ( |
Shear plate grade |
| Stiffener opposite | Embed plate location |
| Extend size to | Bevel shear plate as required ( |
| Seat material | Seat to supporting member |
| Stability angle | Seated plate grade |
| Location | Embed plate location |
Splice plate (bm-to-bm)
(" ![]() Moment " options can also be added)
Moment " options can also be added)
| Web plates on | Splice plate grade |
| Web plate side | Flange plates on |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
||||||||
Field clearance: The user-entered distance (in the primary dimension " Units " or other units ) from the face of the designed connection to the face of the supporting member.
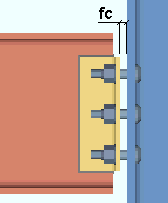
|
fc = field clearance. If this is selected ( |
Status Display: Member status > Left end field clearance and Right end field clearance
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.FieldClearanceFlag
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.FieldClearance
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].FieldClearanceFlag
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].FieldClearance
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].FieldClearanceFlag
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].FieldClearance
Input minus dimension: A positive or negative (-) user-entered distance (in the primary dimension " Units " or other units ) measured parallel with the workline of the beam from the beam's work point to the face of the designed connection on the end of the beam. A positive distance shortens the beam by that amount. A negative (-) distance makes the beam longer. If the beam is sloping, the actual sloped minus dimension must be calculated and entered.
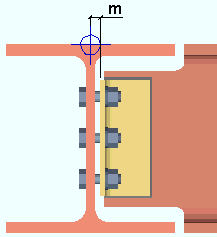
|
m = minus dimension. If this " |
Status Display: Member status > Left end minus dimension and Right end minus dimension
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.MinusDimension
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].MinusDimension
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].MinusDimension
Automatic minus dimension: A system-calculated distance from the beam's work point to the face of the designed connection on this end of the beam.
When this distance applies: If this "
Setbacks " option is selected (
), connection design calculates the half-web or half-depth of the member being framed to and adds the field clearance and rounds up to the nearest 1/16 inch to set the minus dimension. Connection design uses the field clearance entered for Auto Standard Connections or in Field Clearances .
Status Display: Member status > Auto minus dimension (either end)
Status Display: Member status > Left end minus dimension and Right end minus dimension
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.Settings.AutoMinusDimension
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].AutoMinusDimension
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].AutoMinusDimension
Connection setback: The user-entered distance (in the primary dimension " Units " or other units ) from the face of the designed clip angle or bent plate to this end of this beam (the supported beam). This setback to the supported material applies when " Attached to " is set to ' Supported .'
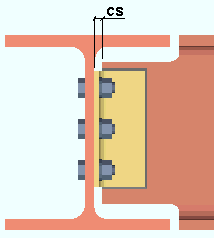
|
cs = connection setback. If this " |
Tip: To set a connection setback between the face of the supporting material and the face of the clip angle, change the " Input minus dimension . " This " Connection setback " sets the dimension to from the face of the clip angle to the supported, not to the supporting.
Clip Angle Settings: End of beam to face of clip angle setback
Status Display: Member status > Left end connection setback and Right end connection setback
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.Settings.ConnectionSetback
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].ConnectionSetback
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].ConnectionSetback
Input material setback: The user-entered distance (in the primary dimension " Units " or other units ) measured parallel with the workline of the beam from the work point for this end of the beam to the beam's main material.
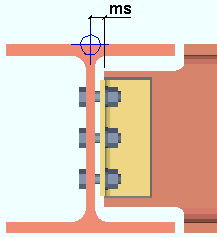
|
ms = material setback. If this " |
Status Display: Member status > Left end material setback and Right end material setback
Status Display: Member status > Has input setback
Change: Input to AUTO Material Setback
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.MaterialSetback
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].MaterialSetback
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].MaterialSetback
Automatic material setback: The distance (in the primary dimension " Units " or other units ) measured parallel with the workline of the beam from the work point at this end of the beam to the end of the beam's main material. When this " ![]() Setbacks " option is selected (
Setbacks " option is selected ( ![]() ), connection design calculates the material setback distance for you. If it is selected for both ends, the " WP to WP length: actual " minus the left- and right-end " Automatic material setback " is the length of the beam's main material.
), connection design calculates the material setback distance for you. If it is selected for both ends, the " WP to WP length: actual " minus the left- and right-end " Automatic material setback " is the length of the beam's main material.
Status Display: Member status > Auto material setback (either end)
Status Display: Member status > Left end material setback and Right end material setback
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.Settings.AutoMaterialSetback
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].AutoMaterialSetback
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].AutoMaterialSetback
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
||||||||
|
| Moment type ( |
Use inner flange plates | Re-entrant cut |
| Design for doublers | End plates | Groove angle |
| Design for stiffeners | Location | Haunch location |
| Col web dblr side | Bolt pattern | |
| Connection material | Bolt type | |
| Connection type | Bolt diameter |
Note: For "
Moment " options to be applied, this beam end's " Input connection type " must be ' End plate ' or ' Shear ' or ' Clip angle ' or ' Splice plate ' or ' Fully welded moment '. If a beam end's " Input connection type " is set to ' User defined ' and that user defined connection is a moment connection, the moment options for that connection are found under the "
Moment " leaf at Home > Project Settings > Job > User Defined Connections , not in the "
Moment " leaf on the Beam Edit window.
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
||||||||
Warning : The loads entered here affect the design of connections. Heavier loads cause stronger connections to be designed; lower loads cause the connection to be designed using lighter materials. Users should make entries to load fields only at the direction of a qualified engineer.
| A banner like the following is shown when the connection on this end of the beam is a " Minimum setup connection ." For such a connection, the " |
| Minimum setup connection capacity |
Shear load (kips or kN) : Auto or a user-entered load (in kips for ' Imperial ', kilonewtons for ' Metric '). The shear end reaction entered here -- under " ![]() Loads " -- will be combined with the " Shear load " entered to the " Gusset Interface Forces " column and then will used in the design of the " System designed connection " on this end of the beam. For beam splices, connection design attempts to synchronize the shear load on each of the two beams being spliced so that each load is the same value. If one beam has an "
Loads " -- will be combined with the " Shear load " entered to the " Gusset Interface Forces " column and then will used in the design of the " System designed connection " on this end of the beam. For beam splices, connection design attempts to synchronize the shear load on each of the two beams being spliced so that each load is the same value. If one beam has an " ![]() Auto " shear load and the other beam has a user-entered shear load, the load on both beam are set equal to the user-entered "
Auto " shear load and the other beam has a user-entered shear load, the load on both beam are set equal to the user-entered " ![]() Shear load ." If both beams have user-entered shear loads and those loads are not the same, the connection fails.
Shear load ." If both beams have user-entered shear loads and those loads are not the same, the connection fails.
| Shear load: |
|
|
| or | ||
| Shear load: |
|
|
If the box for " Auto " is checked (
), the shear end reaction on this end of the beam is calculated automatically, at the percent of ' Uniform allowable load ' or ' Maximum web shear ' set for " Base beam design reaction on % of " in Design Settings . The calculated numerical value -- calculated in this example -- is filled is shown in grayed-out text to indicate that it cannot be changed so long as "
Auto " is checked. A special case: The calculated value shown here for a " Minimum setup connection " is the connection's shear capacity, rather than its allowable shear load.
If the box for " Auto " is not checked (
), you may enter a load (to the desired precision) in the appropriate units specified (here) in parentheses. Right-click shows you the currently entered value to the full precision that connection design uses in its calculations. See the warning before entering a load. Also be aware that, if the connection has passed, when you switch from "
Auto" to "
Auto," the " Maximum shear load " will be reported, indicating the shear capacity of the connection as it is currently designed.
Also see: A special search for beams with Shear loads below minimum setup finds user-input shear end reactions that are less than connection design would have calculated. A change options exists for " Changing beams from input to Auto shear load ." There is a setup option for " Show design loads on beam detail ."
Status Display: Member status > Left end shear load and Right end shear load
Status Display: Connection auto loads > Auto beam shear ()
Change Options: Beams from Input to AUTO Shear Load
End connection failure message: Beam web shear strength failed
End connection failure message: Beam web yield/crippling fails
End connection failure message: User entered loads at splice must match
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.Settings.AutoShearLoad
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.ShearLoad
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].AutoShearLoad
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].ShearLoad
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].MaxShearWithoutFailing
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].AutoShearLoad
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].ShearLoad
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].MaxShearWithoutFailing
Story shear (kips or kN) : 0 (zero) or a user-entered load (in kips for ' Imperial ', kilonewtons for ' Metric '). This " ![]() Loads " option is disabled ( grayed-out ) when the " Moment type " under "
Loads " option is disabled ( grayed-out ) when the " Moment type " under " ![]() Moment " for this end is set to ' Non-moment '.
Moment " for this end is set to ' Non-moment '.
An entry of ' 0 ' (zero) prevents connection design from using story load in its calculations for moment connections on this end of the beam.
A ' user-entered load ' applies to the design of the connection on this end of a beam if this end of the beam frames to a column flange and "
Moment " options have been applied.
Status Display: Member status > Left end story shear and Right end story shear
Moment load ( kip-in or kip-ft or kN-m ): Auto or a user-entered load (in kip-in or kip-ft for ' Imperial ', kilonewton-meters for ' Metric '). The moment entered here -- under " ![]() Loads "-- is used in the design of the connection on this end of the beam if "
Loads "-- is used in the design of the connection on this end of the beam if " ![]() Moment " settings have been applied. This option is disabled ( grayed-out ) when the " Moment type " for this end is set to ' Non-moment ', unless the " User defined connection " for this end is a moment connection, for which case this field is enabled (editable). For moment splice plates, connection design attempts to synchronize the moment load on each of the two beams being spliced so that each load is the same value. If one beam has an "
Moment " settings have been applied. This option is disabled ( grayed-out ) when the " Moment type " for this end is set to ' Non-moment ', unless the " User defined connection " for this end is a moment connection, for which case this field is enabled (editable). For moment splice plates, connection design attempts to synchronize the moment load on each of the two beams being spliced so that each load is the same value. If one beam has an " ![]() Auto" moment load and the other beam has a user-entered moment load, the load on both beam are set equal to the user-entered " Moment load ." If both beams have user-entered moment loads and those loads are not the same, the connection fails.
Auto" moment load and the other beam has a user-entered moment load, the load on both beam are set equal to the user-entered " Moment load ." If both beams have user-entered moment loads and those loads are not the same, the connection fails.
| Moment load: |
|
|
| or | ||
| Moment load: |
|
|
If the box for " Auto " is checked (
), the moment for this end of the beam is calculated automatically, at the " Percent of maximum allowable moment " entered at Home > Project Settings > Job > Design Settings . The calculated numerical value -- calculated in this example -- is shown in grayed-out text to indicate that it cannot be changed so long as "
Auto " is checked. The sign of the left end moment defaults to positive and that of the right end defaults to negative. This is the usual case for gravity loading. For other conditions, such as wind load, the signs may be changed by the user as described below. A special case: The calculated value shown here for a " Minimum setup connection " is the connection's moment capacity, rather than its allowable moment load. Design method considerations: For ' ASD ' or ' LRFD ', the "
Auto" moment load is calculated in accordance with Section F2.1. For ' CISC 8 ' or ' CISC 9 ' , it is calculated in accordance with Clause 13.5. For ' AS 4100 ', it is calculated in accordance with Clause 5.2. Seismic auto loads are calculated using the AISC Seismic Design 2nd Edition, Section F2.3 for connection design methods that use the AISC 13th or 14th Editions. For methods that use the AISC 15th Edition, auto seismic loading is calculated per AISC Seismic Design 3rd Edition, Section F2.3.
If the box for " Auto " is not checked (
), you may enter a positive or negative load in the units specified (here) in parentheses. Right-click shows you the currently entered value to the full precision that connection design uses in its calculations. See the warning before entering a load. Also be aware that, if the connection has passed, when you switch from "
Auto " to "
Auto", the " Maximum moment load " will be reported, indicating the moment capacity of the connection as it is currently designed.
Setup options: " Show design loads on beam detail " lets the beam detail report the moment load. To design moment connections (on the column-side) for up to 125% of the beams maximum allowable moment, check the box for " Design moment connections for greater than 100% ."
Status Display: Member status > Left end moment load and Right end moment load
Status Display: Connection auto loads > Auto beam moment
Change Options: Beams from Input to AUTO Moment Load
End connection failure message: User entered loads at splice must match
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.Settings.AutoMomentLoad
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.MomentForce
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].AutoMomentLoad
Advanced Selection: m.Ends[0].MomentForce
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].AutoMomentLoad
Parametric module: m.Ends[0].MomentForce
Panel zone moment load ( kip-in or kip-ft or kN-m) : Auto or a user-entered load (in kip-in or kip-ft for ' Imperial ', kilonewton-meters for ' Metric '). The panel zone is the column web in the vicinity of a seismic beam moment connection. This load governs the design of web doublers when " Seismic moment frame member " is set to ' Yes ' or, possibly, to ' Automatic ' and " Seismic moment frame type " is set to ' OMF ' or ' IMF ' or ' SMF ' or, possibly, to ' Automatic ' and the left- or right-end " Moment type " is ' Bolted ' or ' Welded '.
If the box for " Auto " is checked (
), the moment for this end of the beam is calculated automatically. The entry made on this window to "
Seismic " > " Uniformly distributed gravity load " affects the auto calculation of this load when the " Seismic moment frame type " is set to ' IMF ' or ' SMF '.
If the box for " Auto " is not checked (
), you may enter a positive or negative load in the units specified (here) in parentheses.
Tension load (kips or kN) : 0 (zero) or a user-entered load (in kips for ' Imperial ', kilonewtons for ' Metric '). A tension load tends to stretch a member in the direction of its length.
An entry of ' 0 ' (zero) prevents connection design from using tension in its calculations for the design of the connection on this end of the beam.
A ' user-entered load ' will be combined with the " Tension load " entered to the " Gusset Interface Forces " column for use in the design of a clip angle or end plate or shear thru plate or single-plate shear (shear tab) connection. Before entering a load, see the warning .
Status Display: Member status > Left end tension load and Right end tension load
End connection failure message: Allowable clip OSL bending strength exceeded
End connection failure message: Axial load not applicable to this connection type
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.TensionLoad
Compression load (kips or kN) : 0 (zero) or a user-entered load (in kips for ' Imperial ', kilonewtons for ' Metric '). A compression load tends to compress or shorten the member.
An entry of ' 0 ' (zero) prevents connection design from using compression in its calculations for the design of the connection on this end of the beam.
A ' user-entered load ' will be combined with the " Compression load " entered to the " Gusset Interface Forces " column for use in the design of a clip angle or end plate or shear thru plate or single-plate shear (shear tab) connection. Before entering a load, see the warning .
Status Display: Member status > Left end compression load and Right end compression load
End connection failure message: Axial load not applicable to this connection type
Report Writer: Member.LeftEnd.MoreEnd.CompressionLoad
Tie force (kips or kN) : Auto or a user-entered load (in kips for ' Imperial ', kilonewtons for ' Metric '). This " ![]() Loads " option is available for most " Connection design methods ." For auto calculation of the tie force to take place, the " Connection design method " can be set to any LRFD or ASD edition.
Loads " option is available for most " Connection design methods ." For auto calculation of the tie force to take place, the " Connection design method " can be set to any LRFD or ASD edition.
|
If the box for " Auto " is checked (
), the tie force is auto calculated when "
Auto-calculate tying loads " is on (checked) at Home > Project Settings > Job > Design Settings . The magnitude of the auto calculated tying load is equal to the shear load for ASD and 2/3 shear load for LRFD. If "
Auto-calculate tying loads " is off (not checked), "
Auto " results in a tie force of ' 0 ' being entered.
If the box for " Auto " is not checked (
), an entry of ' 0 ' (zero) prevents connection design from using the tying force to check the structural integrity of the connection on this end of the beam. A ' user-entered load ' instructs connection design to use this tying force to check the structural integrity of the connection on this end of the beam, as required by Section 1615 of the International Building Code (2015) for high-rise buildings.
------- Gusset Interface Forces -------
|
|
Information in the " Gus int forces " column is read-only . Such a column appears here -- under " |
| Loads on Beam Edit window: |
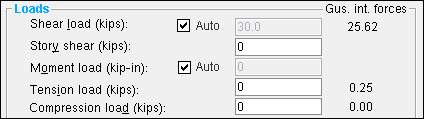
|
| Loads in Design Calculations report for beam: |
|
|
| Warning in Design Calculations for beam: |

|
| Warning in Design Calculations for vertical brace: |

|
If ' a load ' is reported under this column, then connection design combines the value in this column with the value entered to " Shear load " or " Tension load " or " Compression load " and uses the combined value for creating the connection on this end of the beam. The combined loads are reported as " Design loads " in the Design Calculations Report (as illustrated above) and also in the Expanded Connection Design Calculations Report .
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
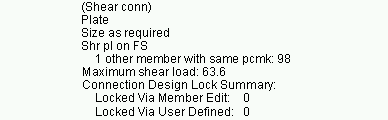
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
End preparation options that are similar to these can be found on the Rolled Section Material window. However, those settings cause the " Main material " to be set to '
' and the affected " Connection " to be "
Graphical ."
These options keep the " Main material " set to '
' and do not make the connection graphical.
Top flange operation : ' None ' or ' Cope plain ' or ' Cope field weld #3 (Standard) ' or ' Cope shop weld #3 (Standard) ' or ' Cut flange width ' or ' Cut flange flush ' or ' Clip flange ' or ' Notch Top/Bottom ' or ' Notch near side/far side ' or ' Cope field weld #1 (FEMA) ' or ' Cope shop weld #1 (FEMA) ' or ' Clip web ' or ' Seismic cope field weld ' or ' Seismic cope shop weld '.
Bottom flange operation : Same as above, except that this applies to the bottom flange.
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Non-Moment Beam Connections
NS Clip / FS Clip ( moment connection components can be added ) (
)
Beam End Pocket ( for a beam with a bearing embed )
Beam Web Doubler ( values of ' 0 ' if no web doublers are designed )
Web Extension Plate
Welded Tee
Bent Plate ( moment connection components can be added ) (
)
End Plate ( non-moment ) (
)
Shear Tee
Shear Thru Plate On [mem num] [end]
Shear Tab
Tab Clips and Copes
Paddle Plate for HSS Beam (
)
Safety Seat ( non-moment beam-to-column connections except beam seats )
Column Reinf Plate ( may also apply to welded moment connections )
Stability Plate ( extended shear tab to a column web )
Seated Tee
Seated Plate
Seated Angle
Web Stability Angle ( for a beam seat )
Top Flange Stability Angle ( for a beam seat )
Web Plate ( beam splice -- moment connection components can be added )
Web Fill Plate ( values of '0' if no fill plates are designed )
Moment Connections
Moment End Plate
Bolts ( end plate moment bolts )
Moment Stiffeners ( for a moment end plate )
Top/Bottom Moment Haunch Stiffener ( moment end plate, Eurocode )
Top/Bottom Moment Plate ( to a web or flange )
Top/Bottom Moment Plate ( welded moment, to a web, shear tab )
Top/Bottom Moment Angle ( flange )
Moment Cap Plate ( welded moment, to top of column flange )
Column Web Doublers ( moment )
Column Flange Stiffeners ( opposite to moment connection )
Moment Stiffeners ( moment end plate )
Moment Flange Plate ( beam splice )
Inner Flange Filler Plates ( beam splice )
Welds ( fully welded moment connection )
Status Display: Search > Connection design locks set
Connection design locks set .
Design Calculations Report: Connection Design Lock Summary
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
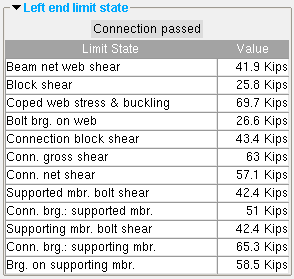
|
The limit states for a clip angle connection on the left end of a beam. The values shown represent the strength capacity of the connection or of the supported member (this beam) or of the supporting member. In this example, the connection passes. |
|
Beam web shear capacity failed
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
- The following are custom components that you may find settings for on the Beam Edit window. The settings for these custom component may be found under a section with one of the following names:
Safety Holes Safety Tabs Beam Flange to Flange Connection Beam Outrigger Beam Stiffeners Beam Ridge Plate HSS Cap Plate Reduced Beam Section Web Penetration with Stiffeners WWF Lifeline Holes Beam Nailer Holes Column Stiffener at Beam Surfaces Connection Void Space Cylinder
Void Space Layout
![]()
"Copy" "Paste" "Save" "Load" apply to all fields on this window. They do the same thing as the "Copy" "Paste" "Save" "Load" buttons ( ![]() ) found in the header portion of individual leaves on this window -- except that they apply to the entire window instead of just an individual leaf or section.
) found in the header portion of individual leaves on this window -- except that they apply to the entire window instead of just an individual leaf or section.
"Properties" opens the Edit Properties window, on which you can make entries to custom properties . If, at the time it was created, your current Job was set to use a legacy flavor, the window that opens is named Custom Properties , not Edit Properties .
The Edit Properties window can also be used to read "
Log " entries or review or type "
Notes ."
Tip: Model > Member > Properties is an alternative to this button. It opens the Edit Properties window directly, without your first having to open a member edit window.
" Status " opens the Member Status Review window, which can give you additional information about the beam, and which you can use to enter status information or designate a member as an existing member .
Note: This button is orange if one or more " Repeat " check boxes on the Member Status Review window do not match the checked-unchecked state of same-named fields in User and Site Options > Site > " Items to Copy/Repeat ." On the Status Review window, the fields that do not match User and Site Options are plotted in red .
" OK " (or the Enter key) closes the Beam Edit window and saves any changes you have made on the window to the member file of the affected beam(s).
Solids on "OK": If the appropriate choice is made to User and Site Options > Modeling > " Automatically process after modeling operation ," then this member will automatically be regenerated ( Create Solids will take place) after your press " OK ." Otherwise, you will have to manually Process and Create Solids in order for changes you made on this window to be fully updated in the 3D model.
Change all: If you Edit Member (one beam only) and make a change that potentially triggers the " Do you want to change all ... " dialog and the 3D model contains more than one beam that has the same piecemark as the beam you changed, a yes-no dialog opens. On it is the question, " Do you want to change all (members with this piecemark). " Press the " Yes " button to change all the members; press the " No " button to change only this beam. Special cases are listed on the table below:
| Do not trigger change all ... | Not changed with change all ... |
| " Sequence " | " Sequence " |
| " Piecemark " | " Toe direction " |
| " Member category " | " Beam rotation " |
| " Member description " | " Web rotation " |
| " Member routes " | " Load s" |
| " Model complete date " | " Model complete date " |
| Example: " Yes " or " No " on the " Do you want to change all ... " dialog changes the " Sequence " of this member (1 beam) only. | |
Option to lock ends of framing members: If you changed the " Model complete date " on this beam and other members have connections to this member, the Lock Ends Framing to Model Complete Members window opens, giving you options to "
Lock ... " the ends of those members that frame to this member.
Minimum setup connection options: Click here .
Defaults for to-be-added beams: If you are adding a new beam and you press " OK ," the settings on this window become the default settings for the next beam you Add in this session of Modeling . Even if all you do is double-click a beam and press " OK " without making any changes on this window, this window's settings become the defaults for the next-added beam. The settings on this window do not become the defaults for new beams if you are editing multiple piecemarks or you press " Cancel ."
" Cancel " (or the Esc key or the ![]() button) closes the Beam Edit window without saving any changes that you have made. " Cancel " does not undo a " Detail Member " operation.
button) closes the Beam Edit window without saving any changes that you have made. " Cancel " does not undo a " Detail Member " operation.
Note: If you opened this window using Add Beam , " Cancel " brings you back to the work point location step of adding a beam.
Tip: Any time you use Edit Member just to review a member (and you do not want to set the defaults for to-be-added members), the best way to close this window is to " Cancel. "
" Reset " undoes any changes made since you opened this window.
Exception: " Reset " does not undo changes made using the " Add View " " Delete View " " Detail Member " " View detail " buttons.
"Design Calc" outputs the Design Calculations report (also referred to as Short Calcs) which includes design calculations, general settings, and left/right end settings. A report for each beam you are editing is output to a destination of your choice as a PDF file. The file automatically opens with your operating system's default PDF application when you are editing one beam at a time.
"Expanded Calc" outputs the Expanded Connection Design Calculations report. First a PDF of the report is output to a destination of your choice. For example, to your desktop. Then the report automatically opens with your operating system's default PDF application.
Expanded Connection Design Calculations give you the calculation results found in the Connection Design Calculations , plus show you the calculations written out, in detail, in the report itself, instead of simply reporting the results.
If you are editing multiple beams with the same piecemark (or different piecemarks), you get a report for each beam.
Connection design failures can be found with the aid of a search or by a quick scan of the document. Calculations that result in a connection failure are identified as " (NO GOOD) " in their concluding line. You might also search for the string "CONNECTION DESIGN FAILURE".